Sales Tax In Utah
Sales tax is an essential component of the revenue system in the United States, and it plays a crucial role in funding various public services and infrastructure. Utah, known for its stunning natural landscapes and thriving economy, has its own unique sales tax regulations that businesses and consumers should be aware of. This comprehensive guide aims to unravel the intricacies of sales tax in Utah, offering a detailed insight into its rates, applicability, and compliance requirements.
Understanding Sales Tax in Utah

Sales tax in Utah is a consumption tax imposed on the sale of tangible personal property and certain services. It is a key revenue source for the state, counties, and municipalities, enabling the government to invest in education, transportation, public safety, and other vital services. The tax is collected at the point of sale and is remitted to the Utah State Tax Commission, which administers and regulates sales tax in the state.
Utah's sales tax structure is notable for its uniformity across the state. Unlike some other states with varying tax rates depending on location, Utah maintains a consistent rate statewide, making compliance simpler for both businesses and consumers. However, this uniformity does not mean a single tax rate applies to all transactions; instead, different tax rates are applied based on the type of transaction and the goods or services involved.
Sales Tax Rates in Utah

The sales tax rate in Utah is composed of three primary components: the state sales tax rate, the county sales tax rate, and the local sales tax rate (applicable in some cities). As of my last update in January 2023, the state sales tax rate in Utah stands at 4.70%. This rate is consistent across the state and is applied to most retail sales, including tangible personal property and certain services.
On top of the state sales tax rate, counties in Utah are authorized to impose an additional county sales tax. The rate of this tax varies from one county to another. For instance, Salt Lake County levies a 1.25% county sales tax, bringing the total sales tax rate to 5.95% within this county. Other counties, like Utah County, have a lower county sales tax rate of 0.10%, resulting in a total sales tax rate of 4.80% in these areas.
Furthermore, certain cities in Utah may also impose a local sales tax, which is added to the state and county sales tax rates. This local sales tax rate is typically used to fund specific projects or initiatives within the city. For example, the city of Provo has a 1.00% local sales tax, leading to a total sales tax rate of 5.70% for purchases made within the city limits.
| Sales Tax Component | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| State Sales Tax | 4.70% |
| County Sales Tax (Varies) | Up to 1.25% |
| Local Sales Tax (Optional) | Up to 1.00% |
It's crucial to note that these tax rates are subject to change, and it's the responsibility of businesses and consumers to stay updated with the latest tax rates applicable in their area. The Utah State Tax Commission provides regular updates and resources to help taxpayers understand and comply with the current sales tax regulations.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Considerations
While most retail sales in Utah are subject to sales tax, there are certain exemptions and special considerations that businesses and consumers should be aware of. These exemptions can significantly impact the tax liability of a transaction, making it essential to understand them thoroughly.
Sales Tax Exemptions
Utah offers various sales tax exemptions for specific goods and services. These exemptions are designed to reduce the tax burden on certain essential items and promote specific economic activities. Some common sales tax exemptions in Utah include:
- Food for Home Consumption: Most unprepared food items for home consumption are exempt from sales tax in Utah. This exemption includes fresh produce, dairy products, meat, and other staple food items. However, prepared foods, such as hot meals from restaurants, are generally taxable.
- Prescription Drugs: Sales of prescription drugs are exempt from sales tax in Utah. This exemption applies to both over-the-counter and prescription medications.
- Manufacturing Equipment: Sales of equipment and machinery used directly in manufacturing processes are exempt from sales tax. This exemption is aimed at supporting Utah's manufacturing sector and encouraging economic growth.
- Certain Agricultural Sales: Sales of agricultural products, such as livestock, crops, and seeds, are generally exempt from sales tax. This exemption promotes Utah's agriculture industry and ensures the competitiveness of local farmers.
- Resale Exemption: Resellers, such as retailers, are exempt from sales tax on their purchases as long as the items are resold. This exemption ensures that the tax is only charged once, at the final point of sale to the consumer.
Special Considerations
In addition to exemptions, there are also special considerations for certain types of transactions in Utah. These considerations may impact the taxability of a transaction or the rate of tax applied.
- Construction Contracts: Sales tax treatment for construction contracts can be complex. Generally, the sale of labor and materials by a contractor is subject to sales tax. However, if the contractor provides a single, lump-sum price for the entire project, the transaction may be exempt from sales tax if certain conditions are met.
- Internet Sales: With the rise of e-commerce, Utah has implemented regulations for internet sales. Out-of-state sellers making sales to Utah residents are generally required to collect and remit sales tax to the state. This ensures that online purchases are taxed in the same way as in-store purchases.
- Short-Term Vehicle Rentals: Rentals of motor vehicles for a term of 30 days or less are subject to a special rental tax rate of 11.75% in Utah. This rate includes the state, county, and local sales tax rates, as well as a specific rental tax rate.
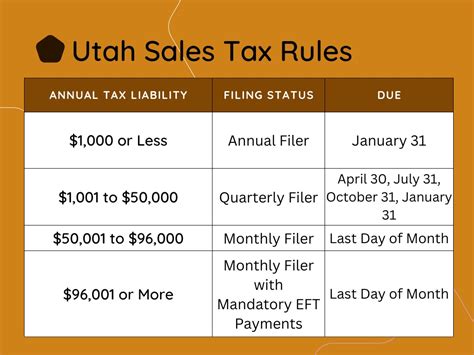
Sales Tax Registration and Compliance
Businesses operating in Utah or making sales into the state are generally required to register with the Utah State Tax Commission and obtain a sales tax permit. This permit authorizes the business to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state, counties, and municipalities.
To register for a sales tax permit, businesses typically need to provide information about their business activities, location, and expected sales. The Utah State Tax Commission provides an online registration process, making it convenient for businesses to comply with their tax obligations.
Once registered, businesses are responsible for collecting the appropriate sales tax rate on each taxable transaction and remitting these funds to the state on a regular basis. The frequency of these remittances depends on the business's expected sales volume and can range from monthly to annually.
Sales Tax Reporting and Payment
Businesses are required to file sales tax returns with the Utah State Tax Commission, reporting the total taxable sales and the amount of tax collected during the reporting period. These returns must be filed electronically, and the due date is typically the 20th day of the month following the reporting period.
Along with the sales tax return, businesses must remit the collected sales tax to the state. The payment can be made online, by mail, or through other authorized methods. It's important for businesses to ensure that their payments are made on time to avoid penalties and interest charges.
Sales Tax Audits
The Utah State Tax Commission may conduct sales tax audits to ensure compliance with the state’s sales tax regulations. These audits can be random or based on specific indicators of non-compliance. During an audit, the tax commission will review a business’s sales records, tax returns, and other relevant documentation to verify the accuracy of reported sales and tax payments.
Businesses should maintain proper records of their sales transactions, including the tax rate applied, the amount of tax collected, and any applicable exemptions. These records can help demonstrate compliance and resolve any issues that may arise during an audit.
Future Implications and Ongoing Changes

The sales tax landscape in Utah, like in many other states, is subject to ongoing changes and developments. These changes can be driven by various factors, including economic trends, legislative actions, and court rulings.
One notable trend in recent years has been the focus on remote sellers and internet sales. With the rise of e-commerce, states are increasingly seeking to collect sales tax on these transactions to ensure a level playing field for local businesses and generate additional revenue. Utah has implemented regulations to require out-of-state sellers to collect and remit sales tax on sales made to Utah residents, aligning with the trends in many other states.
Additionally, the ongoing debate around sales tax on certain services, such as streaming services and digital products, is likely to continue. As technology advances and the nature of commerce evolves, states may need to adapt their sales tax regulations to keep pace with these changes. Utah, like many other states, is closely monitoring these developments and may consider updates to its sales tax laws in the future.
It's crucial for businesses and consumers alike to stay informed about any changes to Utah's sales tax regulations. The Utah State Tax Commission provides regular updates and resources to help taxpayers understand and comply with the latest sales tax requirements. By staying informed and compliant, businesses can avoid penalties and contribute to the state's revenue system effectively.
What is the current sales tax rate in Utah?
+As of my last update, the state sales tax rate in Utah is 4.70%, with additional county and local sales tax rates applied in certain areas.
Are there any sales tax exemptions in Utah?
+Yes, Utah offers various sales tax exemptions, including for food for home consumption, prescription drugs, manufacturing equipment, and certain agricultural sales. It’s important to review the specific exemptions to understand their applicability.
How often do businesses need to remit sales tax in Utah?
+The frequency of sales tax remittance depends on the business’s sales volume. Businesses with higher sales may be required to remit sales tax monthly, while those with lower sales may be able to remit annually. It’s important for businesses to consult the Utah State Tax Commission for specific guidance.
What happens if a business fails to collect or remit sales tax in Utah?
+Failure to collect or remit sales tax can result in penalties and interest charges. Businesses should ensure they understand their sales tax obligations and comply with the state’s regulations to avoid these consequences.
How can businesses stay updated with Utah’s sales tax regulations?
+Businesses can stay informed by regularly checking the Utah State Tax Commission’s website, which provides the latest updates and resources on sales tax regulations. Additionally, businesses can subscribe to the commission’s newsletters and alerts to receive timely notifications of any changes.