Ohio Property Tax

Welcome to an in-depth exploration of Ohio's Property Tax System, a critical component of the state's economy and a key consideration for homeowners and investors alike. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide, shedding light on the intricacies of property taxation in Ohio, its impact on residents, and the factors influencing tax rates across the state.
Understanding Ohio’s Property Tax Landscape

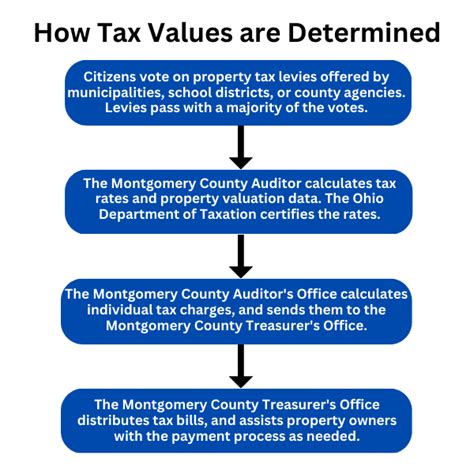
Ohio’s property tax system is a vital revenue source for local governments, school districts, and special purpose districts, funding essential services like education, infrastructure, and public safety. The system is decentralized, with each county setting its tax rates, making Ohio’s property tax landscape diverse and complex.
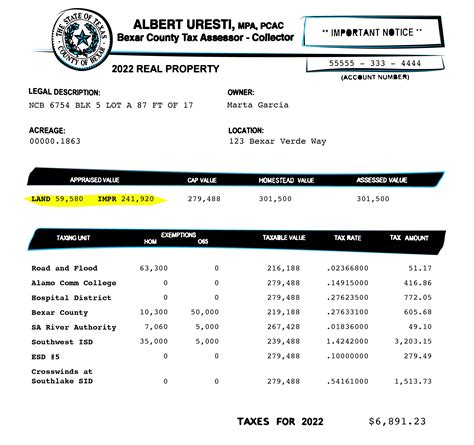
Property taxes in Ohio are calculated based on the taxable value of a property, which is determined by its appraised value minus any applicable exemptions or deductions. The appraised value, or assessed value, is the estimated market value of the property as determined by the county auditor.
The effective tax rate in Ohio varies significantly across the state, influenced by the local millage rates, which are determined by the various taxing authorities within a county. A mill is equal to one-tenth of a cent, and the millage rate represents the number of mills levied on each dollar of a property's taxable value.
| County | Effective Tax Rate (2022) | Average Home Value |
|---|---|---|
| Cuyahoga County | 2.18% | $150,900 |
| Franklin County | 2.34% | $191,400 |
| Hamilton County | 2.43% | $136,500 |
| Montgomery County | 2.26% | $109,300 |
| Summit County | 2.37% | $122,800 |
Factors Influencing Property Tax Rates
Ohio’s property tax rates are influenced by several factors, including the local budget needs of various taxing authorities, the millage rates they set, and the property values within each jurisdiction. Other factors such as state tax incentives, exemptions, and special assessments can also impact the effective tax rate for individual properties.
Property Tax Abatements and Exemptions
Ohio offers a range of property tax abatements and exemptions to eligible homeowners and property owners. These include homestead exemptions for primary residences, veterans’ exemptions, agricultural land exemptions, and tax abatement programs for certain areas or property types. These measures aim to reduce the tax burden for specific groups and promote economic development.
Property Tax Appeal Process
Ohio provides a formal appeal process for property owners who believe their property has been over-assessed or that their tax burden is excessive. The process involves filing an appeal with the county Board of Revision, which will review the property’s assessed value and make a determination. If the appeal is not successful, property owners can further appeal to the Ohio Board of Tax Appeals.
Impact on Homeownership
Ohio’s property tax system has a significant impact on homeownership rates and housing affordability. High property taxes can act as a disincentive for potential homeowners, especially in areas with rapidly increasing property values. Conversely, tax abatements and exemptions can make homeownership more feasible for certain demographics, promoting community development and stability.
Recent Developments and Future Outlook
In recent years, Ohio has implemented various measures to reform its property tax system, including increasing the homestead exemption and implementing tax abatements for certain areas. These reforms aim to reduce the tax burden on homeowners, especially those with lower incomes, and promote economic growth.
Looking ahead, Ohio's property tax landscape is likely to continue evolving, influenced by factors such as changes in the housing market, economic trends, and policy decisions at the state and local levels. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for homeowners, investors, and policymakers alike, as they navigate the complex world of Ohio's property taxation.
Key Takeaways
- Ohio’s property tax system is decentralized, with county governments setting tax rates, leading to significant variations across the state.
- Property taxes are calculated based on the taxable value of a property, determined by its appraised value minus any applicable exemptions.
- Effective tax rates can be influenced by local budget needs, millage rates, property values, and various tax incentives and exemptions.
- The state offers a formal appeal process for property owners to challenge their assessed value or tax burden.
- Recent reforms aim to reduce the tax burden on homeowners and promote economic growth, with a focus on increasing homestead exemptions and implementing tax abatements.
Conclusion
Ohio’s property tax system is a critical component of the state’s fiscal landscape, shaping the economic viability of communities and the financial obligations of homeowners. By understanding the intricacies of this system, residents and investors can make informed decisions about property ownership and investment in Ohio. This article has aimed to provide a comprehensive overview, shedding light on the key aspects of Ohio’s property tax landscape and its impact on the state’s residents.
How often are property values reassessed in Ohio?
+Property values in Ohio are typically reassessed every three years. However, counties can choose to reassess more frequently, and certain events, such as a property transfer, may trigger a reassessment outside of the regular cycle.
Are there any online tools to estimate my property taxes in Ohio?
+Yes, many counties in Ohio provide online property tax estimators on their official websites. These tools allow homeowners to estimate their property taxes based on the current millage rates and their property’s assessed value.
What happens if I don’t pay my property taxes in Ohio?
+Unpaid property taxes in Ohio can lead to significant penalties, interest, and eventually the possibility of tax foreclosure. It’s crucial to stay current on property tax payments to avoid these consequences.
Are there any tax incentives for energy-efficient home improvements in Ohio?
+Yes, Ohio offers tax incentives for energy-efficient home improvements through the Clean Energy Advanced Manufacturing (CEAM) program. This program provides tax credits for the purchase and installation of qualifying energy-efficient equipment and systems.