Tax Nc Sales
Sales tax in North Carolina is a vital aspect of the state's economy and financial landscape. Understanding the intricacies of North Carolina sales tax is crucial for businesses and individuals alike. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the specifics of sales tax in NC, providing an in-depth analysis of the rates, regulations, and best practices for compliance.
Navigating the Complex World of NC Sales Tax

North Carolina’s sales tax system is a dynamic and ever-evolving entity, influenced by a myriad of factors, from state-wide initiatives to local ordinances. This section aims to provide a bird’s-eye view of the sales tax landscape in NC, offering a comprehensive overview for those looking to establish a business or simply understand the financial obligations associated with consumer purchases.
Understanding the Sales Tax Rates
The sales tax rate in North Carolina is a composite of both state and local taxes. The state sales tax rate stands at 4.75%, a uniform rate across the state. However, it’s the local taxes that introduce variability, with municipalities and counties adding their own sales tax rates on top of the state’s.
For instance, the city of Charlotte imposes an additional 2% sales tax, bringing the total sales tax rate for purchases within the city limits to 6.75%. Similarly, the county of Wake has a 2.5% sales tax, resulting in a total sales tax rate of 7.25% for purchases made in Wake County.
| Location | State Tax Rate | Local Tax Rate | Total Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Statewide | 4.75% | Varies by Location | 4.75% - 7.25% |
| Charlotte | 4.75% | 2% | 6.75% |
| Wake County | 4.75% | 2.5% | 7.25% |
It's important to note that these local tax rates can change frequently, often influenced by municipal budgets and voter-approved initiatives. Therefore, it's crucial for businesses and consumers to stay informed about the latest sales tax rates in their specific areas.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Cases
North Carolina offers a range of sales tax exemptions and special cases, which can significantly impact the financial obligations of businesses and consumers. Some common exemptions include:
- Grocery Exemptions: Many food items, including unprepared foods, are exempt from sales tax. However, the definition of "grocery" can vary, and certain food items may be taxable depending on the specific ingredients or preparation methods.
- Manufacturing Exemptions : Manufacturers often benefit from sales tax exemptions on raw materials and equipment used in the production process. This exemption is a significant incentive for businesses considering a manufacturing presence in North Carolina.
- Resale Exemptions: Businesses that resell products, such as retailers, are not required to pay sales tax on the products they purchase for resale. This exemption ensures that sales tax is only paid by the end consumer.
- Charitable Exemptions: Nonprofit organizations and certain religious institutions are often exempt from sales tax, especially when purchases are made for the organization's exempt activities.
These exemptions, while beneficial, can also introduce complexities for businesses. It's crucial to understand the specific requirements and qualifications for each exemption to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
Sales Tax Collection and Remittance
The process of collecting and remitting sales tax is a critical responsibility for businesses operating in North Carolina. The state’s Department of Revenue provides detailed guidelines and resources to assist businesses in this process.
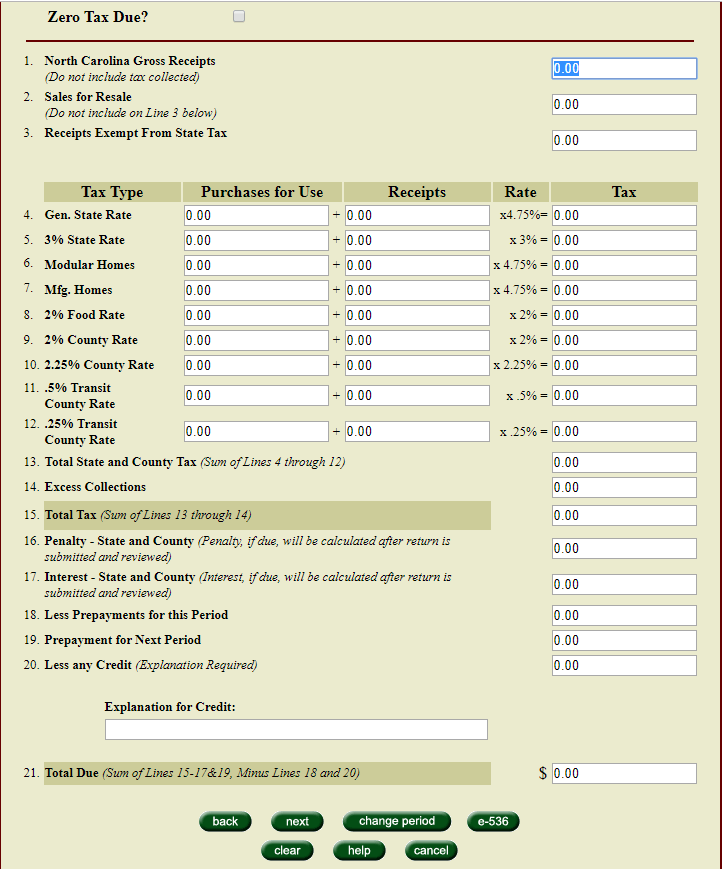
Businesses are generally required to collect sales tax at the point of sale, adding the applicable tax rate to the purchase price. This collected tax is then held in trust by the business until it's remitted to the state on a regular basis, typically monthly or quarterly, depending on the business's tax liability.
The remittance process involves submitting accurate sales tax returns, which detail the total sales and the corresponding tax collected during the reporting period. These returns are typically due on the 20th day of the month following the reporting period. For example, sales tax returns for the month of January would be due on February 20th.
It's important for businesses to maintain accurate records of sales and tax collections to ensure timely and accurate remittance. The state may impose penalties for late or incorrect submissions, so staying organized and informed is crucial.
The Role of Technology in Sales Tax Compliance
In today’s digital age, technology plays a pivotal role in streamlining the sales tax compliance process. A variety of software solutions are available to assist businesses in calculating, collecting, and remitting sales tax accurately and efficiently.
These software tools can integrate with a business's accounting and point-of-sale systems, automating much of the sales tax compliance process. They can calculate the applicable tax rates based on the customer's location, ensure accurate collection at the point of sale, and generate sales tax returns ready for submission.
For businesses with a significant online presence, these tools can be especially beneficial, as they can automatically adjust tax rates based on the customer's shipping address, ensuring compliance with varying local tax rates across the state.
Conclusion: Embracing a Compliance-Focused Approach
Navigating the intricacies of North Carolina’s sales tax system can be a complex task, but it’s a necessary step for any business looking to establish a presence in the state. By understanding the rates, exemptions, and collection processes, businesses can ensure they are compliant with state and local regulations.
Furthermore, leveraging technology and staying informed about the latest tax regulations and changes can significantly reduce the burden of sales tax compliance. It's an investment of time and resources that pays dividends in the form of reduced penalties, increased efficiency, and improved financial management.
For more information on North Carolina's sales tax regulations and resources for compliance, visit the official website of the North Carolina Department of Revenue.
FAQ
What is the state sales tax rate in North Carolina?
+
The state sales tax rate in North Carolina is 4.75%, a uniform rate across the state.
Are there any sales tax exemptions in North Carolina?
+
Yes, North Carolina offers a range of sales tax exemptions, including grocery, manufacturing, resale, and charitable exemptions. These exemptions can significantly impact the financial obligations of businesses and consumers.
How often do businesses need to remit sales tax in North Carolina?
+
Businesses typically remit sales tax on a monthly or quarterly basis, depending on their tax liability. Sales tax returns are due on the 20th day of the month following the reporting period.
What role does technology play in sales tax compliance in North Carolina?
+
Technology, especially sales tax software, can automate many aspects of the sales tax compliance process. These tools can calculate tax rates, ensure accurate collection, and generate sales tax returns, making the process more efficient and accurate.