Do You Pay Tax On Life Insurance
The question of whether life insurance benefits are taxable is a complex one and depends on various factors, including the type of life insurance policy, the jurisdiction, and the purpose for which the proceeds are used. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of life insurance taxation, exploring the different scenarios and providing clarity on this often-confusing topic.
Understanding Life Insurance Taxation

Life insurance policies are financial tools designed to provide financial protection to beneficiaries upon the death of the policyholder. The tax treatment of these policies can vary significantly, and it is essential to understand the nuances to ensure compliance with the law and maximize the benefits for the beneficiaries.
Key Factors Influencing Taxability
-
Policy Type: Different types of life insurance policies have distinct tax implications. For instance, whole life insurance policies, which accumulate cash value over time, may have different tax rules compared to term life insurance policies that provide coverage for a specific period.
-
Jurisdiction: Tax laws vary from country to country and even within different states or provinces. It is crucial to consider the specific tax regulations in the jurisdiction where the policyholder resides and where the policy is issued.
-
Purpose of Proceeds: The way in which the life insurance proceeds are utilized can impact their tax treatment. For example, if the proceeds are used to pay for final expenses or to provide financial support to beneficiaries, the tax implications may differ from using the proceeds for investment purposes.
Taxation of Life Insurance Benefits
Let’s explore the tax treatment of life insurance benefits in different scenarios:
-
Individual Life Insurance Policies: In most cases, the death benefit proceeds from an individual life insurance policy are not subject to income tax for the beneficiary. This is because life insurance is typically viewed as a means to provide financial security and replace lost income for dependents. However, it is essential to note that there may be exceptions, especially if the policyholder has paid premiums with pre-tax dollars or if the policy has a significant cash value component.
-
Group Life Insurance Plans: Many employers offer group life insurance plans as part of their employee benefits package. The tax treatment of these plans can vary. Generally, the death benefit proceeds from a group life insurance plan are not taxable for the beneficiary if the policy is obtained through an employer and the coverage is below a certain threshold. However, if the coverage exceeds a specified amount, the excess portion may be taxable.
-
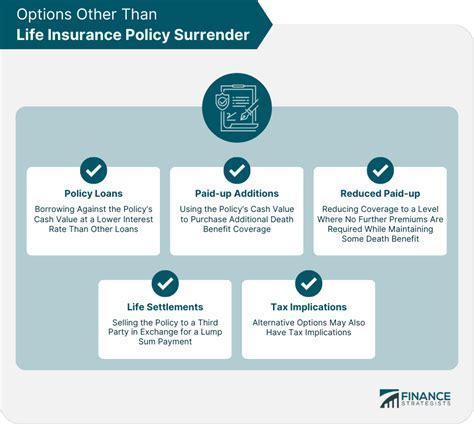
Cash Value Life Insurance: Whole life insurance policies and other policies with a cash value component have different tax considerations. While the death benefit proceeds are typically tax-free, the cash value of the policy may be taxable. The cash value accumulates over time and can be accessed through loans or withdrawals. If the policyholder withdraws funds or surrenders the policy, the cash value may be subject to income tax.
Tax Implications for Policyholders
While the focus is often on the tax treatment of life insurance benefits for beneficiaries, it is essential to consider the tax implications for policyholders as well:
-
Premium Payments: The tax treatment of premium payments depends on the policy type and the policyholder’s circumstances. For example, if an individual uses pre-tax dollars, such as through a flexible spending account (FSA) or health savings account (HSA), to pay for life insurance premiums, there may be tax advantages. However, if the premiums are paid with after-tax dollars, there may be no immediate tax benefit.
-
Policy Loans and Withdrawals: If a policyholder takes out a loan against the cash value of their life insurance policy, the interest accrued on the loan may be taxable. Additionally, if the policyholder surrenders the policy or withdraws funds, the cash value may be subject to income tax, and there may be potential tax penalties if the policy has been in force for less than a specified period.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies

To illustrate the complexity of life insurance taxation, let’s explore a few real-world scenarios:
| Scenario | Tax Treatment |
|---|---|
| John, a self-employed individual, purchases a whole life insurance policy with a 500,000 death benefit. He pays the premiums using after-tax dollars. Upon his death, his beneficiary receives the 500,000 tax-free. | The death benefit proceeds are not taxable for the beneficiary. However, if John had used pre-tax dollars to pay the premiums, there may have been tax implications for the accumulated cash value. |
| Emily, an employee, is enrolled in her company’s group life insurance plan with a 1 million death benefit. The policy is considered a "qualified plan" under tax laws. Upon Emily's passing, her beneficiary receives the full 1 million tax-free. | Since the policy is part of a qualified group plan, the death benefit proceeds are not taxable for the beneficiary. However, if Emily’s coverage had exceeded the threshold for qualified plans, the excess amount may have been taxable. |
| Michael, a business owner, has a whole life insurance policy with a $2 million death benefit and a substantial cash value. He takes out a loan against the cash value to fund his business. The interest on the loan is taxable income for Michael. | The death benefit proceeds would not be taxable for Michael’s beneficiary. However, the interest income from the policy loan is taxable, and Michael must report it on his tax return. |

Expert Insights and Tips
Future Implications and Regulatory Changes
The tax landscape surrounding life insurance is subject to change, and policyholders and beneficiaries should stay informed about any potential regulatory updates. Here are some key considerations for the future:
-
Tax Law Amendments: Tax laws are dynamic, and changes in legislation can impact the tax treatment of life insurance policies. It is essential to stay updated on any amendments or proposals that may affect your policy.
-
International Considerations: If you have life insurance policies in multiple jurisdictions or are an expatriate, the tax treatment can become even more complex. Understanding the tax implications across borders is crucial for accurate financial planning.
-
Policy Modifications: Changes to your life insurance policy, such as increasing coverage or converting a term policy to a whole life policy, may have tax implications. It is advisable to consult a professional before making any significant modifications.
FAQs
Are life insurance benefits always tax-free for beneficiaries?
+In most cases, life insurance benefits are tax-free for beneficiaries. However, there are exceptions, especially for policies with significant cash value components or if the policyholder has paid premiums with pre-tax dollars.
Can I use pre-tax dollars to pay for life insurance premiums?
+Yes, in certain circumstances, you can use pre-tax dollars, such as through an FSA or HSA, to pay for life insurance premiums. This can provide tax advantages, but it’s important to consult a tax professional to understand the implications.
What happens if I take out a loan against my life insurance policy’s cash value?
+When you take out a loan against the cash value of your life insurance policy, the interest accrued on the loan is taxable income. It’s essential to consider the tax implications before taking out a policy loan.
Are there any tax benefits for business owners with life insurance policies?
+Business owners may be able to deduct certain life insurance premiums as a business expense. However, the tax treatment can be complex, and it’s advisable to seek professional advice to maximize tax benefits.
How can I ensure I’m compliant with tax laws regarding my life insurance policy?
+To ensure compliance, it’s crucial to consult with a qualified tax professional or financial advisor. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific circumstances and help you navigate the tax implications of your life insurance policy.
In conclusion, the tax treatment of life insurance policies is a multifaceted topic that requires careful consideration. By understanding the key factors influencing taxability, consulting with professionals, and staying informed about regulatory changes, policyholders and beneficiaries can make informed decisions to maximize the benefits of life insurance while ensuring compliance with tax laws.