Nyc Income Tax Status

Welcome to an in-depth exploration of the income tax landscape in the vibrant city of New York City (NYC). As a bustling metropolis, NYC has its own unique tax regulations and considerations, which can be complex for residents and businesses alike. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding and navigating the NYC income tax system, shedding light on its intricacies and implications.
Understanding NYC’s Income Tax Status
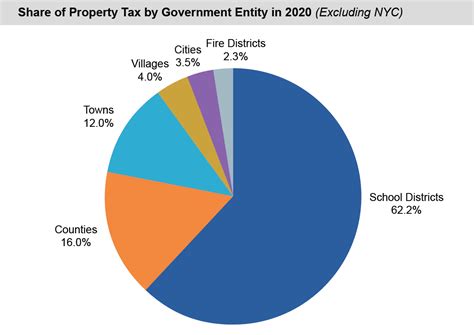
New York City, often referred to as the financial capital of the world, operates under a unique tax structure that differs from the rest of the state. The city’s tax system is intricate, reflecting its diverse population, vibrant economy, and extensive services provided to residents.
NYC imposes a separate city income tax on top of the state income tax, which means that residents and businesses operating within the city limits face a dual tax obligation. This dual tax system is a distinctive feature of NYC's fiscal policy, designed to fund the city's extensive public services and infrastructure.
The NYC income tax is administered by the New York City Department of Finance, which collects and manages the city's revenue. This department plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance with tax regulations and facilitating timely payments from taxpayers.
Tax Rates and Brackets
The city’s income tax rates are progressive, meaning that higher incomes are taxed at higher rates. As of the most recent tax year, the tax rates for NYC residents range from 2.907% to 3.876%, depending on the taxpayer’s income bracket. These rates are subject to periodic adjustments to keep pace with inflation and changing economic conditions.
For non-residents earning income within NYC, the tax rate is a flat 3.876%, regardless of income level. This rate applies to wages, salaries, commissions, and other types of income earned within the city limits.
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to $5,000 | 2.907% |
| $5,000 - $10,000 | 3.108% |
| $10,000 - $20,000 | 3.352% |
| $20,000 - $100,000 | 3.596% |
| $100,000 and above | 3.876% |
It's important to note that these rates are subject to change, and taxpayers should consult the NYC Department of Finance's official website for the most current and accurate tax information.
Taxable Income and Deductions
NYC income tax is calculated based on taxable income, which is the income remaining after certain deductions and adjustments. These deductions include personal exemptions, standard deductions, and potentially itemized deductions for eligible taxpayers.
Eligible residents may also benefit from various tax credits, such as the NYC Resident Credit and the Empire State Child Credit, which can reduce the amount of tax owed. These credits are designed to provide relief to specific groups of taxpayers and are subject to eligibility criteria and income limits.
Compliance and Reporting Requirements

Compliance with NYC income tax regulations is a critical aspect of financial responsibility for residents and businesses. The city’s tax department enforces strict reporting requirements to ensure accurate tax payments and to deter tax evasion.
Registration and Filing Deadlines
Individuals and businesses operating in NYC must register with the NYC Department of Finance to obtain a Business Identification Number (BIN) or a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN). These numbers are essential for all tax-related transactions and communications with the city.
Taxpayers are required to file their income tax returns annually, typically by April 15th for the previous tax year. However, it's crucial to note that specific circumstances, such as filing an extension or being a non-resident, may result in different filing deadlines. It's advisable to consult the NYC tax guidelines or seek professional advice to ensure compliance with the correct filing deadlines.
Electronic Filing and Payment Options
The NYC Department of Finance encourages taxpayers to utilize electronic filing and payment methods for their income tax obligations. These methods offer convenience, efficiency, and a faster processing time compared to traditional paper filing.
The city's official website provides an online filing system that allows taxpayers to complete and submit their returns securely. This system also enables taxpayers to make payments using various electronic methods, such as direct debit, credit card, or electronic funds transfer.
Penalty and Interest Charges
Non-compliance with NYC income tax regulations can result in penalties and interest charges. The city imposes penalties for late filing, underpayment of estimated taxes, and late payment of taxes due. These penalties can significantly increase the taxpayer’s overall liability, so it’s crucial to meet all filing and payment deadlines.
Additionally, interest may accrue on any outstanding tax balance. The interest rate is typically based on the federal short-term rate plus a surcharge, which is adjusted periodically. Taxpayers should be mindful of these potential charges and aim to fulfill their tax obligations promptly to avoid unnecessary financial burdens.
Tax Planning and Strategies
Effective tax planning is essential for individuals and businesses operating in NYC to optimize their financial position and minimize their tax liability. Here are some strategies to consider:
Maximizing Deductions and Credits
Understanding and claiming all eligible deductions and credits is crucial to reducing your taxable income. This includes taking advantage of personal exemptions, standard deductions, and potentially itemized deductions for expenses such as medical costs, charitable donations, and certain business-related expenses.
Additionally, researching and claiming applicable tax credits, such as the NYC Resident Credit or the Child and Dependent Care Credit, can further reduce your tax burden. These credits are designed to provide relief to specific groups of taxpayers and are often overlooked, so it's beneficial to explore all available options.
Utilizing Tax-Advantaged Accounts
Taxpayers can consider utilizing tax-advantaged accounts, such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), to reduce their taxable income and potentially lower their tax liability. These accounts offer tax benefits, such as deductions for contributions or tax-free growth and distributions, which can significantly impact your overall tax position.
Estate and Succession Planning
For individuals with significant assets or businesses, estate planning becomes crucial to minimize tax liability and ensure a smooth transfer of wealth. This includes utilizing strategies such as gifting, establishing trusts, or implementing business succession plans. By proactively addressing these issues, taxpayers can mitigate potential tax consequences and protect their legacy.
Future Implications and Tax Reform
The NYC income tax landscape is subject to ongoing discussions and potential reforms. As the city’s fiscal needs evolve, so too do its tax policies. Here’s a glimpse into some potential future developments:
Tax Reform Proposals
There have been proposals to reform the city’s tax structure, aiming to simplify the system and provide relief to taxpayers. These proposals often involve streamlining tax rates, broadening the tax base, and potentially introducing new tax incentives or credits.
While these reforms are still in the discussion phase, they highlight the city's commitment to maintaining a competitive tax environment while ensuring adequate revenue for essential services.
Impact of Economic Changes
The city’s tax revenue is closely tied to the overall economic performance of NYC and the surrounding region. Economic downturns or recessions can impact tax collections, potentially leading to budget shortfalls and the need for tax adjustments.
Conversely, a thriving economy can result in increased tax revenue, providing the city with resources for infrastructure development, social programs, and other initiatives.
Political and Legislative Influences
NYC’s tax policies are influenced by political and legislative decisions at the city, state, and federal levels. Changes in leadership or shifts in policy priorities can result in tax law amendments, impacting taxpayers across the city.
Staying informed about these political and legislative developments is crucial for taxpayers to understand how potential changes may affect their tax obligations and financial planning.
Conclusion

Navigating the NYC income tax system requires a thorough understanding of its unique regulations and considerations. From progressive tax rates to compliance requirements and potential tax-saving strategies, this article has provided an in-depth exploration of the city’s tax landscape.
By staying informed, seeking professional guidance when needed, and proactively managing their tax obligations, residents and businesses can successfully navigate NYC's tax environment. This comprehensive guide aims to empower taxpayers with the knowledge to make informed decisions and optimize their financial position within the dynamic city of New York.
What is the difference between NYC income tax and state income tax?
+NYC imposes a separate city income tax in addition to the state income tax. This means that residents and businesses operating within the city limits face a dual tax obligation, paying both city and state income taxes.
How often do NYC income tax rates change?
+NYC income tax rates are subject to periodic adjustments to keep pace with inflation and changing economic conditions. These adjustments are typically made annually, and taxpayers should refer to the official NYC Department of Finance website for the most current tax rates.
Are there any tax benefits for residents or businesses operating in NYC?
+Yes, NYC offers various tax credits and deductions to provide relief to specific groups of taxpayers. These include the NYC Resident Credit, the Empire State Child Credit, and potential itemized deductions for eligible expenses. Consulting a tax professional can help identify applicable benefits.
What happens if I miss the income tax filing deadline in NYC?
+Missing the income tax filing deadline can result in penalties and interest charges. The NYC Department of Finance imposes penalties for late filing, underpayment of estimated taxes, and late payment of taxes due. It’s crucial to meet all filing and payment deadlines to avoid these additional financial burdens.
How can I stay informed about NYC’s tax regulations and potential changes?
+To stay informed about NYC’s tax regulations and potential changes, it’s advisable to regularly visit the NYC Department of Finance’s official website. This website provides the latest tax information, including rate changes, filing deadlines, and any proposed or enacted tax reforms.



