Mississippi State Income Tax

Mississippi is one of the seven states in the United States that does not impose a state income tax on its residents. This unique tax structure makes Mississippi an attractive location for individuals seeking to minimize their tax liabilities and maximize their disposable income.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of Mississippi's state income tax system, exploring its history, the benefits it offers, and the potential implications for individuals and businesses. By understanding the state's tax policies, we can gain valuable insights into its economic landscape and the opportunities it presents.
A State Without Income Tax: Unraveling Mississippi's Tax System

Mississippi's decision to forgo a state income tax is a strategic move that sets it apart from most other states. While many states rely on income taxes as a significant source of revenue, Mississippi has opted for an alternative approach, primarily focusing on other forms of taxation to fund its operations.
The state's tax system is primarily based on sales and use taxes, as well as various excise taxes. This structure allows Mississippi to generate revenue while keeping the burden on individuals and businesses relatively low compared to states with income taxes.
The Benefits of No Income Tax
The absence of a state income tax in Mississippi offers several advantages to its residents and businesses. Let's explore some of the key benefits:
- Lower Tax Burden: Without an income tax, individuals in Mississippi enjoy a reduced overall tax liability. This means more disposable income, which can be allocated towards savings, investments, or personal expenses.
- Competitive Business Environment: Businesses operating in Mississippi benefit from a lower cost of doing business. The absence of an income tax can make the state an attractive location for companies looking to reduce their tax obligations and increase their profitability.
- Simplified Tax Filing: Filing taxes in Mississippi is often simpler and less time-consuming for individuals and businesses. The lack of income tax forms and calculations can save valuable time and resources.
- Attracting Residents and Businesses: The no-income-tax policy has the potential to attract new residents and businesses to Mississippi. For individuals, the prospect of lower taxes can be a significant incentive to relocate, especially for those with higher incomes.
Mississippi's Tax Revenue Sources
While Mississippi does not collect income tax, it generates revenue through a diverse range of taxes. Here's an overview of the state's primary revenue sources:
| Tax Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Sales and Use Tax | Mississippi imposes a state sales tax of 7% on most goods and services. Local governments may also levy additional sales taxes, resulting in varying tax rates across the state. |
| Excise Taxes | The state collects excise taxes on specific goods and activities, including gasoline, tobacco, alcohol, and motor vehicle sales. These taxes are often levied at fixed rates or as a percentage of the sale price. |
| Property Taxes | Property taxes are assessed at the local level and vary across counties and municipalities. These taxes contribute significantly to local government revenues. |
| Franchise Taxes | Businesses operating in Mississippi are subject to franchise taxes, which are based on the company's capital stock or net worth. These taxes provide a stable source of revenue for the state. |
| Other Taxes | Mississippi also collects various other taxes, such as severance taxes on natural resources, estate taxes, and taxes on insurance premiums. |
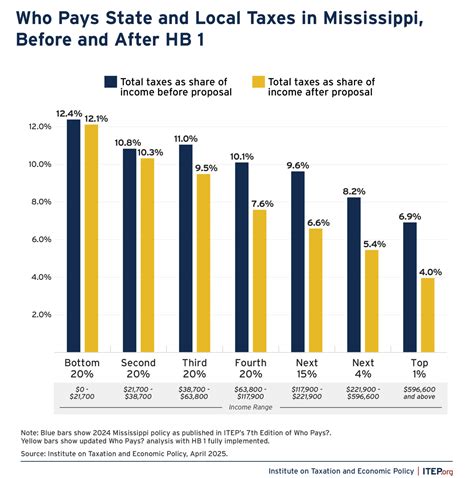
Comparative Analysis: Mississippi's Tax Climate
To understand the implications of Mississippi's tax system, let's compare it with states that impose income taxes. Here's a comparative analysis:
Tax Burden
States with income taxes often have a higher overall tax burden on their residents. While Mississippi may have lower sales and use taxes compared to some states, the absence of an income tax significantly reduces the overall tax liability for individuals and businesses.
Economic Impact
Mississippi's tax structure has the potential to stimulate economic growth. By attracting businesses and individuals with lower tax rates, the state can foster job creation, investment, and a more vibrant economy. However, it's essential to consider the long-term sustainability of this strategy and its impact on public services and infrastructure.
Revenue Generation
Mississippi's revenue generation primarily relies on consumption taxes, which can be more volatile and dependent on economic conditions. In contrast, states with income taxes have a more stable and consistent revenue stream. This difference in revenue sources can impact the state's ability to fund essential services and infrastructure projects.
Implications and Considerations
While Mississippi's no-income-tax policy offers advantages, it's crucial to consider the potential implications:
- Limited Funding for Public Services: Relying primarily on consumption taxes may limit the state's ability to fund critical public services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. This can lead to budget constraints and potential cuts in essential programs.
- Inequality and Progressive Taxation: The absence of an income tax can result in a less progressive tax system, as wealthier individuals may benefit more from the lower tax burden. This can contribute to income inequality and a regressive tax structure.
- Economic Sustainability: While the no-income-tax policy may attract businesses and residents in the short term, the long-term sustainability of this strategy needs careful consideration. Mississippi must ensure it can provide the necessary infrastructure and services to support its growing population and businesses.
Conclusion: Navigating Mississippi's Tax-Free Horizon
Mississippi's decision to forgo a state income tax presents both opportunities and challenges. The state's unique tax system has the potential to drive economic growth, attract investment, and provide a competitive advantage. However, it also requires careful planning and consideration of the long-term implications on public services and economic sustainability.
As we navigate Mississippi's tax-free horizon, it is essential to strike a balance between attracting businesses and residents and ensuring the state's fiscal health and well-being. By understanding the intricacies of Mississippi's tax system, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions and contribute to the state's continued prosperity.
Does Mississippi have any plans to introduce an income tax in the future?
+
Currently, there are no concrete plans to introduce an income tax in Mississippi. The state’s leadership has expressed a commitment to maintaining the no-income-tax policy, citing its economic benefits. However, tax policies can evolve over time, so it is essential to stay informed about any potential changes.
How does Mississippi’s tax system impact its business climate?
+
Mississippi’s tax system, particularly the absence of an income tax, creates a favorable business climate. Businesses can operate with reduced tax obligations, which can enhance their profitability and competitiveness. This, in turn, attracts new businesses and investment, contributing to economic growth.
What are the potential drawbacks of a consumption-based tax system like Mississippi’s?
+
A consumption-based tax system can be regressive, as it places a higher burden on lower-income individuals who spend a larger proportion of their income on necessities. Additionally, the reliance on consumption taxes can make the state’s revenue vulnerable to economic downturns, as consumer spending may decline during such periods.