Wa Sales Tax

Welcome to a comprehensive guide on the world of Washington State Sales Tax, a critical component of the state's revenue system and a topic of interest for businesses and consumers alike. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the sales tax landscape in Washington, exploring its intricacies, rates, and impact on various industries. By the end of this exploration, readers will have a solid understanding of the state's sales tax regulations and their implications.
Understanding Washington’s Sales Tax Structure
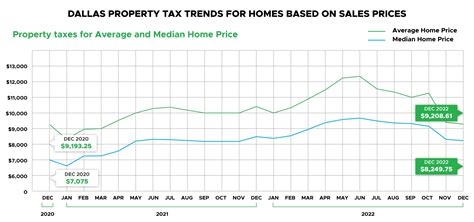
Washington State’s sales tax system is a vital aspect of its economy, contributing significantly to the state’s revenue stream. This section will delve into the fundamentals of the sales tax, providing a clear understanding of its mechanics and importance.
Washington, like many other states, imposes a sales tax on the sale of tangible goods and some services. This tax is collected by retailers at the point of sale and then remitted to the Washington State Department of Revenue, which oversees tax administration and enforcement. The sales tax rate is not a flat percentage across the state but varies depending on the location of the sale and the type of product or service being purchased.
The state's sales tax is comprised of two primary components: the state sales tax rate and local sales tax rates. The state sales tax rate is set at 6.5%, but local jurisdictions, including cities and counties, can levy additional taxes, resulting in a combined rate that can vary significantly from one area to another.
| Location | Total Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Seattle | 10.1% |
| Spokane | 8.9% |
| Tacoma | 9.4% |
| Olympia | 8.4% |
| State Average | 7.5% |

These varying rates can create a complex landscape for businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions, as they must ensure compliance with each area's specific tax requirements. The state also offers specific tax exemptions and incentives, which can provide relief to certain industries or situations.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Incentives
Washington State provides several sales tax exemptions and incentives to promote specific economic activities and support certain industries. These exemptions can significantly impact a business’s tax liability and are an essential consideration for any entity operating in the state.
- Food and Grocery Exemption: Most unprepared food products, including groceries, are exempt from sales tax in Washington. This exemption aims to reduce the tax burden on essential household items and support the state's agricultural industry.
- Manufacturing Exemption: Certain manufacturing equipment and supplies are exempt from sales tax. This exemption is designed to encourage manufacturing activities and attract new businesses to the state.
- Research and Development Tax Credit: Washington offers a tax credit for qualifying research and development activities, providing a significant incentive for innovative companies to establish or expand their operations in the state.
- Retail Sales Tax Deferral: For certain construction projects, the state allows a deferral of retail sales tax on materials used. This incentive aims to support the construction industry and encourage large-scale development projects.
Sales Tax Collection and Remittance

The process of collecting and remitting sales tax in Washington State is a critical responsibility for businesses, ensuring compliance with state regulations and timely revenue generation for the government.
Registration and Licensing
Any business operating in Washington State and engaging in taxable sales or services must register with the Department of Revenue and obtain a Business License. This process ensures that the business is officially recognized by the state and can collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the government.
The registration process involves providing detailed information about the business, including its legal structure, ownership, and primary activities. The Department of Revenue reviews this information to determine the business's tax obligations and provide the necessary guidance for compliance.
Sales Tax Calculation and Collection
Businesses are responsible for calculating the applicable sales tax rate for each transaction, based on the location of the sale and the nature of the product or service. This rate is then added to the sale price, and the total amount, including tax, is collected from the customer at the point of sale.
It's crucial for businesses to maintain accurate records of all sales transactions, including the tax collected on each, to ensure proper reporting and remittance. These records must be retained for a minimum of four years to comply with audit requirements.
Remittance Process
Sales tax collected by businesses must be remitted to the Department of Revenue on a regular basis. The frequency of remittance depends on the business’s tax liability and can range from monthly to annually. Businesses with higher tax liabilities typically remit more frequently to ensure timely payment and avoid penalties.
The remittance process involves submitting a detailed report of all taxable sales and the associated tax collected during the reporting period. This report is accompanied by the remitted tax amount, which is then deposited into the state's general fund.
Compliance and Enforcement
Compliance with Washington State’s sales tax regulations is a critical aspect of doing business in the state, and the state takes enforcement seriously to ensure a fair and equitable tax system.
Audit and Inspection
The Department of Revenue conducts regular audits and inspections to ensure businesses are compliant with sales tax laws. These audits can be random or targeted, based on specific concerns or indicators of potential non-compliance.
During an audit, the Department reviews the business's sales records, tax returns, and other financial documents to verify the accuracy of reported sales and tax payments. If discrepancies are found, the business may be required to pay additional taxes, penalties, and interest.
Penalties and Interest
Washington State imposes penalties for non-compliance with sales tax regulations. These penalties can include late payment fees, failure-to-file fees, and penalties for underreporting sales or tax liabilities.
In addition to penalties, interest may also accrue on unpaid tax liabilities. The interest rate is typically based on the federal short-term rate plus a state-determined percentage, and it can significantly increase the total amount owed over time.
| Penalty Type | Penalty Rate |
|---|---|
| Late Payment | 1.5% per month up to 15% |
| Failure to File | $50 or 10% of tax due, whichever is greater |
| Underreporting | 25% of the underreported tax |
Appeal Process
If a business disagrees with the findings of an audit or believes it has been unfairly penalized, it has the right to appeal the decision. The appeal process involves a formal review by the Department of Revenue, which may lead to a reduction or elimination of penalties and interest.
It's essential for businesses to maintain accurate records and a good relationship with the Department to facilitate a smooth appeal process if needed.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
Washington State’s sales tax system has a significant impact on both businesses and consumers, influencing economic activities and consumer behavior within the state.
Impact on Businesses
For businesses, the sales tax system can present both challenges and opportunities. On the one hand, businesses must navigate a complex tax landscape, ensure compliance, and manage the administrative burden of collecting and remitting sales tax. This can be particularly challenging for small businesses with limited resources.
On the other hand, businesses can leverage the state's sales tax system to their advantage by understanding the exemptions and incentives available. By strategically utilizing these provisions, businesses can reduce their tax liabilities, enhance profitability, and potentially attract new customers.
Impact on Consumers
Consumers in Washington State bear the direct impact of the sales tax on their purchases. The tax adds to the cost of goods and services, influencing consumer behavior and purchasing decisions. Higher sales tax rates can discourage purchases, especially for discretionary items, while lower rates can stimulate demand.
However, it's important to note that the sales tax is often a small percentage of the overall cost of a purchase, especially for high-value items. Additionally, the state's exemptions for essential items like groceries can reduce the tax burden on consumers, making it more affordable to purchase necessary goods.
Regional Differences
The varying sales tax rates across the state can create regional differences in consumer behavior and business strategies. Businesses in areas with higher tax rates may need to adapt their pricing strategies to remain competitive, while consumers in these areas may be more price-conscious.
Understanding these regional differences is crucial for businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions within the state. By tailoring their strategies to each region, businesses can optimize their sales and profitability across Washington.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes

Washington State’s sales tax system, like any tax regime, is subject to ongoing review and potential changes to meet evolving economic conditions and policy priorities.
Proposed Changes
There have been several proposed changes to Washington’s sales tax system in recent years, driven by a range of factors including economic development, fairness, and revenue generation.
- Expansion of Taxable Items: Some proposals suggest expanding the list of taxable items to include certain services and digital products, which are currently exempt in Washington.
- Uniform Sales Tax Rate: There have been discussions about implementing a uniform sales tax rate across the state, eliminating the variability in rates between different jurisdictions.
- Online Sales Tax Collection: With the growth of e-commerce, there is a push to require online retailers to collect and remit sales tax on purchases made by Washington residents, ensuring fair competition with brick-and-mortar stores.
Economic Impact
Any changes to the sales tax system can have significant economic implications. Expanding the list of taxable items could generate additional revenue for the state, but it might also discourage certain economic activities and shift consumer behavior towards exempt items.
A uniform sales tax rate could simplify the tax system and reduce administrative burdens for businesses, but it might also result in higher taxes for some areas, potentially impacting local economies.
Policy Considerations
When considering changes to the sales tax system, policymakers must balance various factors, including revenue generation, fairness, and economic impact. They must also ensure that any changes align with the state’s overall economic development goals and priorities.
For instance, while expanding the list of taxable items might increase revenue, it could also disproportionately affect certain industries or consumers, potentially leading to economic inequality. Therefore, any proposed changes must be carefully evaluated to ensure they promote a healthy and equitable economic environment.
Conclusion
Washington State’s sales tax system is a complex yet vital component of its economic landscape, influencing the activities of businesses and consumers alike. By understanding the intricacies of the system, businesses can navigate the regulatory environment effectively, take advantage of available exemptions and incentives, and optimize their operations for success.
For consumers, understanding the sales tax system can help them make informed purchasing decisions and navigate the state's economic landscape with confidence. Whether it's leveraging exemptions for essential items or understanding regional variations in tax rates, knowledge is power in the world of Washington's sales tax.
As the state's economic landscape continues to evolve, so too will its sales tax system. By staying informed about proposed changes and their potential impact, businesses and consumers can adapt to new realities and continue thriving in Washington's dynamic economy.
What is the current sales tax rate in Washington State?
+
The current state sales tax rate in Washington is 6.5%, but local jurisdictions can add additional taxes, resulting in a combined rate that varies across the state. The average combined rate is approximately 7.5%, but it can range from 8.4% to 10.1% depending on the location.
How often do businesses need to remit sales tax in Washington?
+
The frequency of sales tax remittance depends on a business’s tax liability. Businesses with higher tax liabilities typically remit more frequently, such as monthly or quarterly. Those with lower liabilities may remit semi-annually or annually.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with Washington’s sales tax regulations?
+
Non-compliance with Washington’s sales tax regulations can result in various penalties, including late payment fees, failure-to-file fees, and underreporting penalties. Interest may also accrue on unpaid tax liabilities. Additionally, businesses may be subject to audits and inspections by the Department of Revenue.
Are there any sales tax exemptions in Washington State?
+
Yes, Washington State offers several sales tax exemptions. These include exemptions for unprepared food products, manufacturing equipment and supplies, research and development activities, and certain construction projects. Understanding these exemptions can help businesses reduce their tax liabilities.