Property Tax Dallas
Property taxes in Dallas, Texas, are a crucial aspect of the local economy and an essential revenue source for various governmental bodies. These taxes fund public services and infrastructure, impacting residents' daily lives and business operations. Understanding the intricacies of property taxes in Dallas is vital for homeowners, investors, and businesses operating within the city.
Property Tax Assessment Process in Dallas

The property tax system in Dallas is governed by state laws and regulations, with the city’s Appraisal District playing a central role in the assessment process. Each year, the Dallas Central Appraisal District (DCAD) is tasked with determining the taxable value of all properties within its jurisdiction.
This comprehensive process involves:
- Property Appraisal: Professional appraisers from DCAD assess properties based on factors like location, size, condition, and recent sales data. This process ensures an accurate valuation for tax purposes.
- Notices of Appraised Value: Once the appraisal is complete, DCAD sends out Notice of Appraised Value to property owners, detailing the proposed taxable value for the upcoming year.
- Protest and Review: Property owners have the right to protest their appraised value if they believe it is inaccurate or unfair. DCAD provides a formal review process, including hearings, to address these concerns.
- Final Valuation: After the protest period, DCAD finalizes the taxable values, which form the basis for property tax calculations.
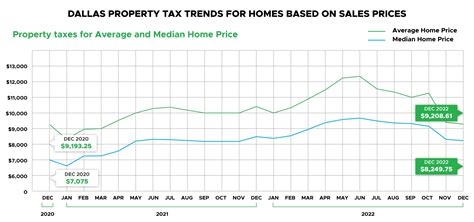
The Impact of Property Values on Taxes
Property values in Dallas can fluctuate due to various factors, including market trends, improvements made to the property, and general economic conditions. These changes directly influence the taxable value and, consequently, the property taxes owed.
| Property Type | Average Value Increase (%) |
|---|---|
| Residential Homes | 4.2 |
| Commercial Properties | 3.7 |
| Land (Vacant) | 2.9 |
Calculating Property Taxes in Dallas
Once the taxable value of a property is established, the actual tax amount is calculated using a tax rate, which is set by various taxing entities within Dallas.
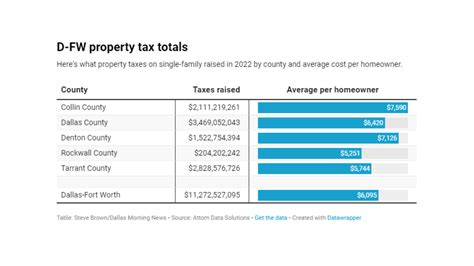
Taxing Entities and Their Rates
Dallas property taxes are collected by multiple governmental bodies, each with its own tax rate. These entities include:
- Dallas County: Responsible for county-wide services and infrastructure.
- Dallas Independent School District (DISD): Funds public education within the city.
- City of Dallas: Provides municipal services like police, fire, and utilities.
- Special Districts: Entities like water districts or transportation authorities that provide specific services.
Each of these entities sets its tax rate annually, which is then applied to the taxable value of the property to calculate the total tax due.
| Taxing Entity | 2023 Tax Rate (per $100 valuation) |
|---|---|
| Dallas County | $0.3840 |
| DISD | $1.3925 |
| City of Dallas | $0.5877 |
| Special Districts | Varies by district |
Example Tax Calculation
Let’s consider a residential property in Dallas with a taxable value of $250,000. Using the tax rates above, we can calculate the estimated property taxes as follows:
Total Tax = (Taxable Value) * (Sum of Tax Rates)
Total Tax = $250,000 * ($0.3840 + $1.3925 + $0.5877 + Special District Rate)
Assuming a special district rate of $0.2500, the estimated property taxes for this property would be:
Total Tax ≈ $250,000 * ($2.5642 + $0.2500) ≈ $651,050
Payment Options and Deadlines
Property taxes in Dallas are typically due by January 31st of each year. However, taxpayers have the option to pay their taxes in two installments:
- First Installment: Due by January 31st
- Second Installment: Due by July 1st
Failure to pay property taxes on time can result in penalties, interest, and, in extreme cases, tax foreclosure.
Online Payment and Tax Relief Programs
Dallas offers convenient online payment options for property taxes, allowing taxpayers to pay securely via credit card or e-check. Additionally, the city provides various tax relief programs for eligible homeowners, including:
- Over-65 Homestead Exemption: Property tax exemption for homeowners aged 65 or older.
- Disabled Veterans Exemption: Exemption for disabled veterans or their surviving spouses.
- Residential Homestead Cap: Limits the annual increase in taxable value for homeowners with a residential homestead.
Impact of Property Taxes on Real Estate Market
Property taxes in Dallas can significantly influence real estate trends and investment strategies. High property taxes can deter potential buyers or investors, while lower taxes can make a property more attractive and affordable.
Case Study: Property Tax Reform and Market Response
In recent years, Dallas has implemented tax reforms aimed at reducing the tax burden on homeowners. For instance, the Texas Constitution’s “Robin Hood” school finance system, which redistributes property taxes from wealthier school districts to poorer ones, has been a topic of debate and reform efforts.
These reforms have led to:
- Increased buyer confidence and market activity.
- Stimulated investment in certain areas, especially those with lower tax rates.
- Encouraged homeowners to protest their appraised values more frequently, ensuring fairer assessments.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes

The property tax landscape in Dallas is subject to ongoing changes and reforms, influenced by economic conditions, political decisions, and community needs. Here are some potential future developments:
- Tax Rate Adjustments: Taxing entities may reconsider their tax rates based on budgetary requirements and public sentiment.
- Appraisal Reform: Continued efforts to ensure fair and accurate appraisals, especially for unique properties or those with recent improvements.
- Online Services Expansion: Further development of digital platforms for tax payments, protests, and information access.
- Community Engagement: Increased involvement of taxpayers in the budgeting process, providing input on tax allocation and services.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of property taxes in Dallas is essential for anyone with a stake in the city’s real estate market. By staying informed about assessment processes, tax rates, and potential reforms, homeowners, investors, and businesses can make informed decisions and navigate the property tax landscape effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I protest my property’s appraised value in Dallas?
+To protest your property’s appraised value, you must file a written protest with the Dallas Central Appraisal District (DCAD) within the specified deadline. You can do this online, by mail, or in person. DCAD will then schedule a hearing to review your protest. Prepare evidence to support your case, such as recent sales data or professional appraisals, to increase your chances of a successful protest.
Are there any tax breaks or exemptions for homeowners in Dallas?
+Yes, Dallas offers several tax relief programs for homeowners. These include the Over-65 Homestead Exemption, Disabled Veterans Exemption, and the Residential Homestead Cap. Each program has specific eligibility criteria, so it’s essential to understand which ones you may qualify for.
What happens if I don’t pay my property taxes on time in Dallas?
+Failure to pay property taxes on time can result in penalties, interest, and potential tax foreclosure. It’s important to stay informed about payment deadlines and consider setting up automatic payments or reminders to ensure timely payments.
How do property taxes in Dallas affect the real estate market and investment opportunities?
+Property taxes can significantly impact the real estate market in Dallas. High property taxes can deter potential buyers and investors, making properties less attractive. Conversely, lower taxes can stimulate market activity and make investment opportunities more viable. Understanding the tax landscape is crucial for investors to make informed decisions.
Are there any online resources or tools available to help me estimate my property taxes in Dallas?
+Yes, Dallas provides online resources to help taxpayers estimate their property taxes. The DCAD website offers tools to calculate estimated taxes based on current tax rates and appraised values. Additionally, real estate websites and property tax calculators can provide rough estimates, although they may not account for all variables.