Rental Income Tax Rate

Understanding the Rental Income Tax Rate is crucial for anyone who owns or intends to invest in rental properties. This tax rate can significantly impact the profitability of your real estate ventures, and it's essential to stay informed about the current regulations and potential deductions to maximize your returns.
Unraveling the Rental Income Tax Rate
The taxation of rental income is a complex topic, varying across jurisdictions and depending on several factors. In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of rental income tax rates, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of how these rates are determined and the strategies you can employ to optimize your tax obligations.
Understanding the Basics of Rental Income Taxation
Rental income is generally treated as ordinary income for tax purposes, which means it is taxed at the taxpayer’s ordinary income tax rate. However, this is just the starting point, and several deductions and credits can reduce the taxable income derived from rental properties.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) categorizes rental income as either active income or passive income. Active income is derived from properties where the owner actively participates in management, while passive income comes from properties where the owner has little to no involvement in day-to-day operations. This distinction is crucial as it determines the type of deductions and credits available.
| Income Type | Deduction Type |
|---|---|
| Active Income | Business Expenses |
| Passive Income | Passive Activity Losses |

Determining Your Rental Income Tax Rate
The tax rate applicable to your rental income depends on several factors, including your tax bracket, the type of income, and any applicable tax deductions or credits. Here’s a breakdown of these key considerations:
Tax Brackets and Marginal Tax Rates
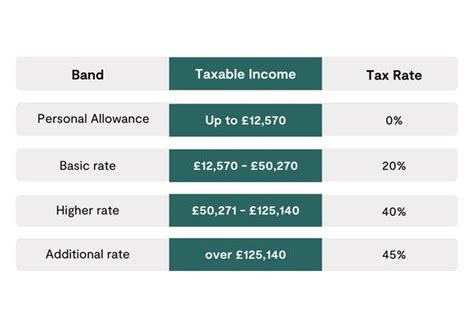
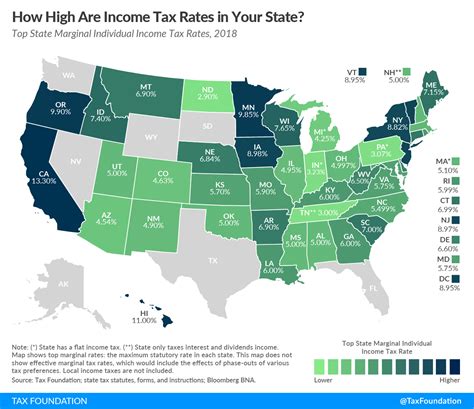
The United States tax system operates on a progressive tax rate structure, meaning the more income you earn, the higher your tax rate. Rental income is typically taxed at the taxpayer’s marginal tax rate, which is the highest tax rate applied to the last dollar of income earned.
For instance, if you fall into the 22% tax bracket, it means that income up to a certain threshold is taxed at 10%, the next portion is taxed at 12%, and the income above that threshold is taxed at 22%. This progressive structure ensures that higher-income earners pay a larger proportion of their income in taxes.
Rental Income Classification
As mentioned earlier, rental income can be classified as either active or passive income. Active income, where the owner is actively involved in property management, is taxed as ordinary income. However, passive income, where the owner has minimal involvement, is subject to the passive activity loss (PAL) rules, which can limit deductions.
Tax Deductions and Credits
Rental property owners can benefit from various tax deductions and credits, which can significantly reduce their taxable income. These deductions include:
- Mortgage Interest Deduction: Owners can deduct the interest paid on mortgages for their rental properties.
- Depreciation: This allows owners to recover the cost of their property over time, providing a tax benefit.
- Property Taxes: Owners can deduct property taxes paid on their rental properties.
- Maintenance and Repair Costs: These expenses are deductible, but there are certain rules and limitations to be aware of.
Maximizing Your Rental Income through Tax Strategies
While understanding the tax rates is crucial, it’s equally important to employ effective tax strategies to minimize your tax obligations. Here are some strategies to consider:
Utilize All Eligible Deductions
Ensure you claim all the deductions you’re entitled to. This includes not only the standard deductions mentioned above but also other expenses like insurance, utilities, legal fees, and travel costs related to your rental property.
Strategic Property Acquisition and Financing
The way you acquire and finance your rental properties can impact your tax obligations. Consider strategies like purchasing through an LLC or using a 1031 exchange to defer capital gains taxes.
Maximize Depreciation Benefits
Depreciation is a powerful tool for rental property owners. By understanding the rules and regulations around depreciation, you can maximize this deduction and reduce your taxable income.
Keep Detailed Records
Accurate record-keeping is essential for claiming deductions and credits. Maintain detailed records of all income, expenses, and improvements to your rental properties.
Stay Informed about Tax Changes
Tax laws and regulations are subject to change. Stay updated with the latest tax reforms and adjustments to ensure you’re taking advantage of any new benefits or deductions.
Future Implications and Considerations
As the real estate market and tax laws evolve, it’s essential to stay informed about potential changes that could impact your rental income tax rate. Here are some future considerations:
Changing Tax Landscapes
Tax policies are subject to change with new administrations and economic shifts. Stay vigilant about potential changes to tax brackets, deductions, and credits that could impact your rental income taxation.
Real Estate Market Trends
The performance of the real estate market can influence your rental income and, consequently, your tax obligations. Keep an eye on market trends and consider how they might affect your rental portfolio.
Long-Term Rental Strategies
When planning your rental investments, consider the long-term implications. Strategies like holding properties for long periods or passing them on to heirs can have significant tax benefits.
Conclusion
Understanding and optimizing your Rental Income Tax Rate is a crucial aspect of real estate investment. By staying informed about tax regulations, utilizing effective tax strategies, and keeping abreast of market trends, you can ensure that your rental ventures remain profitable and compliant with the law.
How often do rental income tax rates change?
+Rental income tax rates are subject to periodic adjustments, typically coinciding with changes in tax laws or economic conditions. It is advisable to consult with a tax professional or stay updated with tax news to understand the latest rates and any applicable changes.
Are there any tax benefits for long-term rental property ownership?
+Yes, long-term rental property ownership can offer several tax benefits. These include the ability to deduct a larger portion of depreciation and the potential for lower capital gains taxes when selling the property.
Can I deduct rental property expenses if I rent out my second home part-time?
+Yes, you can deduct expenses for rental properties, including second homes, as long as they are used primarily for rental purposes and you meet the necessary criteria. However, there are specific rules and limitations to be aware of, so it’s best to consult a tax professional.



