Mt Income Tax
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on Mt Income Tax, an essential aspect of financial planning and management for individuals and businesses alike. This article aims to delve into the intricacies of Mt Income Tax, providing valuable insights, expert analysis, and practical advice to help you navigate the complex world of taxation.
Understanding Mt Income Tax: A Comprehensive Overview

Mt Income Tax, short for Mount Income Tax, is a vital component of the taxation system in various jurisdictions worldwide. It refers to the levy imposed on an individual’s or entity’s income, which can include wages, salaries, investments, and business profits. Mt Income Tax plays a crucial role in funding public services, infrastructure development, and social welfare programs, making it an integral part of any functioning economy.
The concept of Mt Income Tax is not a new one; it has evolved over centuries, with different countries adopting unique taxation systems to suit their economic needs and societal priorities. While the fundamentals of income taxation remain similar across jurisdictions, the specific rates, exemptions, and deductions can vary significantly, making it essential to understand the nuances of Mt Income Tax in your particular region.
Key Components of Mt Income Tax
To comprehend Mt Income Tax effectively, it is essential to break down its key components:
- Taxable Income: This refers to the portion of an individual’s or entity’s income that is subject to taxation. It is calculated by subtracting allowable deductions and exemptions from the total income earned.
- Tax Rates: Mt Income Tax operates on a progressive rate system, meaning the tax rate increases as income levels rise. This ensures that higher earners contribute a larger proportion of their income to taxation.
- Tax Credits and Deductions: Various tax credits and deductions are available to reduce the overall tax liability. These can include deductions for retirement contributions, medical expenses, education costs, and more.
- Tax Filing and Payment: Taxpayers are typically required to file an annual tax return, declaring their income and calculating their tax liability. Payment of Mt Income Tax is usually due at the time of filing or in installments throughout the year.
Mt Income Tax: A Deep Dive into the System

In this section, we will explore the Mt Income Tax system in more detail, shedding light on its complexities and providing practical tips for optimal tax management.
Taxable Income Calculation
Determining taxable income is a critical step in the Mt Income Tax process. It involves identifying all sources of income, such as employment earnings, investment returns, rental income, and business profits. From there, allowable deductions and exemptions are applied to arrive at the taxable income figure. Some common deductions include:
- Standard Deduction: A fixed amount that reduces taxable income, applicable to most taxpayers.
- Personal Exemptions: Additional deductions based on the number of dependents or eligible family members.
- Business Expenses: For business owners, deductions for expenses like office rent, supplies, and employee salaries can significantly reduce taxable income.
It is crucial to maintain accurate records of income and expenses to ensure compliance with tax regulations and to maximize deductions.
Progressive Tax Rates
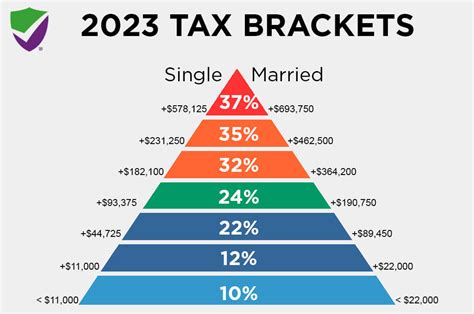
Mt Income Tax operates on a progressive tax rate structure, which means higher income levels are taxed at higher rates. This system aims to promote fairness and ensure that those with higher earning capacities contribute a larger share of their income to taxation. The specific tax brackets and rates can vary widely depending on the jurisdiction. For instance, in the United States, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) sets seven tax brackets ranging from 10% to 37%, while in the United Kingdom, there are three main income tax rates: 20%, 40%, and 45%.
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 0 to $9,950 | 10% |
| $9,951 to $40,525 | 12% |
| $40,526 to $86,375 | 22% |
| $86,376 to $164,925 | 24% |
| $164,926 to $209,425 | 32% |
| $209,426 to $523,600 | 35% |
| $523,601 and above | 37% |
Tax Credits and Deductions
Mt Income Tax offers various tax credits and deductions to reduce the overall tax burden. These incentives are designed to encourage certain behaviors, such as saving for retirement, investing in education, or supporting charitable causes. Some common tax credits and deductions include:
- Child Tax Credit: A credit available to taxpayers with qualifying children, providing a financial benefit for families with dependent children.
- Student Loan Interest Deduction: Taxpayers can deduct the interest paid on student loans, encouraging investment in education and reducing the tax burden for those pursuing higher education.
- Charitable Contributions Deduction: Donations to qualified charitable organizations can be deducted from taxable income, incentivizing philanthropy and supporting non-profit sectors.
Tax Filing and Payment
Taxpayers are typically required to file an annual tax return, declaring their income, calculating their tax liability, and claiming any applicable deductions or credits. The tax filing process can be complex, and it is essential to ensure accuracy to avoid penalties or audits. Taxpayers have the option to file their returns themselves or engage the services of a tax professional, such as a certified public accountant (CPA) or enrolled agent (EA), who can provide expert guidance and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Payment of Mt Income Tax is due at the time of filing or in installments throughout the year. Failure to pay taxes on time can result in penalties and interest charges, so it is crucial to stay on top of your tax obligations.
Maximizing Your Tax Strategy: Expert Tips
Navigating the Mt Income Tax system can be challenging, but with the right strategies, you can optimize your tax planning and minimize your tax liability. Here are some expert tips to help you make the most of your tax situation:
Understand Your Tax Bracket
Knowing your tax bracket is crucial to effective tax planning. Your tax bracket determines the rate at which your income is taxed, so it is essential to understand how your income level affects your tax liability. Adjusting your income strategically, such as through tax-efficient investments or retirement contributions, can help you stay within a lower tax bracket and reduce your overall tax burden.
Maximize Deductions and Credits
Take advantage of all the deductions and credits available to you. Research and understand the various tax incentives offered by your jurisdiction, and ensure you meet the eligibility criteria to claim them. For example, if you have qualifying children, be sure to claim the Child Tax Credit, which can provide a significant financial benefit. Additionally, consider contributing to retirement accounts like 401(k)s or IRAs, as these contributions are often tax-deductible and can reduce your taxable income.
Utilize Tax-Efficient Investment Strategies
Investing can be a powerful tool for reducing your tax liability. Certain investment vehicles, such as tax-free municipal bonds or retirement accounts, offer tax advantages. For instance, investing in a Roth IRA allows your investments to grow tax-free, and you can withdraw your contributions tax-free at any time. Consult with a financial advisor to explore tax-efficient investment options that align with your financial goals.
Consider Tax-Loss Harvesting
Tax-loss harvesting is a strategy where you sell investments that have declined in value to offset gains from other investments. By realizing capital losses, you can reduce your taxable income and potentially lower your tax bill. This strategy is particularly useful for investors with a well-diversified portfolio.
Stay Informed about Tax Law Changes
Tax laws are subject to change, and keeping up-to-date with these changes is essential for effective tax planning. Stay informed about any new tax laws, regulations, or incentives that may impact your tax situation. This knowledge can help you adjust your financial strategies accordingly and take advantage of any new opportunities.
The Future of Mt Income Tax: Trends and Implications
As the world evolves, so does the landscape of taxation. Here, we explore some emerging trends and their potential implications for Mt Income Tax:
Digitalization and Tax Compliance
The rise of digital technologies has transformed the way tax systems operate. Digital platforms and online filing systems have streamlined the tax filing process, making it more accessible and efficient. Additionally, digital records and data analytics have enhanced tax authorities’ ability to detect and prevent tax evasion, ensuring greater compliance with tax regulations.
International Tax Cooperation
In an increasingly globalized world, international tax cooperation is becoming more critical. Countries are working together to combat tax evasion and ensure that multinational corporations pay their fair share of taxes. Initiatives like the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) project, led by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), aim to establish a more unified and transparent international tax system.
Tax Reform and Simplification
Many jurisdictions are considering tax reform to simplify the tax system and make it more efficient. This can involve reducing tax rates, consolidating tax brackets, and eliminating complex deductions and credits. Simplification aims to make the tax system more transparent and easier to navigate, benefiting both taxpayers and tax authorities.
Environmental Taxation
With growing concerns about climate change, environmental taxation is gaining traction. Governments are exploring ways to use taxation to incentivize sustainable practices and discourage environmentally harmful behaviors. This could include carbon taxes, waste disposal taxes, or incentives for adopting green technologies.
Taxation of Digital Services
The rise of the digital economy has presented challenges for tax authorities. Digital services, such as online advertising and e-commerce, often transcend traditional borders, making it difficult to determine tax jurisdiction. Countries are developing new strategies to tax digital services fairly and ensure that digital businesses contribute to public finances.
Conclusion

Mt Income Tax is a complex yet essential aspect of financial management. Understanding the system, staying informed about tax laws, and implementing effective tax strategies can help you optimize your financial situation and contribute to the well-being of your community and nation. As the world continues to evolve, the tax landscape will adapt, and staying ahead of these changes will be crucial for successful tax planning.
FAQ
What is the difference between a tax deduction and a tax credit?
+
A tax deduction reduces your taxable income, while a tax credit directly reduces your tax liability. Deductions are subtracted from your income to calculate your taxable income, while credits are applied after taxable income is determined. Credits often provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction in your tax bill, making them more valuable than deductions.
How can I stay up-to-date with tax law changes?
+
Staying informed about tax law changes is crucial. Subscribe to reputable tax news sources, follow tax-related blogs and websites, and consider joining tax-focused professional organizations or online communities. These resources can provide timely updates on tax law changes and help you stay ahead of the curve.
What are the penalties for tax evasion or non-compliance?
+
Penalties for tax evasion or non-compliance can be severe. They may include fines, interest charges, and even criminal prosecution in cases of deliberate tax evasion. It is crucial to maintain accurate records, file your tax returns on time, and pay your taxes in full to avoid these penalties.