Tax 2018 Brackets

Welcome to a comprehensive guide on the tax brackets for the year 2018. Understanding tax brackets is crucial for individuals and businesses to navigate their financial obligations effectively. This article will delve into the details of the 2018 tax brackets, providing valuable insights into how tax rates were structured and how they impacted taxpayers.
The Landscape of Tax Brackets in 2018
In 2018, the United States tax system operated with a progressive tax structure, meaning that taxpayers were subjected to different tax rates depending on their income levels. This progressive nature aimed to ensure fairness and contribute to the overall economic stability of the nation.
The tax brackets for 2018 were set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and applied to both individual taxpayers and married couples filing jointly. These brackets determined the applicable tax rate for each income level, with higher earners facing higher tax rates. Let's explore the specifics of these brackets and their implications.
Tax Bracket Structure for 2018
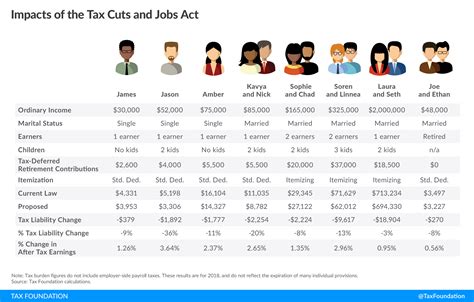
The 2018 tax brackets were divided into seven distinct categories, each corresponding to a specific tax rate. These brackets were as follows:
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 10% | For taxable income up to $9,525 |
| 12% | Applicable to taxable income ranging from $9,526 to $38,700 |
| 22% | Taxable income between $38,701 and $82,500 |
| 24% | Income falling between $82,501 and $157,500 |
| 32% | Taxable income from $157,501 to $200,000 |
| 35% | Income exceeding $200,000 up to $500,000 |
| 37% | Highest tax bracket for taxable income above $500,000 |

These tax brackets applied to various income sources, including wages, salaries, self-employment income, and investment earnings. It's important to note that these brackets and tax rates were applicable to the 2018 tax year, and any changes made in subsequent years would not retroactively affect taxpayers' obligations for 2018.
Understanding the Progressive Tax System
The progressive tax system is designed to ensure that higher-income earners contribute a larger proportion of their income to the tax pool. This system aims to promote economic equality and provide a balanced approach to tax collection. In the 2018 tax brackets, we can observe this progressive nature, with tax rates increasing as income levels rise.
For instance, an individual with a taxable income of $25,000 would fall into the 12% tax bracket, paying taxes at this rate on their income between $9,526 and $25,000. On the other hand, an individual with a taxable income of $500,000 would be subject to the 37% tax rate for their income above $500,000, while their income within the lower brackets would be taxed at the corresponding rates.
Impact on Taxpayers and the Economy
The 2018 tax brackets had a significant impact on taxpayers’ financial planning and overall economic activity. For individuals and families, understanding these brackets helped in budgeting and managing their finances effectively. Taxpayers could calculate their approximate tax liability based on their expected income, allowing for better financial decision-making.
Moreover, the progressive tax system played a crucial role in shaping economic policies. By taxing higher-income earners at a higher rate, the government aimed to reduce income inequality and provide resources for social welfare programs. This redistribution of wealth can have positive effects on the economy, promoting consumer spending, investment, and overall economic growth.
Case Study: Analyzing the Impact of 2018 Tax Brackets
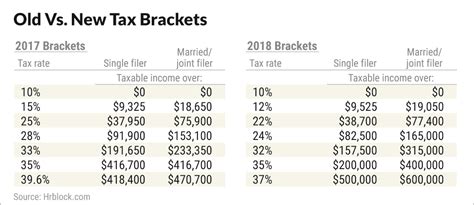
To illustrate the practical implications of the 2018 tax brackets, let’s consider a hypothetical case study. Imagine a married couple, the Smiths, who filed their taxes jointly in 2018.
The Smith Family’s Income and Tax Liability
Mr. and Mrs. Smith, both working professionals, had a combined taxable income of $120,000 for the year 2018. Let’s break down their tax liability based on the 2018 tax brackets:
- The first $19,050 of their income (up to the 10% tax bracket) would be taxed at a rate of 10%, resulting in a tax liability of $1,905.
- The income between $19,051 and $38,700 (falling within the 12% tax bracket) would be taxed at 12%, amounting to a tax liability of $2,364.
- Their income from $38,701 to $120,000 (covering the 22% and 24% tax brackets) would be taxed at the respective rates, resulting in a combined tax liability of $20,436.
In total, the Smiths would owe a tax liability of $24,705 for the year 2018, based on their income and the applicable tax brackets.
Impact on Financial Planning and Savings
Understanding their tax liability based on the 2018 tax brackets allowed the Smiths to plan their finances effectively. They could allocate their resources accordingly, considering their after-tax income and savings goals. This awareness enabled them to make informed decisions about investments, retirement planning, and other financial commitments.
Additionally, the Smiths could explore tax-efficient strategies to optimize their tax obligations. For instance, they might consider contributing to tax-advantaged retirement accounts or exploring tax credits and deductions to reduce their overall tax liability. Such strategies, guided by a thorough understanding of the tax brackets, can significantly impact an individual's financial well-being.
Future Implications and Tax Policy Changes
The tax brackets for 2018 provided a foundation for taxpayers’ financial planning and compliance. However, it’s essential to recognize that tax policies are dynamic and subject to change. In the years following 2018, there have been notable adjustments to the tax landscape, impacting individuals and businesses alike.
Tax Reform and Its Impact
In 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) was enacted, bringing significant changes to the U.S. tax code. This reform altered tax brackets, rates, and various provisions, impacting taxpayers’ obligations and opportunities.
The TCJA reduced tax rates across several brackets and expanded the standard deduction, offering taxpayers more flexibility in their filing choices. Additionally, the reform introduced a new bracket for pass-through businesses, impacting entities like sole proprietorships, partnerships, and S corporations.
Staying Informed and Adapting to Changes
Taxpayers and businesses must stay informed about these ongoing changes to ensure compliance and optimize their financial strategies. Keeping up with tax policy updates allows individuals to take advantage of new opportunities, such as expanded tax credits or deductions, and adjust their financial plans accordingly.
For businesses, understanding the impact of tax reforms is crucial for strategic decision-making. Changes in tax rates and provisions can influence investment choices, business expansion plans, and overall financial health. Staying proactive in monitoring tax policies ensures businesses can navigate these changes effectively and make informed choices to maximize their financial outcomes.
Conclusion: Navigating the Tax Landscape
The tax brackets for 2018 served as a crucial framework for taxpayers to understand their financial obligations and plan their finances accordingly. The progressive nature of the tax system aimed to promote economic fairness and stability.
By analyzing the 2018 tax brackets, individuals and businesses gained insights into their tax liabilities and explored strategies to optimize their financial positions. The case study of the Smith family demonstrated how understanding tax brackets can impact financial planning and savings goals.
However, it's essential to recognize that tax policies are dynamic, and ongoing changes require taxpayers and businesses to stay informed and adapt their strategies. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act brought significant reforms, impacting tax rates and provisions. Staying proactive in monitoring tax policies ensures individuals and businesses can navigate the tax landscape effectively and make informed financial decisions.
How often do tax brackets change, and why?
+Tax brackets are subject to change annually, typically as part of tax legislation or policy adjustments. These changes can reflect economic conditions, inflation rates, and government initiatives. It’s essential for taxpayers to stay updated on these changes to ensure compliance and optimize their tax strategies.
What is the difference between tax brackets and tax rates?
+Tax brackets refer to the income ranges associated with specific tax rates. Tax rates, on the other hand, are the percentages at which income within each bracket is taxed. For instance, the 2018 tax brackets included rates of 10%, 12%, and so on, indicating the percentage of tax applied to income within those brackets.
How can individuals optimize their tax obligations based on tax brackets?
+Individuals can optimize their tax obligations by exploring tax-efficient strategies such as contributing to retirement accounts, claiming applicable tax credits and deductions, and understanding the implications of their income sources. A thorough understanding of tax brackets and rates allows individuals to make informed financial decisions.
What is the impact of tax reforms like the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act on small businesses?
+Tax reforms like the TCJA can have significant implications for small businesses. These reforms may offer reduced tax rates, expanded deductions, or new opportunities for pass-through entities. Small businesses should stay informed about these changes to ensure they can take advantage of new provisions and adjust their financial strategies accordingly.