Irs Tax Return Staffing Cuts
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is a federal agency responsible for collecting taxes and enforcing tax laws in the United States. It plays a critical role in ensuring the nation's fiscal stability and supporting essential government services. However, recent years have seen a significant decline in IRS resources, particularly in terms of staffing, which has raised concerns about its ability to effectively administer the tax system.
This article delves into the implications of the IRS's tax return staffing cuts, examining the potential impacts on taxpayers, tax compliance, and the overall efficiency of the tax administration process. By exploring these issues, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the challenges faced by the IRS and offer insights into potential solutions.
The IRS Staffing Crisis: A Snapshot
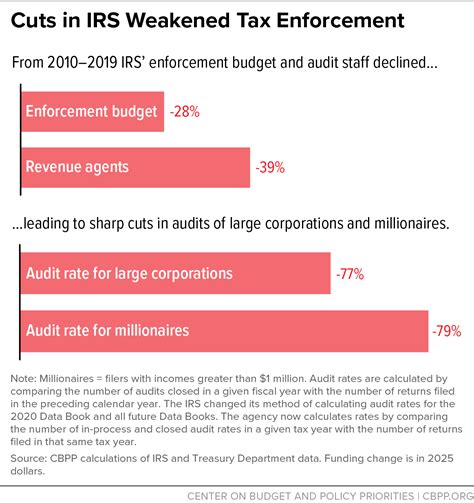
The IRS has been facing a persistent and alarming decline in its workforce over the past decade. This trend has accelerated in recent years, with the agency losing approximately 20,000 full-time employees since 2010. This significant reduction in staffing has occurred despite an increasing tax filer population and a growing complexity of the tax code.
The impact of these cuts is particularly evident in the IRS's ability to handle tax returns. The agency's customer service and examination functions have borne the brunt of these reductions, with staffing levels in these areas dropping by nearly 30% since 2010. This has resulted in longer wait times for taxpayers seeking assistance and a decrease in the number of tax returns audited, potentially leading to revenue losses for the government.
| Year | Full-Time Employees | Customer Service Staff | Examination Staff |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 100,000 | 25,000 | 20,000 |
| 2020 | 80,000 | 17,500 | 14,000 |

Impact on Taxpayer Services

One of the most immediate consequences of the IRS staffing cuts is the deterioration of taxpayer services. With fewer staff available, the agency has struggled to keep up with the demand for assistance, leading to significant delays in response times.
For instance, taxpayers who call the IRS's toll-free assistance lines often encounter long hold times, with some waiting for hours before their call is answered. In 2020, the IRS reported that it was only able to answer 58% of all incoming calls, leaving nearly half of taxpayers who sought assistance via the phone without a response.
The impact is even more pronounced for taxpayers with more complex issues. Specialized assistance, such as that provided by the IRS's Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS), has seen wait times increase significantly. The TAS, which helps taxpayers resolve problems with the IRS, reported that the average wait time for a case resolution increased from 100 days in 2010 to 205 days in 2020.
Online Services: A Growing Gap
While the IRS has encouraged taxpayers to use its online services, the agency’s staffing cuts have also impacted its ability to maintain and improve these platforms. This has resulted in a growing gap between the services the IRS offers online and the needs of taxpayers.
For example, the IRS's Get Transcript service, which allows taxpayers to view and print their tax transcripts online, experienced a significant outage in 2021 due to technical issues. The service was offline for over a month, leaving taxpayers without access to critical tax information during a crucial filing period.
Moreover, the IRS's online services often lack the personalized assistance that taxpayers may require. For taxpayers facing complex issues, such as identity theft or significant tax debt, online tools may not provide sufficient guidance, leading to confusion and potential non-compliance.
Effects on Tax Compliance and Revenue Collection
The IRS’s staffing cuts have also had a profound impact on the agency’s ability to enforce tax compliance and collect revenue. With fewer staff available for audit and enforcement activities, the IRS has been forced to reduce its scrutiny of tax returns, potentially leading to revenue losses for the government.
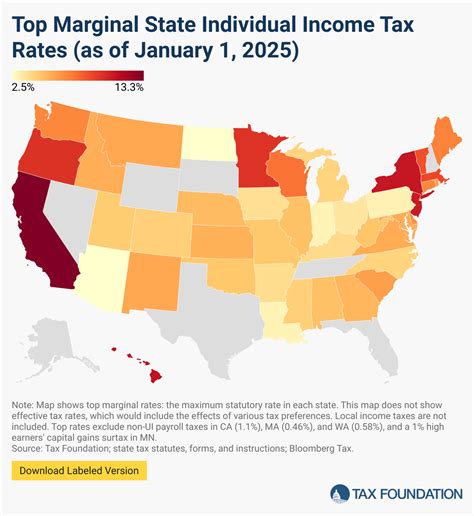
Data from the IRS's Statistical Data Reports reveals a stark decline in audit coverage over the past decade. In 2010, the IRS audited approximately 1.1% of all individual tax returns filed. By 2020, this figure had dropped to 0.45%, representing a significant decrease in the agency's audit activity.
| Year | Individual Tax Returns Filed | Audits Conducted | Audit Coverage Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 140,000,000 | 1,540,000 | 1.1% |
| 2020 | 150,000,000 | 675,000 | 0.45% |
This decline in audit coverage has likely contributed to a rise in tax non-compliance. A study by the Treasury Inspector General for Tax Administration (TIGTA) found that the IRS's ability to identify and address tax non-compliance had decreased significantly since 2010. The study attributed this decline to the agency's staffing and budget cuts, particularly in the areas of audit and enforcement.
The Cost of Non-Compliance
The impact of reduced audit coverage is not limited to potential revenue losses. Non-compliance with tax laws can have broader economic and social consequences. It can lead to an increase in the tax gap, which is the difference between taxes owed and taxes paid voluntarily and on time. A larger tax gap means less revenue for the government to fund essential services and programs, potentially impacting areas such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
Furthermore, non-compliance can create an unfair tax burden on honest taxpayers who pay their taxes fully and on time. It can also undermine public trust in the tax system, leading to a decline in voluntary tax compliance and a potential increase in tax evasion.
Future Implications and Potential Solutions
The IRS’s staffing cuts and their subsequent impacts on taxpayer services and tax compliance present a complex challenge. However, there are potential solutions that could help the agency address these issues and improve its overall efficiency.
Increasing Staffing Levels
One of the most direct ways to address the IRS’s staffing crisis is to increase its workforce. This could involve hiring more full-time employees, particularly in critical areas such as customer service and examination. Additionally, the IRS could explore options for training and retaining existing staff to ensure they are equipped to handle the complex and evolving tax landscape.
While increasing staffing levels may require additional funding, the potential benefits are significant. A larger workforce could lead to improved taxpayer services, including shorter wait times and more personalized assistance. It could also enhance the IRS's ability to enforce tax compliance, potentially reducing the tax gap and increasing revenue collection.
Modernizing Technology and Processes
In addition to increasing staffing, the IRS could benefit from modernizing its technology and processes. This could involve investing in new systems and software to improve the efficiency of tax administration. For example, the agency could explore ways to streamline its audit processes, making them more effective and less resource-intensive.
The IRS could also look to digital solutions to enhance its online services. By improving the usability and functionality of its online platforms, the agency could encourage more taxpayers to utilize these services, reducing the demand on its call centers and in-person assistance.
Expanding Taxpayer Education and Outreach
Another potential solution is to focus on taxpayer education and outreach. By providing taxpayers with the tools and resources they need to understand and comply with tax laws, the IRS could reduce the demand for personalized assistance and potentially decrease the rate of non-compliance.
This could involve launching public awareness campaigns, offering educational resources on its website, and partnering with community organizations to reach underserved populations. By empowering taxpayers to better understand their tax obligations, the IRS could potentially reduce the workload on its staff and improve overall tax compliance.
Collaboration and Data Sharing
The IRS could also benefit from increased collaboration and data sharing with other government agencies and private sector partners. By sharing data and resources, the IRS could potentially identify and address tax non-compliance more effectively. For example, the agency could collaborate with state tax authorities to compare data and identify potential instances of tax evasion.
Additionally, the IRS could explore partnerships with financial institutions and technology companies to develop innovative solutions for tax administration. These partnerships could lead to the development of new tools and platforms that enhance the IRS's ability to enforce tax compliance and improve taxpayer services.
How have IRS staffing cuts impacted tax return processing times?
+Staffing cuts have led to longer processing times for tax returns. With fewer staff available, the IRS has struggled to keep up with the volume of returns, resulting in delays. In some cases, taxpayers have experienced processing times of several months, particularly for more complex returns.
What are the potential consequences of reduced audit coverage?
+Reduced audit coverage can lead to revenue losses for the government and an increase in tax non-compliance. It may also result in an unfair tax burden on honest taxpayers and undermine public trust in the tax system.
How can the IRS improve its online services to better serve taxpayers?
+The IRS can enhance its online services by investing in user-friendly platforms and providing comprehensive resources. This could include offering detailed guides, interactive tools, and personalized assistance features to ensure taxpayers can navigate the tax system effectively.
What role can taxpayer education play in improving tax compliance?
+Taxpayer education is crucial for improving tax compliance. By providing clear and accessible information, the IRS can empower taxpayers to understand their obligations and make informed decisions. This can lead to a reduction in non-compliance and potentially decrease the workload on IRS staff.
In conclusion, the IRS’s tax return staffing cuts have had far-reaching implications for taxpayers and the overall efficiency of the tax administration process. The agency’s ability to provide timely assistance and enforce tax compliance has been significantly impacted. However, with the right strategies, including increased staffing, technology modernization, taxpayer education, and collaboration, the IRS can overcome these challenges and continue to serve the nation effectively.