Income Tax Rate For Virginia
The income tax landscape in Virginia is an intricate system that varies based on individual circumstances. This comprehensive guide will explore the nuances of Virginia's income tax structure, shedding light on the rates, brackets, and unique aspects that impact taxpayers.
For a single filer with an annual income of 50,000, the applicable tax rate would be 5.75%. This is because the income exceeds the threshold for the fourth tax bracket (17,000), and the entire income falls within the top tax bracket.
Are there any tax credits available for Virginia residents with low incomes?
+Yes, Virginia offers a Low-Income Tax Credit for eligible residents. This credit can reduce the amount of tax owed by up to 300 for individuals and $600 for married couples filing jointly. The eligibility criteria are based on income and family size.">What is the income tax rate for Virginia residents with an annual income of 50,000? +
For a single filer with an annual income of 50,000, the applicable tax rate would be 5.75%. This is because the income exceeds the threshold for the fourth tax bracket (17,000), and the entire income falls within the top tax bracket.
Are there any tax credits available for Virginia residents with low incomes?
+Understanding Virginia’s Income Tax Rates
Virginia operates a progressive income tax system, meaning the tax rate increases as your income rises. This approach ensures that individuals with higher incomes contribute a larger proportion of their earnings towards state revenue. The Commonwealth of Virginia offers five income tax brackets, each with its own tax rate. These brackets are adjusted annually to account for inflation and economic changes.
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 1. Single filers with income up to $3,000 | 2% |
| 2. Single filers with income between $3,001 and $5,000 | 3% |
| 3. Single filers with income between $5,001 and $17,000 | 5% |
| 4. Single filers with income over $17,000 | 5.75% |
| 5. Married filing jointly with income over $14,000 | 5.75% |

These rates apply to Virginia residents and non-residents with Virginia-sourced income. It's important to note that the tax brackets and rates are subject to change, so it's advisable to refer to the Virginia Department of Taxation for the most current information.
Virginia’s Income Tax Brackets and Their Impact
The income tax brackets in Virginia play a crucial role in determining an individual’s tax liability. For instance, a single filer with an annual income of 20,000 would fall into the third bracket, paying a tax rate of 5% on the portion of their income between 5,001 and 17,000, and a rate of 5.75% on the income over 17,000.
Additionally, Virginia offers a variety of deductions and credits that can reduce the amount of tax you owe. These include deductions for medical expenses, charitable contributions, and certain business expenses. The state also provides credits for low-income individuals, families with children, and those who invest in certain economic development initiatives.
Comparative Analysis: Virginia vs. Other States
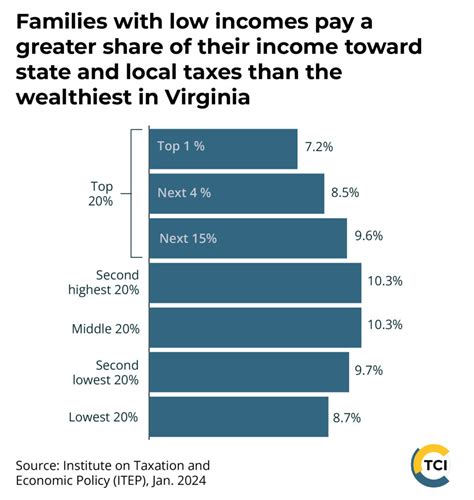
When compared to other states, Virginia’s income tax structure stands out for its progressive nature and relatively low top tax rate. Many states have higher top tax rates, with some reaching as high as 13.3% in California. Virginia’s 5.75% top tax rate is considerably lower, making it a more tax-friendly state for high-income earners.
Furthermore, Virginia's income tax system is unique in that it does not offer a standard deduction. Instead, it provides a personal exemption, which is an amount that you can deduct from your taxable income for yourself and each of your dependents. This exemption amount is adjusted annually to keep pace with inflation.
Virginia’s Tax Incentives and Business Climate
Virginia’s income tax structure is designed to encourage economic growth and investment. The state offers a range of tax incentives for businesses, including tax credits for job creation, research and development, and investment in certain industries. These incentives aim to attract businesses and create a competitive business climate.
For instance, the Commonwealth offers a Research and Development Tax Credit, which provides a credit against Virginia income tax for qualified research expenses. This credit can be carried forward for up to 15 years, making it an attractive incentive for businesses engaged in research and innovation.
Tax Planning Strategies for Virginians
Navigating Virginia’s income tax system effectively requires a strategic approach. Here are some key strategies to consider:
- Maximize deductions and credits: Take advantage of the deductions and credits available to reduce your taxable income. This could include deducting business expenses, charitable contributions, or claiming the low-income credit if eligible.
- Optimize investment strategies: Virginia's tax incentives for investment can provide significant benefits. Consider investing in eligible industries or initiatives to take advantage of the available tax credits.
- Review tax brackets annually: Keep up-to-date with the latest tax brackets and rates. Adjust your financial strategies accordingly to ensure you're optimizing your tax position.
- Seek professional advice: Complex tax situations may require the expertise of a tax professional. Consider consulting a certified public accountant (CPA) or tax attorney to ensure you're making the most of your tax planning opportunities.
The Role of Technology in Tax Preparation
In today’s digital age, technology plays a significant role in tax preparation. Virginia taxpayers can benefit from a range of tax preparation software and online tools that simplify the process. These tools can help with everything from calculating deductions to preparing and filing tax returns.
For example, popular tax preparation software like TurboTax and H&R Block offer Virginia-specific tax forms and guidance. These platforms can help taxpayers navigate the complexities of Virginia's tax system, ensuring accurate and efficient tax filing.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes
As with any tax system, Virginia’s income tax structure is subject to potential changes and reforms. The state’s tax policies are influenced by a range of factors, including economic conditions, political dynamics, and the need for revenue to fund public services.
In recent years, there have been discussions about potential reforms to Virginia's tax system. These include proposals to flatten the tax rate structure, introduce a state-level sales tax, or modify the tax brackets to provide more relief for middle-income earners. While these proposals have not yet been implemented, they highlight the ongoing efforts to modernize and improve the tax system.
The Impact of Remote Work on Virginia’s Tax Landscape
The rise of remote work, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, has presented new challenges and opportunities for Virginia’s tax system. With more individuals working remotely across state lines, the issue of tax residency and apportionment has become more complex.
Virginia has implemented guidelines to determine tax residency for remote workers. Generally, if you work remotely for a Virginia-based employer, you are considered a Virginia resident for tax purposes. However, the state also recognizes that individuals may have multiple state residencies, and it offers guidelines to help determine your primary state of residence for tax purposes.
Conclusion
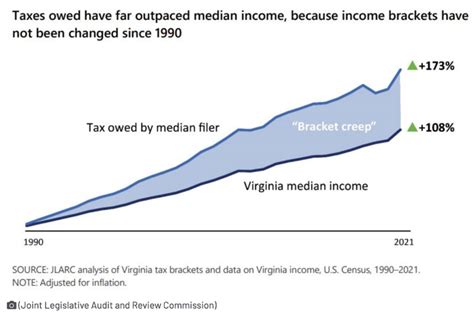
Virginia’s income tax system is a carefully designed structure that aims to balance the needs of the state’s residents and businesses. With its progressive tax rates, incentives for investment, and focus on economic growth, Virginia offers a tax environment that is both competitive and supportive.
Understanding the intricacies of Virginia's tax system is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. By staying informed and adopting strategic tax planning approaches, taxpayers can navigate the system effectively and ensure they are optimizing their financial positions.
What is the income tax rate for Virginia residents with an annual income of 50,000?</h3> <span class="faq-toggle">+</span> </div> <div class="faq-answer"> <p>For a single filer with an annual income of 50,000, the applicable tax rate would be 5.75%. This is because the income exceeds the threshold for the fourth tax bracket (17,000), and the entire income falls within the top tax bracket.</p> </div> </div> <div class="faq-item"> <div class="faq-question"> <h3>Are there any tax credits available for Virginia residents with low incomes?</h3> <span class="faq-toggle">+</span> </div> <div class="faq-answer"> <p>Yes, Virginia offers a Low-Income Tax Credit for eligible residents. This credit can reduce the amount of tax owed by up to 300 for individuals and $600 for married couples filing jointly. The eligibility criteria are based on income and family size.
Can non-residents with Virginia-sourced income claim deductions or credits?
+Non-residents with Virginia-sourced income can claim certain deductions and credits, such as the Research and Development Tax Credit or the Low-Income Tax Credit, if they meet the eligibility requirements. However, they may not be able to claim all deductions and credits available to residents.