Wisconsin State Tax Brackets
Understanding Wisconsin State Tax Brackets: A Comprehensive Guide for Taxpayers
When it comes to understanding the intricacies of state taxes, Wisconsin residents have a unique system to navigate. Wisconsin's progressive tax structure means that taxpayers are placed into specific tax brackets, and the income earned within those brackets is taxed at varying rates. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to Wisconsin's state tax brackets, helping residents and businesses make sense of their tax obligations and plan their financial strategies accordingly.
Wisconsin's tax system is designed to ensure fairness and contribute to the state's revenue. By understanding the tax brackets and how they apply to your income, you can make informed decisions about your finances and potentially optimize your tax situation. Let's delve into the details of Wisconsin's tax brackets and explore the key aspects that impact taxpayers.
The Progressive Nature of Wisconsin’s Tax System

Wisconsin’s tax system operates on a progressive basis, which means that taxpayers are subjected to different tax rates depending on their income level. This approach aims to distribute the tax burden fairly across the population, ensuring that those with higher incomes contribute a larger share. Understanding the progressive nature of Wisconsin’s tax system is crucial for taxpayers to assess their tax liability accurately.
Tax Brackets and Income Thresholds
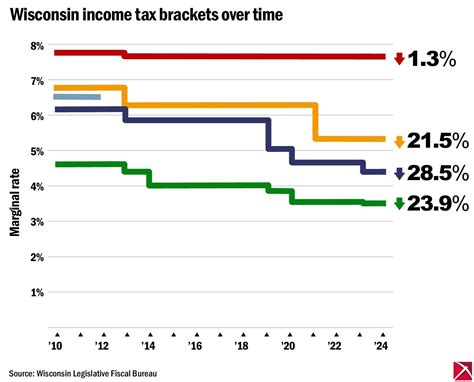
Wisconsin’s tax brackets are divided into several income ranges, and each bracket is associated with a specific tax rate. As your income increases, you may find yourself moving into higher tax brackets, which come with incrementally higher tax rates. The income thresholds for each bracket are set by the Wisconsin Department of Revenue and may be adjusted periodically to account for inflation and economic changes.
Currently, Wisconsin has four income tax brackets, each with its own tax rate. These brackets are as follows:
| Tax Bracket | Income Range | Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Up to $12,250 | 3.73% |
| 2 | $12,251 - $24,500 | 4.85% |
| 3 | $24,501 - $127,000 | 5.97% |
| 4 | Over $127,000 | 7.65% |

These income ranges and tax rates are applicable for the 2023 tax year and may be subject to change in future years. It's essential to stay updated with the latest tax information to ensure accurate tax planning.
How Tax Brackets Affect Your Tax Liability
The impact of tax brackets on your tax liability depends on your total taxable income. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how tax brackets work in Wisconsin:
- Single Taxpayers: If you're a single filer, your taxable income is divided into the appropriate tax brackets. For instance, if your income is $50,000, you'll pay 3.73% on the first $12,250, 4.85% on the next $12,250, and so on, until your entire income is taxed at the applicable rates.
- Married Filing Jointly: For married couples filing jointly, the tax brackets are applied to your combined income. This means that if your joint income is $100,000, you'll pay taxes according to the tax rates for each bracket as your income falls within those ranges.
- Head of Household: Taxpayers filing as Head of Household also have their own set of tax brackets and rates. These brackets are designed to provide some tax relief for single parents or individuals supporting dependents.
Strategies for Tax Optimization
Understanding Wisconsin’s tax brackets can help you implement strategies to optimize your tax situation. Here are a few tips to consider:
- Maximize Deductions and Credits: Explore the various deductions and tax credits available to you. These can help reduce your taxable income and potentially lower your overall tax liability. Common deductions include mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and certain business expenses.
- Strategic Income Management: If you have the flexibility, consider strategies to manage your income across tax years. For example, if you expect a significant increase in income, you might explore options to spread that income over multiple years to avoid jumping into a higher tax bracket.
- Utilize Retirement Accounts: Contributions to tax-advantaged retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s or IRAs, can reduce your taxable income. This not only helps lower your tax liability but also provides long-term benefits for your retirement savings.
Future Implications and Tax Reform
Wisconsin’s tax system is subject to periodic reviews and potential reforms. While the current tax brackets provide a stable framework for taxpayers, it’s essential to stay informed about any proposed changes or adjustments to the tax code. Tax reform initiatives can impact the number of brackets, income thresholds, and tax rates, which would, in turn, affect your tax liability.
Staying engaged with tax-related news and updates is crucial for taxpayers to adapt their financial strategies accordingly. By being proactive and aware of potential changes, you can ensure that your tax planning remains effective and aligned with the evolving tax landscape.
Conclusion: Navigating Wisconsin’s Tax Landscape
Understanding Wisconsin’s state tax brackets is a fundamental step in managing your financial obligations and planning for the future. By grasping the progressive nature of the tax system and the impact of tax brackets on your income, you can make informed decisions about your finances and optimize your tax situation. Remember, tax planning is a continuous process, and staying updated with the latest tax information is key to successful financial management.
Whether you're a resident or a business owner in Wisconsin, this guide aims to provide valuable insights into the state's tax system. By leveraging the knowledge gained from this article, you can approach your tax obligations with confidence and make the most of the opportunities available within Wisconsin's tax framework.
What is the tax rate for Wisconsin’s highest tax bracket in 2023?
+For the 2023 tax year, the highest tax bracket in Wisconsin has a rate of 7.65% for incomes over $127,000.
Are there any tax credits or deductions that can reduce my taxable income in Wisconsin?
+Yes, Wisconsin offers various tax credits and deductions, including the Homestead Credit, Property Tax Credit, and Earned Income Tax Credit. These can help reduce your taxable income and potentially lower your tax liability.
How often are Wisconsin’s tax brackets and rates adjusted?
+Wisconsin’s tax brackets and rates are typically adjusted annually to account for inflation and economic changes. The adjustments are made based on the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and other economic indicators.
Can I estimate my tax liability based on Wisconsin’s tax brackets?
+Yes, you can estimate your tax liability by breaking down your income into the appropriate tax brackets and applying the corresponding tax rates. However, it’s important to note that this estimation does not account for deductions, credits, or other tax adjustments that may apply to your specific situation.
Are there any online tools or resources to help me calculate my Wisconsin state taxes?
+Yes, the Wisconsin Department of Revenue provides an online tax estimator tool on their website. This tool allows you to input your income and deductions to estimate your tax liability. Additionally, various tax preparation software and online calculators are available to assist with tax calculations.