Georgia Tax Return
Tax season is upon us, and for Georgians, it's time to navigate the intricacies of the Georgia Tax Return process. As a knowledgeable expert in the field, I'm here to guide you through this complex journey, ensuring you understand every step and maximizing your potential for a successful outcome. With a unique blend of technical expertise and practical advice, let's delve into the world of Georgia taxes and discover the strategies that will help you conquer this annual financial challenge.
Understanding the Basics: Georgia Tax Landscape
The Georgia tax system is a complex web of regulations, deductions, and credits, designed to collect revenue for the state’s operations. As a resident or business owner, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental principles to ensure compliance and optimize your financial strategies.
Georgia operates under a progressive tax system, meaning that as your income increases, so does your tax rate. The state offers six income tax brackets, ranging from 1% to 6%, depending on your taxable income. This structure ensures that those with higher incomes contribute a larger portion of their earnings to the state's revenue.
One unique aspect of Georgia's tax system is the homestead exemption, which provides property tax relief to homeowners. This exemption reduces the assessed value of a homeowner's property, thereby lowering their property taxes. It's a significant benefit for many Georgians, helping to make homeownership more affordable.
Key Tax Forms and Deadlines
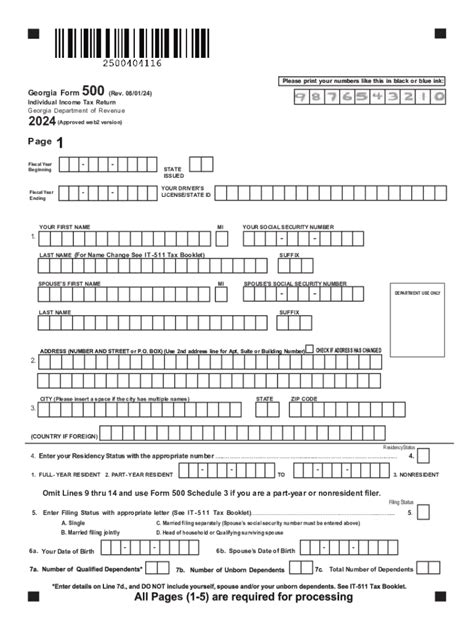
The primary tax form for individuals in Georgia is the Form 500, which is used to calculate your state income tax liability. This form must be filed by the April 15th deadline, aligning with the federal tax deadline. For businesses, the requirements vary based on the type of entity, with Form 600 being the most common for corporate income tax returns.
It's crucial to note that Georgia offers an automatic 60-day extension for filing your state tax return. However, this extension does not apply to the payment of any tax due, so it's essential to plan accordingly to avoid penalties and interest.
Maximizing Deductions and Credits

Understanding the various deductions and credits available in Georgia can significantly impact your tax liability. These incentives are designed to encourage specific behaviors or support certain sectors of the economy, and by taking advantage of them, you can reduce your tax burden.
Common Deductions in Georgia
- Standard Deduction: All Georgians are eligible for a standard deduction, which reduces your taxable income by a set amount. The standard deduction amount varies based on your filing status.
- Itemized Deductions: If your itemized deductions exceed the standard deduction, you may opt to itemize. This includes expenses such as mortgage interest, state and local taxes, charitable contributions, and medical expenses.
- Education Expenses: Georgia offers a deduction for qualified education expenses, including tuition and fees, up to a certain limit.
Credits to Consider
- HOPE Scholarship Credit: This credit is available to Georgia residents who have qualified for the HOPE Scholarship. It provides a credit against your state income tax liability, helping to offset the cost of higher education.
- Film Tax Credit: Georgia’s thriving film industry benefits from a generous tax credit program. Productions that meet certain criteria can claim a credit against their state income tax liability, making Georgia an attractive filming location.
- Renewable Energy Credits: The state encourages the adoption of renewable energy sources by offering tax credits for the installation of solar, wind, and other renewable energy systems.
| Credit Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Child Tax Credit | A credit for each qualifying child under the age of 17. |
| Elderly/Disabled Taxpayer Credit | A credit for taxpayers who are elderly or disabled, based on certain income limits. |
| Georgia Education Expense Credit | A credit for qualified education expenses, including tuition and fees. |

E-Filing and Payment Options
Georgia offers convenient electronic filing (e-filing) options for both individual and business taxpayers. The state’s official website provides a user-friendly interface for taxpayers to file their returns and make payments online. This method is not only faster but also reduces the chances of errors compared to traditional paper filing.
Payment Plans and Installment Agreements
If you’re unable to pay your tax liability in full by the deadline, Georgia offers payment plans and installment agreements to help you manage your debt. These plans allow you to pay your taxes over time, with interest and potential fees applied. It’s crucial to set up these arrangements before the due date to avoid additional penalties.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
Navigating the Georgia tax landscape can be challenging, and there are several common pitfalls that taxpayers should be aware of. From misunderstanding the state’s tax laws to overlooking deductions, these mistakes can lead to unnecessary penalties and missed opportunities.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
- Misinterpreting Residency Status: Georgia has specific rules for determining residency, which can impact your tax obligations. It’s crucial to understand these rules to ensure you’re filing the correct returns and claiming the right deductions.
- Overlooking Property Tax Credits: Georgia offers various property tax credits, including the Senior Property Tax Exemption and the Homeowner Tax Relief Grant Program. Make sure to explore these options to reduce your property tax burden.
- Not Staying Updated with Tax Law Changes: Georgia’s tax laws evolve annually, and staying informed is crucial. Changes can impact deductions, credits, and even filing requirements. Consider subscribing to tax newsletters or consulting a professional to stay abreast of these changes.
Seeking Professional Guidance

The world of taxes can be complex, and for many, seeking professional guidance is a wise decision. Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) and tax attorneys are well-versed in the intricacies of Georgia’s tax laws and can provide tailored advice to meet your specific needs.
When to Consult a Professional
- Complex Tax Situations: If you have multiple sources of income, own a business, or have significant investments, your tax situation may be more complex. A professional can help navigate these complexities and ensure you’re optimizing your tax strategies.
- Audits and Disputes: In the event of an audit or dispute with the Georgia Department of Revenue, having a professional by your side can be invaluable. They can represent your interests and help resolve these situations efficiently.
- Planning for the Future: Professionals can provide long-term tax planning strategies, helping you minimize your tax burden over time. This includes planning for retirement, estate planning, and business tax strategies.
Staying Informed and Prepared
Tax season can be stressful, but with the right knowledge and preparation, you can navigate the Georgia tax landscape with confidence. By understanding the basics, maximizing deductions and credits, utilizing e-filing options, and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can ensure a successful and stress-free tax experience.
Final Tips for a Smooth Tax Season
- Start early and gather all necessary documents well in advance.
- Consider using tax preparation software to simplify the process.
- Stay updated with the latest tax news and changes to ensure you’re aware of any new opportunities or requirements.
- If you have questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to reach out to the Georgia Department of Revenue or a tax professional for guidance.
Conclusion
The Georgia Tax Return process is a crucial annual event for residents and businesses alike. By understanding the state’s tax system, maximizing deductions and credits, utilizing e-filing options, and seeking professional guidance when needed, you can ensure a successful and stress-free tax experience. Remember, staying informed and prepared is key to navigating the complexities of Georgia’s tax landscape.
What is the deadline for filing my Georgia tax return?
+The deadline for filing your Georgia tax return is typically aligned with the federal tax deadline, which is April 15th for individual returns. However, it’s important to note that this date may vary for certain taxpayers or under specific circumstances. Always refer to the official Georgia Department of Revenue website for the most up-to-date information.
Can I e-file my Georgia tax return, and what are the benefits?
+Yes, Georgia offers electronic filing (e-filing) for both individual and business taxpayers. The benefits of e-filing include faster processing, reduced chances of errors, and the convenience of filing from anywhere with an internet connection. E-filing is a secure and efficient way to submit your tax return and is highly recommended by the state.
What happens if I can’t pay my taxes by the deadline?
+If you’re unable to pay your taxes in full by the deadline, Georgia offers payment plans and installment agreements to help you manage your debt. These plans allow you to pay your taxes over time with interest and potential fees. It’s important to set up these arrangements before the due date to avoid additional penalties.
Are there any resources available to help me understand Georgia’s tax laws and deductions?
+Yes, the Georgia Department of Revenue provides extensive resources, including tax guides, publications, and FAQs, to help taxpayers understand their obligations and maximize their deductions. Additionally, there are numerous tax preparation software options and professional tax advisors who can provide personalized guidance.
What should I do if I’m audited by the Georgia Department of Revenue?
+If you receive notice of an audit from the Georgia Department of Revenue, it’s important to remain calm and cooperative. Consider seeking professional representation to guide you through the process. Audits can be complex, and having a tax professional by your side can help ensure a favorable outcome.



