What Is Wisconsin Sales Tax

The Wisconsin sales tax is a consumption tax imposed by the state of Wisconsin on the sale of goods and certain services. It is an important source of revenue for the state, contributing significantly to the funding of essential public services and infrastructure. Understanding the Wisconsin sales tax is crucial for businesses and consumers alike, as it affects their financial obligations and purchasing decisions.
Wisconsin's sales tax is administered by the Wisconsin Department of Revenue, which sets the rates and regulations for the tax. The state's sales tax system is designed to be fair and equitable, with provisions for various exemptions and special rates for specific industries.
Wisconsin Sales Tax Rates
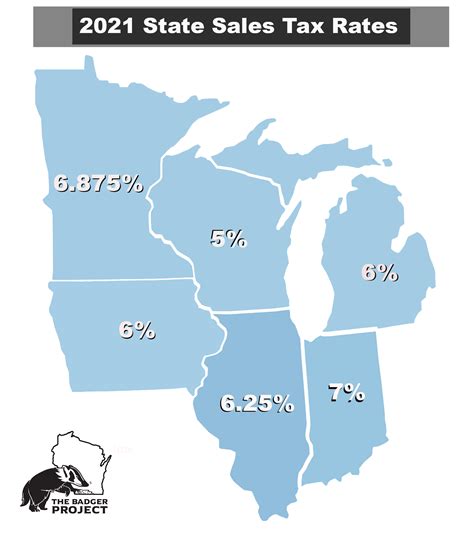
The Wisconsin sales tax operates on a multi-tiered system, with different rates applicable to different types of transactions. The statewide sales tax rate in Wisconsin is currently set at 5%, which is applicable to most retail sales. However, it’s important to note that local jurisdictions within Wisconsin can also impose additional county and municipal sales taxes, resulting in varying effective tax rates across the state.
For instance, Milwaukee County has a county sales tax rate of 0.5%, while the City of Madison has a municipal sales tax rate of 0.5%. These local taxes are often used to fund specific projects or initiatives within those jurisdictions. Therefore, the total sales tax rate a consumer pays can vary significantly depending on their location within the state.
Here's a table illustrating some of the varying effective sales tax rates across different counties in Wisconsin:
| County | Total Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Dane County | 5.5% |
| Milwaukee County | 5.5% |
| Brown County | 5.5% |
| Outagamie County | 5.5% |
| Kenosha County | 5.5% |

Special Tax Rates and Exemptions
Wisconsin’s sales tax system also includes special rates and exemptions for certain industries and transactions. For instance, the state offers a reduced sales tax rate of 5% on food and food ingredients for home consumption, which helps to make groceries more affordable for Wisconsin residents.
Additionally, the state provides sales tax exemptions for specific items such as prescription medications, most agricultural products, and manufacturing equipment. These exemptions are designed to support certain industries and encourage economic growth within the state.
Sales Tax Registration and Collection
Businesses operating in Wisconsin are responsible for registering with the Wisconsin Department of Revenue to obtain a sales tax permit. This permit allows them to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state. The sales tax registration process involves providing detailed information about the business, its location(s), and the types of goods and services it offers.
Once registered, businesses are required to collect the appropriate sales tax rate from customers at the point of sale. This tax is then remitted to the state on a regular basis, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis depending on the business's sales volume.
Sales Tax Compliance and Audits
To ensure compliance with sales tax regulations, the Wisconsin Department of Revenue conducts periodic audits of businesses. These audits aim to verify that businesses are accurately collecting and remitting the correct amount of sales tax. Failure to comply with sales tax regulations can result in penalties and interest charges.
The state also provides resources and guidance to help businesses understand their sales tax obligations. This includes educational materials, workshops, and online tools to assist with sales tax registration, filing, and payment processes.
The Impact of Wisconsin Sales Tax on the Economy
Wisconsin’s sales tax plays a significant role in the state’s economy. It is a primary source of revenue for the state government, helping to fund essential services such as education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and public safety. The revenue generated from sales tax also supports local governments and municipalities in providing community services and maintaining local infrastructure.
From an economic perspective, the sales tax can influence consumer behavior and business operations. Businesses must consider the sales tax rate when setting their prices, as it can impact their competitiveness in the market. Consumers, on the other hand, factor the sales tax into their purchasing decisions, especially for big-ticket items. The varying sales tax rates across the state can also impact where consumers choose to make their purchases, with some opting for lower-taxed jurisdictions.
Future Considerations and Reforms
As with any tax system, Wisconsin’s sales tax is subject to ongoing evaluation and potential reforms. The state’s policymakers and tax experts regularly assess the fairness, efficiency, and economic impact of the sales tax. This includes examining the distribution of the tax burden, the potential for tax evasion, and the impact of the sales tax on different industries and consumer segments.
Potential reforms could include adjustments to the sales tax rates, expansion or reduction of tax exemptions, or even a shift towards other forms of taxation. For instance, there have been discussions about the possibility of implementing a value-added tax (VAT) or exploring other alternative tax structures to ensure a more equitable and sustainable revenue system.
In conclusion, the Wisconsin sales tax is a vital component of the state's fiscal framework, providing essential revenue for public services and infrastructure. While it may impact consumer choices and business operations, the state's sales tax system is designed to be fair and transparent. As Wisconsin continues to evolve economically, the sales tax will remain a key focus area for policymakers and stakeholders, ensuring a balanced approach to revenue generation and economic growth.
What is the statewide sales tax rate in Wisconsin?
+The statewide sales tax rate in Wisconsin is 5%.
Are there any counties with higher sales tax rates in Wisconsin?
+Yes, several counties in Wisconsin have additional county and municipal sales taxes, resulting in higher effective sales tax rates. For example, Dane County and Milwaukee County have total sales tax rates of 5.5%.
Are there any sales tax exemptions in Wisconsin?
+Yes, Wisconsin offers sales tax exemptions for certain items such as prescription medications, most agricultural products, and manufacturing equipment.
How often do businesses need to remit sales tax in Wisconsin?
+Businesses in Wisconsin typically remit sales tax on a monthly or quarterly basis, depending on their sales volume.
What happens if a business fails to comply with sales tax regulations in Wisconsin?
+Businesses that fail to comply with sales tax regulations in Wisconsin may face penalties and interest charges. The state conducts periodic audits to ensure compliance.