What Is Sales Tax In Ohio
Sales tax is a crucial aspect of commerce in Ohio, impacting both businesses and consumers alike. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of sales tax in Ohio, covering its definitions, rates, applications, and implications. Whether you're a business owner, consumer, or simply curious about Ohio's tax system, this article will provide you with the knowledge you need to navigate sales tax regulations effectively.
Understanding Sales Tax in Ohio

Sales tax in Ohio is a consumption tax levied on the sale of tangible personal property and certain services. It is a critical revenue source for the state, contributing significantly to its overall budget. Ohio’s sales tax system is designed to ensure a fair and efficient collection process, benefiting the state’s infrastructure, education, and various public services.
The sales tax in Ohio is administered by the Ohio Department of Taxation, which oversees compliance, enforcement, and taxpayer assistance. The department provides resources and guidance to help businesses and individuals understand their tax obligations, offering a range of tools and services to ensure compliance with state tax laws.
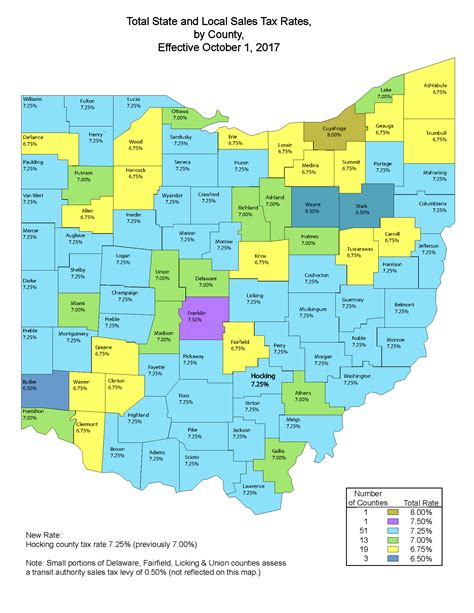
Sales Tax Rate in Ohio
Ohio’s sales tax rate is structured as a combination of state and local taxes. The state sales tax rate is set at 5.75%, which is applicable across the state. However, local governments, such as counties and municipalities, have the authority to levy additional sales taxes to support their specific needs.
The local sales tax rates can vary depending on the jurisdiction, with some areas having higher rates to fund local projects and services. As a result, the total sales tax rate in Ohio can range from the state's base rate of 5.75% to a higher combined rate, including local taxes. It's essential for businesses and consumers to be aware of these variations when conducting transactions.
| State Sales Tax Rate | 5.75% |
|---|---|
| Local Sales Tax Rate | Varies by Jurisdiction |

For instance, the city of Columbus, Ohio, has a local sales tax rate of 2%, bringing the total sales tax rate within the city to 7.75%. On the other hand, rural areas may have lower local sales tax rates, resulting in a combined rate closer to the state's base rate.
Taxable and Exempt Items
Not all goods and services are subject to sales tax in Ohio. The state maintains a list of items that are considered taxable and those that are exempt. Understanding these categories is crucial for businesses to ensure accurate tax collection and for consumers to know when they may expect to pay sales tax.
Taxable items in Ohio typically include tangible personal property, such as clothing, electronics, and household goods. Services like repairs, rentals, and certain professional services are also subject to sales tax. However, there are exceptions, and some items are exempt from sales tax.
- Exemptions may include certain food items, prescription medications, and educational materials.
- Sales tax may also be waived for specific transactions, such as those made by government entities or qualifying non-profit organizations.
- It's important to note that these exemptions and waivers are subject to change, so staying informed about the latest regulations is essential.
Sales Tax Registration and Collection
Businesses operating in Ohio are required to register for a Sales Tax Permit if they meet certain criteria. This permit allows businesses to collect and remit sales tax to the state. The registration process involves providing essential business information and obtaining a unique identification number.
Once registered, businesses must collect sales tax from customers at the point of sale. This responsibility extends to both online and brick-and-mortar retailers. The collected sales tax must be remitted to the Ohio Department of Taxation at regular intervals, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis, depending on the business's tax liability.
Failing to register or comply with sales tax regulations can result in penalties and interest charges. Therefore, it is crucial for businesses to stay informed about their obligations and seek professional advice when needed.
Sales Tax Filing and Payment
Filing sales tax returns in Ohio is a crucial step in the tax process. Businesses must file returns periodically, providing details about their taxable sales and the amount of tax collected. These returns are typically due on a monthly or quarterly basis, depending on the business’s tax liability and registration status.
Along with filing the returns, businesses must also remit the collected sales tax to the Ohio Department of Taxation. This can be done through various payment methods, including online payments, wire transfers, or by mailing a check. It's essential to ensure timely payment to avoid penalties and interest charges.
The Ohio Department of Taxation provides resources and guidance to assist businesses in filing and paying sales tax. This includes online filing systems, payment portals, and detailed instructions to ensure a smooth and efficient process.
Sales Tax for Remote Sellers
With the rise of e-commerce, Ohio, like many other states, has implemented regulations for remote sellers. Remote sellers are businesses that sell goods or services to Ohio residents without having a physical presence in the state. These regulations ensure that sales tax is collected and remitted, even for out-of-state sellers.
Remote sellers must register with the Ohio Department of Taxation and collect sales tax on transactions with Ohio customers. This requirement applies to both online retailers and marketplace facilitators. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in penalties and the potential for enforcement actions.
Ohio's regulations for remote sellers are designed to level the playing field for in-state businesses and ensure a fair tax system. By collecting sales tax from remote sellers, the state aims to prevent tax evasion and support its revenue streams.
Sales Tax for Online Transactions
Online transactions have become an integral part of modern commerce, and Ohio’s sales tax regulations apply to these transactions as well. Whether a business operates solely online or has a physical presence, it must collect and remit sales tax on online sales to Ohio residents.
The responsibility for collecting sales tax falls on the seller, regardless of whether the transaction takes place on their website, an e-commerce platform, or through a social media channel. This ensures that sales tax is collected consistently across various online sales channels.
Ohio's online sales tax regulations are in line with the Wayfair decision, a landmark Supreme Court ruling that allows states to collect sales tax from out-of-state sellers with substantial connections to the state. This ruling has significantly impacted the way online sales are taxed, ensuring a more uniform approach across the country.
Sales Tax Compliance and Enforcement
The Ohio Department of Taxation takes sales tax compliance seriously and has implemented measures to enforce tax regulations. Non-compliance can result in penalties, interest charges, and even legal action. The department has a dedicated team to investigate and audit businesses for sales tax compliance.
Businesses found to be in violation of sales tax regulations may face significant consequences. These can include fines, penalties, and the requirement to pay back taxes, interest, and penalties. In severe cases, business owners may also face personal liability for tax debts.
To avoid such situations, businesses should stay informed about sales tax regulations, register for a Sales Tax Permit if applicable, and collect and remit sales tax accurately. Seeking professional tax advice and utilizing the resources provided by the Ohio Department of Taxation can help businesses maintain compliance and avoid potential issues.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Credits
Ohio offers various sales tax exemptions and credits to certain businesses and individuals. These incentives are designed to promote specific industries, support economic development, and assist taxpayers facing financial hardship.
- For instance, resale certificates allow businesses to purchase goods without paying sales tax, provided they will resell those goods to consumers. This exemption is essential for businesses to maintain their profitability and avoid double taxation.
- Manufacturers and producers may qualify for manufacturing exemptions, which exempt certain raw materials and equipment from sales tax.
- There are also sales tax holidays during which specific items, such as school supplies or energy-efficient appliances, are exempt from sales tax for a limited time.
- Businesses and individuals may also be eligible for sales tax credits, which can reduce the amount of tax owed or provide a refund. These credits are often tied to specific activities or purchases.
It's crucial for businesses and taxpayers to stay informed about these exemptions and credits, as they can significantly impact their tax liability. Consulting with tax professionals and staying updated on Ohio's tax regulations can help ensure eligibility and proper utilization of these incentives.
Sales Tax and Business Growth
Sales tax regulations can have a significant impact on a business’s growth and expansion plans. Understanding and complying with these regulations is essential for businesses looking to establish a strong presence in Ohio.
For instance, businesses considering expansion into new markets or jurisdictions within Ohio must be aware of the varying local sales tax rates. Proper planning and budgeting for these additional taxes are crucial to ensure a successful expansion. Additionally, businesses should consider the impact of sales tax on their pricing strategies and overall financial planning.
Furthermore, businesses should be mindful of their obligations when it comes to sales tax registration and compliance. Failing to register or comply with sales tax regulations can lead to significant penalties and damage a business's reputation. Seeking professional advice and utilizing the resources provided by the Ohio Department of Taxation can help businesses navigate these challenges and ensure a smooth expansion process.
The Future of Sales Tax in Ohio
Sales tax regulations are dynamic and subject to change over time. Ohio, like many other states, is continuously evaluating its tax system to ensure fairness, efficiency, and compliance with evolving economic trends.
As e-commerce continues to grow, Ohio may further refine its regulations for remote sellers and online transactions. This could involve implementing new technologies for tax collection and enforcement, as well as exploring ways to simplify the tax filing process for businesses.
Additionally, Ohio may consider expanding its sales tax base to include additional services or goods, particularly those related to the digital economy. This could involve taxing certain digital products or services, such as streaming media or software-as-a-service offerings.
Furthermore, Ohio may explore the possibility of adopting a sales tax nexus, which would define the circumstances under which out-of-state sellers are required to collect and remit sales tax to the state. This could have significant implications for online retailers and marketplace facilitators.
As Ohio continues to adapt its sales tax regulations, it will strive to maintain a balance between generating revenue for essential public services and supporting the growth and competitiveness of its businesses. Staying informed about these potential changes is crucial for businesses and taxpayers to ensure compliance and adapt their strategies accordingly.
What happens if I don’t register for a Sales Tax Permit in Ohio when required?
+Failing to register for a Sales Tax Permit when required can result in penalties and interest charges. The Ohio Department of Taxation may impose fines and require you to pay back taxes, along with penalties and interest. In some cases, business owners may also face personal liability for tax debts.
How often do I need to file and pay sales tax in Ohio?
+The frequency of filing and paying sales tax in Ohio depends on your business’s tax liability and registration status. Typically, businesses file sales tax returns and remit payments on a monthly or quarterly basis. It’s important to check your registration requirements and consult with tax professionals to determine the appropriate filing frequency for your business.
Are there any sales tax holidays in Ohio, and what items are typically exempt during these periods?
+Yes, Ohio does have sales tax holidays, during which specific items are exempt from sales tax for a limited time. These holidays often coincide with back-to-school shopping or energy-efficient appliance purchases. The exempt items can vary, so it’s essential to check the official guidelines and dates for each sales tax holiday.
How can I stay updated on changes to sales tax regulations in Ohio?
+Staying informed about changes to sales tax regulations in Ohio is crucial for compliance. You can subscribe to updates and notifications from the Ohio Department of Taxation’s website. Additionally, consulting with tax professionals and staying engaged with industry news and resources can help you stay ahead of any regulatory changes.



