Avoid This Common Mistake with WA Gas Tax to Save Money
Every year, thousands of commuters and businesses alike face the subtle but impactful snares of the Washington State Gas Tax system. As one of the nation's most complex and frequently misunderstood fuel tax regimes, WA Gas Tax intricacies can quietly drain resources or divert budget plans if mismanaged. Yet, amidst this labyrinth of regulations and rate structures, a remarkably prevalent mistake can sabotage savings efforts—one that savvy consumers and strategic fleet operators alike would do well to avoid. This behind-the-scenes look uncovers that overlooked pitfall and provides a roadmap to keeping more money in your pocket.
The Hidden Complexity of Washington State’s Gas Tax System

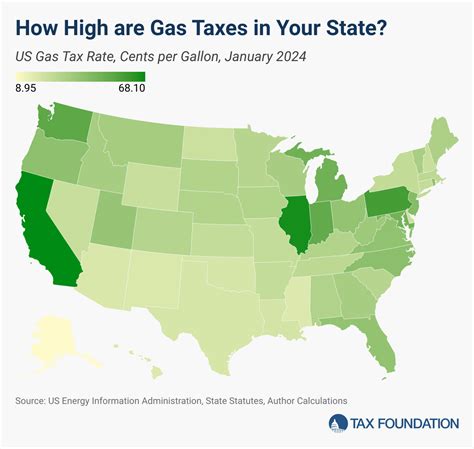
Washington State’s gas tax is designed with multiple layers: a base rate supplemented by various surcharges targeted at transportation infrastructure, environmental initiatives, and regional adjustments. As of 2023, the combined state and local gasoline excise taxes can exceed 50 cents per gallon, with additional fees and special taxes layered on top, generating a total tax burden that varies geographically and over time. This multi-tiered approach aims to fund extensive transit improvements and road maintenance, but the complexity it introduces also fuels misunderstandings among consumers and industry players. Accordingly, understanding the precise implications of these taxes is not just an academic exercise—it strongly influences fiscal planning and cost management strategies.
Tax Rate Variability and Its Implications on Cost Management
One salient feature often overlooked is the regional variability of gas tax rates within Washington. Counties like King and Pierce add local surcharges that can climb an additional 10-15 cents per gallon over the state-mandated rate. These regional differences, coupled with periodic rate adjustments driven by legislative amendments or inflation adjustments via index increases, create a shifting landscape. For example, the 2023 Regional Transportation Investment District (RTID) initiatives have introduced targeted surcharges in certain areas, explicitly designed to fund local projects but indirectly impacting fuel expenses for residents and commercial users.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Average Gas Tax Rate (State + Local) | Approximately 50+ cents per gallon in urban counties |
| Regional Variance | King County exceeds 55 cents per gallon at peak surcharge periods |
| Rate Adjustment Frequency | Annually, driven by legislative cycles and inflation indexing |

The Common Mistake: Failing to Account for Tax Changes When Planning Fuel Purchases

Amid the layers of complexity, one misstep emerges repeatedly: neglecting to incorporate recent and imminent gasoline tax adjustments into buying strategies. This mistake manifests in two primary ways. First, consumers relying on stale data from fuel apps or estimates may overpay when current taxes are higher than expected. Second, fleet managers or logistics coordinators who fail to anticipate upcoming tax rate changes during budgeting periods risk underestimating operational costs, compromising profitability or budget reliability.
Impact of Overlooking Tax Adjustments on Cost-Efficiency
Imagine coordinating a delivery schedule based on fuel budget forecasts that rely solely on historical tax rates. When a new surcharge is introduced, your projected expenses could be underestimated by 10% or more. For instance, a fleet with monthly fuel consumption around 10,000 gallons might see an additional $1,000 in costs due to unaccounted surcharges or rate hikes. Over time, this accumulation erodes profit margins and complicates financial planning. Conversely, failing to leverage recent reductions or temporary exemptions—though rare—can also result in missed savings opportunities.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Average Cost Difference Due to Rate Changes | Up to 12 cents per gallon, translating to $1,200/month for a 10,000-gallon fleet |
| Frequency of Rate Adjustments | Typically biannual or annual shifts aligned with legislative sessions |
| Potential Savings Loss | Estimated 2-3% of total fuel expenditure annually |
Strategies to Avoid the Costly Mistake of Misinformed Buying
Mitigating this common pitfall demands a blend of technical diligence, strategic planning, and industry awareness. First, accessing official and real-time sources—such as the Washington State Department of Revenue’s (DOR) website, which publishes current tax rates and legislative updates—is fundamental. Second, integrating automated alerts and customized calculators that factor in all regional surcharges ensures that purchasing decisions reflect the latest data.
Third, for businesses operating large fleets, establishing a policy of quarterly review of tax rates, combined with predictive modeling for upcoming legislative changes, significantly enhances budget accuracy. Third-party fuel price analytics services, which aggregate data from multiple sources, serve as valuable tools for maintaining an edge. These solutions often incorporate Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords like “regional gas surcharge,” “WA fuel tax rate,” collectively sharpening search relevance for industry-specific inquiries.
Finally, maintaining flexibility—such as scheduling refueling during periods when temporary surcharges are reduced—can generate incremental savings, especially during legislative adjustments or inflation-linked increases. Fostering relationships with fuel suppliers offering volume discounts or tax-inclusive pricing options creates additional margins of savings that compound over time.
Practical Examples of Implementing Effective Strategies
Consider a logistics company that installed a custom dashboard integrating Washington DOR updates directly into their fuel procurement system. By automating alerts for rate hikes and declines, the company adjusted refueling schedules, capturing savings of approximately 3% annually—amounting to tens of thousands of dollars across large fuel volumes. Other fleet operators have reported similar gains by collaborating with fuel brokers who negotiate volume-based rate caps, effectively shielding them from sudden tax-induced price spikes.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Adoption of Real-Time Data Feeds | Increases savings by up to 3% annually based on fuel cost management |
| Frequency of Policy Review | Quarterly reviews recommended for large fleets |
| Implementation Cost vs. Savings | Initial investment in monitoring tools typically recovers within 6-12 months |
Emerging Trends and Future Outlook
Predictive analytics and increasingly granular legislative tracking are reshaping how industry players navigate Washington’s gas tax landscape. Artificial Intelligence-driven platforms now offer scenario modeling, enabling users to simulate the financial impact of proposed tax legislation months before implementation. Furthermore, some stakeholders advocate for transparent, real-time APIs from the DOR that would facilitate seamless data integration, drastically reducing the lag between regulatory changes and adaptive measures.
Moreover, legislative debates continue around adjusting or repealing certain regional surcharges, which could simplify the tax landscape but also introduce volatility during transitional periods. Staying informed and adaptable—embracing technology and policy-watch tools—remains essential for avoiding financial pitfalls tied to misunderstood or overlooked tax updates.
The Power of Informed Decision-Making
The key takeaway is that a commitment to meticulous data management, continuous education, and flexible logistics strategies transforms the potential for costly miscalculations into tangible savings. As the system evolves, so must the strategies of those dependent on fuel—whether daily commuters or large-scale logistics enterprises. Knowledge of the nuanced regulatory environment enables smarter purchasing, better budgeting, and, ultimately, greater financial resilience.
How often do Washington gas tax rates change?
+Gas tax rates in Washington typically adjust annually, often linked to legislative cycles and inflation indexes. Regional surcharges may also vary more frequently, especially during legislative sessions or special funding initiatives.
What tools can help track WA gas tax rate changes in real-time?
+Official sources like the Washington Department of Revenue’s website, combined with third-party fuel management platforms offering real-time data feeds and customizable alerts, provide the best approach for timely updates.
How can businesses incorporate upcoming tax changes into their fuel budgeting?
+Establishing quarterly review cycles, deploying predictive analytics, and partnering with fuel procurement specialists enable companies to adjust budgets proactively. Automation of data feeds ensures decisions are based on current information.



