Corporation Tax Rate In Canada

Canada's corporate tax structure is a multifaceted system, designed to provide a competitive environment for businesses while contributing to the country's economic growth and development. Understanding the nuances of this tax system is crucial for businesses, especially those operating in multiple provinces or planning their international expansion. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the corporate tax rates across Canada, exploring the variations between provinces, the applicable tax brackets, and the factors that influence these rates.
The Canadian Corporate Tax Landscape

Canada boasts a robust corporate tax system, renowned for its competitiveness on the global stage. The country's federal government sets the base rate for corporate taxes, which is then supplemented by provincial rates, resulting in a combined federal-provincial tax rate. This two-tiered system allows for regional variations, enabling provinces to tailor their tax structures to suit their economic goals and needs.
The federal corporate tax rate stands at 15%, a competitive rate that contributes to Canada's attractiveness as a business destination. However, when combined with provincial rates, the overall tax burden can vary significantly, with some provinces opting for lower rates to encourage investment and economic activity.
Provincial Variations: A Snapshot
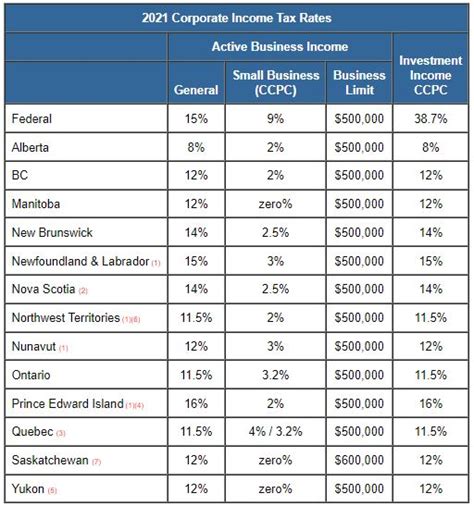
Each province in Canada has the autonomy to set its own corporate tax rate, resulting in a diverse landscape of tax structures. Here's a brief overview of the corporate tax rates across some key provinces:
| Province | Corporate Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Alberta | 12% |
| British Columbia | 11.5% |
| Ontario | 11.5% |
| Quebec | 11.5% |
| Nova Scotia | 16% |
| New Brunswick | 14% |

It's important to note that these rates are subject to change, and businesses should refer to the latest tax regulations for accurate information. The rates can also vary depending on the type of corporation and its specific activities, with some provinces offering reduced rates for small businesses or certain industries.
Factors Influencing Corporate Tax Rates
The corporate tax rates in Canada are influenced by a variety of factors, each designed to encourage specific economic behaviors or support particular industries. Some key considerations include:
- Economic Development Strategies: Provinces often use tax rates as a tool to encourage economic growth and development. Lower tax rates can attract businesses and investment, particularly in sectors deemed strategic for the province's economy.
- Industry Incentives: Certain industries may be eligible for reduced tax rates or tax incentives to encourage their growth and establishment in the province. This can include sectors such as manufacturing, technology, or renewable energy.
- Regional Equity: Provinces may adjust tax rates to promote regional equity, ensuring that businesses across different areas of the province are treated fairly and have access to similar economic opportunities.
- Revenue Requirements: While competitive tax rates are desirable, provinces also need to generate sufficient revenue to fund public services and infrastructure. This balance between competitiveness and revenue generation can influence the setting of corporate tax rates.
Corporate Tax Brackets and Thresholds
Canada's corporate tax system operates on a graduated rate structure, meaning that the tax rate increases as the corporation's taxable income rises. This system ensures that larger corporations, with higher profits, contribute a greater share of their income to the tax system.
Federal Tax Brackets
The federal government sets the following tax brackets for corporate income:
| Taxable Income Range | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $500,000 | 15% |
| $500,000 - $1,000,000 | 27.5% |
| Over $1,000,000 | 38% |
These brackets are designed to ensure a progressive tax system, where larger corporations contribute a higher proportion of their income to the federal government.
Provincial Tax Brackets
Similar to the federal system, provinces also utilize graduated tax brackets. The specific brackets and rates vary between provinces, allowing them to tailor their tax structures to their unique economic needs.
For instance, Ontario's corporate tax brackets are as follows:
| Taxable Income Range | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $500,000 | 11.5% |
| $500,001 - $600,000 | 12.5% |
| $600,001 - $700,000 | 13.5% |
| $700,001 - $800,000 | 14.5% |
| Over $800,000 | 15.5% |
As you can see, Ontario's tax brackets are more granular, ensuring a progressive tax structure that encourages economic growth while generating necessary revenue.
Tax Thresholds and Exemptions
In addition to tax brackets, Canada's corporate tax system also incorporates various thresholds and exemptions. These mechanisms further refine the tax system, offering incentives and support to specific sectors or types of businesses.
For example, many provinces offer a small business deduction, which provides a reduced tax rate for corporations with lower levels of income. This deduction aims to support small businesses and encourage their growth and development.
Additionally, certain industries or sectors may be eligible for tax credits or exemptions, particularly those involved in research and development, film production, or environmental initiatives. These incentives are designed to foster innovation, creativity, and sustainability within the Canadian economy.
The Impact of Corporate Tax Rates on Business Operations
Corporate tax rates play a pivotal role in shaping the business landscape in Canada. These rates influence a wide range of business decisions, from where a company chooses to locate its operations to how it structures its financial strategies.
Attracting Investment and Talent
Competitive corporate tax rates are a powerful tool for attracting investment and talent to a province or region. Lower tax rates can make a location more attractive for businesses, particularly those with significant tax liabilities. This, in turn, can lead to increased economic activity, job creation, and a boost to the local economy.
Moreover, lower tax rates can also make a province more appealing to high-net-worth individuals and professionals, who may choose to locate their businesses or careers in areas with more favorable tax environments. This influx of talent can further enhance the province's economic potential and contribute to its long-term growth.
Influencing Business Strategy
The corporate tax rate can significantly influence a business's strategic decisions. Companies may opt to restructure their operations or even relocate to take advantage of more favorable tax environments. This can lead to complex tax planning strategies, with businesses seeking to optimize their tax liabilities while remaining compliant with regulations.
For instance, a business with operations across multiple provinces may choose to allocate its income across these provinces to benefit from lower tax rates in certain regions. This requires a nuanced understanding of the tax regulations in each province and the ability to effectively manage the company's financial operations.
Impact on Economic Growth
The corporate tax rate is a key component in a province's economic growth strategy. Lower tax rates can encourage business expansion, investment, and job creation, all of which contribute to a thriving economy. Conversely, higher tax rates can deter investment and hinder economic growth, particularly in sectors with thin profit margins.
Furthermore, a competitive tax environment can make a province more attractive for foreign investment, as international businesses seek locations with favorable tax structures. This influx of foreign capital can drive innovation, create new industries, and boost the province's global competitiveness.
Conclusion: Navigating Canada's Corporate Tax Landscape
Canada's corporate tax system is a complex yet flexible structure, designed to support the country's economic growth while generating revenue for essential public services. The variations in tax rates across provinces provide a unique landscape, offering businesses a range of options and incentives to consider.
For businesses operating in Canada, understanding the corporate tax rates and their implications is crucial. This knowledge enables businesses to make strategic decisions, optimize their tax liabilities, and contribute effectively to the Canadian economy. Whether it's leveraging tax incentives, structuring operations to benefit from lower rates, or simply staying compliant with regulations, a comprehensive understanding of the corporate tax landscape is essential.
As the Canadian economy continues to evolve, so too will its corporate tax system. Staying informed about these changes and adapting strategies accordingly will be key to success in this dynamic environment. By staying ahead of the curve, businesses can ensure they remain competitive, compliant, and well-positioned for growth in the years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average corporate tax rate in Canada?
+
The average corporate tax rate in Canada, including both federal and provincial rates, is approximately 26.5%. However, this rate can vary significantly depending on the province and the specific circumstances of the corporation.
Are there any tax incentives for certain industries in Canada?
+
Yes, Canada offers a range of tax incentives for various industries. These can include tax credits for research and development, film production, and clean energy initiatives. Additionally, certain provinces may offer specific incentives to attract investment in strategic sectors.
How often are corporate tax rates reviewed and updated in Canada?
+
Corporate tax rates in Canada are typically reviewed and updated on an annual basis. However, significant changes may occur more infrequently, usually as part of broader economic policy shifts or budget announcements.



