Sales Tax North Carolina

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Sales Tax in North Carolina, a state known for its vibrant economy and diverse business landscape. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of sales tax laws, regulations, and practices specific to North Carolina, providing you with an in-depth understanding of this essential aspect of business operations within the state.
Understanding Sales Tax in North Carolina
Sales tax in North Carolina is a vital component of the state’s revenue system, contributing significantly to its overall economic growth and development. The state’s sales tax is governed by the North Carolina Department of Revenue, which enforces and regulates tax laws to ensure compliance and fair taxation across various industries.
As of January 2024, the statewide sales tax rate in North Carolina is 4.75%, which applies to the sale of tangible personal property and certain services. However, it's essential to note that sales tax rates can vary depending on the jurisdiction, with local municipalities and counties often imposing additional taxes. These local sales tax rates are added to the statewide rate, resulting in a combined sales tax that businesses must collect and remit to the appropriate authorities.
Sales Tax Registration and Compliance
Any business operating in North Carolina and engaging in taxable sales or purchases must obtain a Sales and Use Tax Certificate of Registration from the North Carolina Department of Revenue. This certificate authorizes the business to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state and ensures compliance with tax laws.
The registration process involves completing the appropriate forms, providing business details, and understanding the tax obligations specific to the industry. Once registered, businesses are responsible for calculating and collecting sales tax accurately, ensuring proper documentation, and submitting timely tax returns to the department.
| Registration Requirements | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Online Registration | Businesses can register online through the North Carolina Department of Revenue's website, simplifying the process and reducing administrative burden. |
| Taxable Sales Threshold | North Carolina does not have a minimum sales threshold for sales tax registration. Any business making taxable sales must register, regardless of transaction volume. |
| Out-of-State Sellers | Out-of-state sellers with significant economic presence in North Carolina are also required to register and collect sales tax on their transactions within the state. |

Sales Tax Rates and Exemptions
Understanding the sales tax rates and exemptions in North Carolina is crucial for businesses to accurately calculate and collect taxes. The statewide sales tax rate of 4.75% is applicable to most tangible personal property and certain services. However, it’s important to note that certain items are exempt from sales tax, such as:
- Groceries and food items for home consumption.
- Prescription medications and certain medical devices.
- Residential utilities like electricity, water, and gas.
- Educational materials and certain school supplies.
- Selected agricultural products and livestock.
Additionally, certain jurisdictions within North Carolina may have specific exemptions or reduced tax rates for particular industries or transactions. For instance, some counties offer tourism development tax incentives or special event sales tax exemptions to promote economic growth and tourism.
Sales Tax Calculation and Collection
Businesses in North Carolina are responsible for calculating sales tax accurately based on the applicable tax rates and exempt items. This involves understanding the taxable base, which is the total value of taxable sales or purchases, and applying the appropriate tax rate to this base.
Once calculated, businesses must collect sales tax from customers at the point of sale. This is typically done by adding the sales tax to the purchase price and displaying it separately on the sales receipt. It's essential to provide clear and transparent pricing information to customers, ensuring they understand the tax components of their transactions.
Sales Tax Returns and Remittance
Registered businesses in North Carolina are required to file sales tax returns on a regular basis, typically monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on their tax obligations and transaction volume. These returns involve providing detailed information about taxable sales, purchases, and any applicable exemptions.
Along with the tax returns, businesses must remit the collected sales tax to the North Carolina Department of Revenue. This process involves submitting the tax amount due, along with any necessary supporting documentation, within the specified time frame to ensure timely compliance.
Sales Tax Compliance and Penalties

Maintaining sales tax compliance is crucial for businesses operating in North Carolina to avoid legal consequences and potential financial penalties. The North Carolina Department of Revenue enforces strict regulations to ensure tax compliance, and businesses that fail to meet their tax obligations may face significant repercussions.
Common Compliance Issues
Some common compliance issues that businesses should be aware of include:
- Failure to Register: Businesses operating in North Carolina must obtain a Sales and Use Tax Certificate of Registration. Failure to register can result in penalties and interest on the tax due, along with potential legal consequences.
- Inaccurate Tax Calculation: Businesses must accurately calculate sales tax based on the applicable tax rates and exempt items. Incorrect calculations can lead to under- or over-collection of tax, resulting in penalties and audits.
- Late Filing and Payment: Sales tax returns and payments must be submitted by the due date. Late filings or payments can incur penalties, interest, and additional administrative fees.
- Record-Keeping and Documentation: Proper record-keeping is essential for sales tax compliance. Businesses must maintain accurate records of taxable sales, purchases, and exemptions to support their tax returns and audits.
Penalties and Interest
The North Carolina Department of Revenue imposes penalties and interest on businesses that fail to comply with sales tax laws. These penalties can be significant and are designed to discourage non-compliance.
Penalties for late filing or payment can range from 5% to 25% of the tax due, depending on the severity of the infraction and the business's compliance history. Additionally, interest accrues on the unpaid tax amount, typically at a rate of 0.5% per month until the balance is paid in full.
Sales Tax Audits
The North Carolina Department of Revenue conducts sales tax audits to ensure compliance and identify potential tax evasion. Audits can be random or targeted based on specific criteria, such as high-risk industries or suspicious tax filings.
During an audit, the department reviews a business's sales tax records, receipts, and documentation to verify the accuracy of tax returns and payments. If discrepancies are found, the business may be required to pay additional tax, penalties, and interest, along with providing further documentation to support their compliance.
Sales Tax and E-Commerce in North Carolina
With the rise of e-commerce, sales tax collection and compliance have become more complex for online businesses operating in North Carolina. The state has implemented specific regulations and guidelines to address the unique challenges posed by e-commerce transactions.
Sales Tax Nexus in North Carolina
A business is considered to have a sales tax nexus in North Carolina if it has a physical presence or a substantial connection to the state. This includes having a physical store, warehouse, or office, as well as having employees or affiliates working within the state.
Online businesses, such as those operating e-commerce platforms or drop-shipping services, may also have a sales tax nexus in North Carolina if they meet certain criteria. This includes having a significant number of transactions or sales within the state or utilizing in-state resources, such as advertising or marketing services.
Sales Tax Collection for E-Commerce
Online businesses with a sales tax nexus in North Carolina are required to collect and remit sales tax on their transactions within the state. This includes sales made through their websites, online marketplaces, or other e-commerce platforms.
To simplify sales tax collection for e-commerce businesses, North Carolina has implemented Sales Tax Simplification Laws, which provide guidelines and resources to help businesses accurately calculate and collect sales tax. These laws also address the challenges of sourcing, which involves determining the applicable tax rate based on the customer's location.
Marketplace Facilitator Laws
North Carolina has also implemented Marketplace Facilitator Laws, which hold online marketplaces and platforms responsible for collecting and remitting sales tax on behalf of their third-party sellers. This law applies to marketplaces that facilitate the sale of tangible personal property or certain services and have a significant economic presence in the state.
Marketplace facilitators must register with the North Carolina Department of Revenue, collect sales tax from their sellers, and remit the tax to the state. This simplifies sales tax compliance for small businesses selling through online marketplaces, as the marketplace takes on the responsibility of tax collection and remittance.
Future Implications and Industry Insights
As the business landscape in North Carolina continues to evolve, sales tax laws and regulations are likely to adapt to meet the changing needs of the state’s economy. Here are some future implications and industry insights to consider:
Sales Tax Rate Changes
Sales tax rates in North Carolina may undergo changes in the future, either at the statewide or local level. While the current statewide rate of 4.75% has remained stable, local jurisdictions may adjust their tax rates to support economic development initiatives or address budgetary concerns.
Businesses should stay informed about potential rate changes and understand their impact on tax obligations. This ensures accurate tax calculation and collection, preventing compliance issues and potential penalties.
Sales Tax Automation
With the increasing complexity of sales tax compliance, businesses are turning to sales tax automation solutions to streamline their tax obligations. These solutions use advanced technology to automate tax calculation, collection, and remittance, reducing the administrative burden on businesses.
Sales tax automation can help businesses stay compliant with changing tax laws, accurately calculate taxes across multiple jurisdictions, and simplify the tax filing process. By leveraging these solutions, businesses can focus on their core operations while ensuring tax compliance.
Remote Work and Sales Tax Nexus
The rise of remote work has introduced new challenges for determining sales tax nexus. With employees or affiliates working remotely across state lines, businesses must carefully consider their sales tax obligations. North Carolina’s tax laws recognize the concept of economic nexus, which considers the economic presence of a business in the state, even without a physical presence.
Businesses should evaluate their remote work policies and the extent of their remote operations within North Carolina to determine their sales tax nexus. This ensures compliance with the state's tax laws and prevents potential audits or penalties.
Conclusion: Navigating Sales Tax in North Carolina
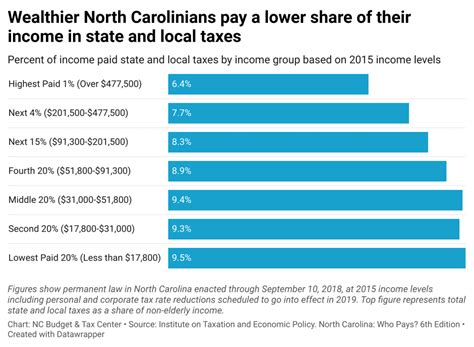
Sales tax in North Carolina is a critical aspect of business operations, impacting both revenue generation and compliance obligations. By understanding the state’s sales tax laws, rates, and exemptions, businesses can accurately calculate and collect sales tax, ensuring compliance with the North Carolina Department of Revenue.
As the business landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about sales tax regulations and leveraging automation solutions can help businesses navigate the complexities of sales tax compliance. With a proactive approach to tax compliance, businesses can focus on their core operations and contribute to the economic growth of North Carolina.
How often do I need to file sales tax returns in North Carolina?
+The frequency of filing sales tax returns depends on your tax obligations and transaction volume. Most businesses file monthly or quarterly, but some may be required to file annually. It’s important to consult with the North Carolina Department of Revenue to determine your specific filing frequency.
What happens if I fail to register for sales tax in North Carolina?
+Failing to register for sales tax in North Carolina can result in significant penalties and interest on the tax due. Additionally, you may face legal consequences and audits. It’s crucial to obtain a Sales and Use Tax Certificate of Registration to ensure compliance and avoid these repercussions.
Are there any sales tax holidays in North Carolina?
+Yes, North Carolina offers specific sales tax holidays throughout the year. These holidays provide tax-free shopping for certain items, such as school supplies, clothing, and electronics. The dates and eligible items vary, so it’s important to stay updated with the state’s sales tax calendar to take advantage of these savings.