Virginia Sales Tax Cars
Understanding the intricacies of sales tax can be a challenging task, especially when it comes to purchasing a vehicle. In the state of Virginia, the sales tax on cars is a critical aspect for both buyers and sellers to comprehend. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the specific regulations and procedures surrounding Virginia's sales tax on cars, ensuring that you navigate the process with clarity and confidence.
Virginia’s Sales Tax: An Overview

Virginia imposes a sales and use tax on tangible personal property and certain services, including the purchase of vehicles. This tax is collected by the Virginia Department of Taxation and is crucial for generating revenue to support various state initiatives and programs. The sales tax rate in Virginia varies depending on the jurisdiction, with a state sales tax rate of 4.3% as of 2023. However, this rate can increase due to additional local taxes, which can range from 0% to 2.5%.
When purchasing a vehicle in Virginia, it's essential to be aware of the specific sales tax regulations to ensure compliance and avoid any potential legal issues. Here's a detailed breakdown of the process and key considerations:
Calculating Sales Tax on Vehicles
The sales tax rate applicable to a vehicle purchase is determined by the jurisdiction where the vehicle will be primarily registered and garaged. This means that if you plan to register and keep the vehicle in a particular city or county, you’ll need to pay the sales tax rate specific to that location.
For instance, if you're purchasing a vehicle in Arlington County, the sales tax rate would be the sum of the state sales tax rate (4.3%) and the local tax rate for Arlington County (1.2%), resulting in a total sales tax rate of 5.5% for that jurisdiction.
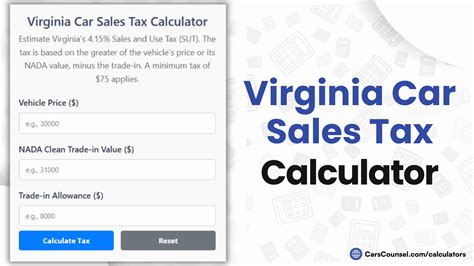
To calculate the sales tax amount for your vehicle purchase, you'll need to multiply the vehicle's purchase price by the applicable sales tax rate. For example, if you're buying a car for $25,000 in Arlington County, the sales tax amount would be calculated as follows:
| State Sales Tax Rate | 4.3% |
|---|---|
| Local Tax Rate (Arlington County) | 1.2% |
| Total Sales Tax Rate | 5.5% |
| Vehicle Purchase Price | $25,000 |
| Sales Tax Amount | $1,375 |

Therefore, the sales tax amount for this purchase would be $1,375, which is 5.5% of the vehicle's purchase price.
Exemptions and Special Cases
While the general sales tax rate applies to most vehicle purchases, there are specific exemptions and special cases to consider:
- Military Sales Tax Exemption: Active-duty military personnel stationed in Virginia may be eligible for a sales tax exemption on the purchase of a vehicle. This exemption applies to both new and used vehicles and is designed to support military families. To claim this exemption, you'll need to provide proper documentation and complete the necessary forms.
- Trade-Ins and Used Vehicles: When trading in a vehicle as part of a purchase, the sales tax is typically calculated based on the difference between the trade-in value and the purchase price of the new vehicle. Additionally, when buying a used vehicle from a private seller, the sales tax is usually calculated based on the purchase price or the fair market value of the vehicle, whichever is higher.
- Leasing and Rental Vehicles: Leasing a vehicle in Virginia is subject to sales tax, similar to purchasing a vehicle. The tax is calculated based on the monthly lease payments, and you'll need to pay the applicable sales tax to the leasing company. Rental vehicles are also subject to sales tax, which is typically included in the rental rate.
Payment and Filing Requirements
After purchasing a vehicle in Virginia, you’ll need to remit the sales tax to the Virginia Department of Taxation. The payment can be made online, by mail, or in person at a local tax office. It’s crucial to keep accurate records of your purchase and sales tax payment, as you may need to provide this information during the vehicle registration process.
If you're a Virginia resident and you purchase a vehicle out-of-state, you'll still need to pay Virginia sales tax. In this case, you'll be required to file a Use Tax Return to report the purchase and pay the applicable sales tax. The use tax is essentially a tax on items purchased outside of Virginia but used or stored within the state.
Sales Tax and Vehicle Registration

The sales tax you pay when purchasing a vehicle in Virginia is a crucial component of the vehicle registration process. When you register your vehicle with the Virginia Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV), you’ll need to provide proof of sales tax payment to complete the registration.
Here's a step-by-step guide to understanding the connection between sales tax and vehicle registration:
- Sales Tax Payment: As mentioned earlier, you'll need to pay the applicable sales tax based on the purchase price and the jurisdiction where the vehicle will be registered and garaged. This payment should be made promptly to avoid penalties and delays in the registration process.
- Vehicle Registration Application: To register your vehicle in Virginia, you'll need to complete the appropriate application form. This form typically requires information about the vehicle, including the make, model, year, and Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). You'll also need to provide proof of insurance and a valid driver's license.
- Proof of Sales Tax Payment: Along with the registration application, you'll need to submit proof that the sales tax has been paid. This can be in the form of a receipt or a payment confirmation from the Virginia Department of Taxation. The DMV will verify that the sales tax has been paid before processing your registration.
- Title Transfer or New Title Application: If you're purchasing a used vehicle from a private seller, you'll need to complete a title transfer. This involves obtaining a signed title from the seller and submitting it along with the registration application. If you're purchasing a new vehicle from a dealership, the dealership will typically handle the title application process for you.
- Registration and Plates: Once the DMV receives your completed application, proof of sales tax payment, and other required documents, they will process your registration. You'll receive a registration certificate and license plates for your vehicle. It's important to ensure that all information on the registration certificate is accurate, as this document is a legal record of your vehicle's registration.
By understanding the relationship between sales tax and vehicle registration, you can ensure a smoother process and avoid any potential issues. It's essential to keep all documentation related to your vehicle purchase and registration organized and easily accessible.
Future Implications and Considerations
As the landscape of transportation and vehicle ownership evolves, it’s important to consider the potential future implications of Virginia’s sales tax on cars. With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs) and autonomous technology, the state’s revenue streams and tax policies may need to adapt to accommodate these changes.
Electric Vehicles and Sales Tax
The increasing popularity of electric vehicles presents a unique challenge for sales tax collection. Unlike traditional gasoline-powered vehicles, EVs do not incur fuel taxes, which are a significant source of revenue for many states. As a result, states like Virginia may need to explore alternative methods of taxation to ensure a stable revenue stream.
One potential solution is the implementation of a road usage fee or a mileage-based tax for electric vehicles. This approach would ensure that EV owners contribute to the maintenance and improvement of Virginia's transportation infrastructure, similar to how fuel taxes are used for traditional vehicles.
Additionally, as the cost of electric vehicles continues to decrease and their range and performance improve, the demand for EVs is expected to rise. This shift could impact the overall sales tax revenue generated from vehicle purchases. Virginia may need to consider adjustments to its sales tax rates or explore other revenue-generating measures to accommodate this changing market.
Autonomous Technology and Sales Tax
The integration of autonomous technology into vehicles is another emerging trend that could impact Virginia’s sales tax policies. As self-driving cars become more prevalent, the state may need to reconsider how sales tax is applied to these vehicles.
For instance, if autonomous technology becomes a standard feature in new vehicles, it may be necessary to revise the sales tax calculation to include the value of this advanced technology. This could involve adding a separate tax rate or adjusting the existing rates to account for the increased value and complexity of autonomous vehicles.
Furthermore, as autonomous vehicles become more common, there may be a shift towards shared mobility models, such as ride-sharing or subscription services. These business models could impact the traditional vehicle ownership structure and, consequently, the way sales tax is collected. Virginia may need to explore innovative tax structures to ensure that sales tax revenue is collected fairly and effectively in this evolving landscape.
Conclusion: Staying Informed and Adapting to Change
In conclusion, understanding Virginia’s sales tax on cars is essential for both buyers and sellers to ensure compliance and contribute to the state’s revenue stream. By familiarizing yourself with the specific regulations, calculation methods, and potential exemptions, you can navigate the process with confidence.
As the transportation industry continues to evolve, it's crucial to stay informed about potential changes to sales tax policies. The rise of electric vehicles and autonomous technology presents unique challenges and opportunities for states like Virginia. By staying abreast of these developments and adapting to changing market dynamics, the state can ensure a stable and sustainable revenue stream to support its initiatives and programs.
Whether you're purchasing a traditional gasoline-powered vehicle or exploring the latest electric or autonomous models, being aware of the sales tax implications is a key aspect of responsible vehicle ownership. Stay informed, and you'll be well-equipped to make informed decisions and contribute to Virginia's vibrant automotive landscape.
How often do sales tax rates change in Virginia?
+Sales tax rates in Virginia can change annually, typically as part of the state’s budgeting process. However, local jurisdictions may also have the authority to adjust their local tax rates, so it’s important to stay updated on any changes specific to your area.
Are there any online tools to calculate sales tax for vehicle purchases in Virginia?
+Yes, the Virginia Department of Taxation provides an online Sales Tax Calculator on their website. This tool allows you to input the purchase price of your vehicle and the applicable jurisdiction to estimate the sales tax amount. It’s a useful resource for getting an accurate estimate before making a purchase.
What happens if I purchase a vehicle from a private seller in Virginia?
+When purchasing a vehicle from a private seller in Virginia, you’ll need to calculate the sales tax based on the purchase price or the fair market value of the vehicle, whichever is higher. You’ll then remit the sales tax to the Virginia Department of Taxation and provide proof of payment during the vehicle registration process.
Can I claim a sales tax deduction on my federal tax return for vehicle purchases in Virginia?
+No, sales tax on vehicle purchases in Virginia is not deductible for federal income tax purposes. However, it’s important to consult with a tax professional or refer to the IRS guidelines to understand any potential deductions or credits you may be eligible for.