Remittance Tax

In the intricate world of international finance and taxation, remittances play a pivotal role, especially when it comes to the flow of funds across borders. The process of sending and receiving money internationally, known as remittance, is not only a critical financial service but also a subject of significant regulatory and tax considerations. This article delves deep into the realm of remittance tax, exploring its complexities, implications, and the strategies that individuals and businesses can employ to navigate this intricate landscape.
Unraveling the Complexity of Remittance Tax

Remittance tax is a multifaceted aspect of international finance, encompassing a wide range of regulations and practices that vary significantly across different countries and jurisdictions. The taxation of remittances is not a uniform process, and understanding the unique rules and rates in each country is essential for anyone engaged in international money transfers.
At its core, remittance tax refers to the levy imposed on funds sent or received across international borders. This tax is typically a percentage of the total remitted amount and is often subject to various deductions, exemptions, and other tax relief measures. The specific rate and application of remittance tax depend on several factors, including the sender's and recipient's country, the purpose of the remittance, and the amount being transferred.
For instance, consider the case of Ms. Zhang, a Chinese national working in the United States. When she sends money back to her family in China, she encounters a complex web of tax regulations. In this scenario, Ms. Zhang's remittance is subject to both U.S. and Chinese tax laws, which can lead to double taxation if not properly managed. This example highlights the critical need for a comprehensive understanding of international tax laws and the potential strategies to mitigate tax liabilities.
The Global Landscape of Remittance Taxation
The global landscape of remittance taxation is diverse and constantly evolving. While some countries impose a straightforward remittance tax on all incoming and outgoing transfers, others employ more nuanced approaches. For example, certain jurisdictions levy taxes only on outgoing remittances, while others exempt specific categories of transfers, such as those for educational or medical purposes.
In the European Union, the application of remittance tax varies significantly among member states. Countries like Germany and France impose a flat rate on outgoing remittances, while others, such as the United Kingdom, have more complex systems that consider factors like the relationship between the sender and recipient and the purpose of the transfer. This diversity in tax laws underscores the importance of thorough research and expert advice when dealing with international remittances.
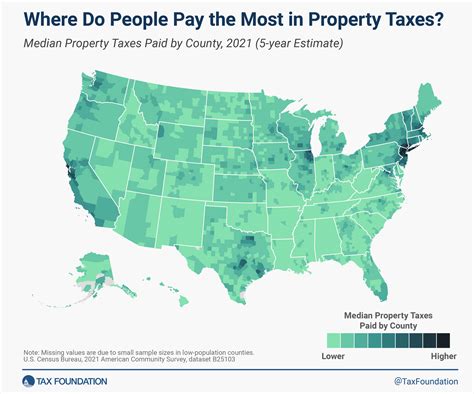
| Country | Remittance Tax Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| United States | 0-30 |
| China | 0-20 |
| United Kingdom | 0-25 |
| India | 0-30 |
| Brazil | 0-25 |
Navigating the Tax Implications of Remittances
Understanding the tax implications of remittances is a critical aspect of financial planning, especially for individuals and businesses engaged in international transactions. The complexity of remittance tax laws can lead to significant financial burdens if not properly navigated. Here, we explore some key strategies and considerations to manage these tax implications effectively.
Optimizing Remittance Tax Strategies
One of the primary strategies to optimize remittance tax is to take advantage of tax treaties and agreements between countries. These treaties often provide provisions to avoid double taxation and can offer substantial tax benefits. For instance, the Convention Between the Government of the United States of America and the Government of the People’s Republic of China for the Avoidance of Double Taxation and the Prevention of Fiscal Evasion with Respect to Taxes on Income, commonly known as the U.S.-China Tax Treaty, provides a framework for individuals like Ms. Zhang to reduce their tax liabilities when sending money between the two countries.
Additionally, understanding the tax exemptions and reliefs available in each jurisdiction is crucial. Many countries offer exemptions for certain types of remittances, such as those for educational fees, medical expenses, or humanitarian aid. By leveraging these exemptions, individuals and businesses can minimize their tax obligations and ensure compliance with local regulations.
Compliance and Reporting Requirements
Compliance with remittance tax laws is a critical aspect of international financial transactions. Failure to comply with these regulations can lead to significant penalties and legal consequences. To ensure compliance, individuals and businesses must understand the reporting requirements for both the sending and receiving countries.
In most jurisdictions, there are specific thresholds for reporting remittances. For example, the United States requires individuals to report all remittances over a certain amount, regardless of the purpose or recipient. Similarly, many countries mandate the disclosure of the purpose of the remittance and the identity of the recipient, especially for large transfers.
The Future of Remittance Taxation: Trends and Innovations
The world of remittance taxation is evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements, changing regulatory landscapes, and the increasing demand for efficient and transparent financial services. As we look to the future, several trends and innovations are shaping the way remittances are taxed and managed.
Digitalization and Blockchain Technology
The rise of digital payments and blockchain technology is revolutionizing the remittance industry. With the increasing adoption of cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based payment systems, the traditional methods of remittance taxation are being challenged. Blockchain technology offers a transparent and secure platform for cross-border transactions, potentially reducing the need for complex tax regulations and compliance procedures.
For instance, the use of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin for remittances can bypass traditional banking systems and their associated taxes. However, the tax treatment of cryptocurrencies is still evolving, and many countries are developing specific regulations to address this new form of payment. The future of remittance taxation may involve a shift towards taxing the gains from cryptocurrency transactions rather than the transactions themselves.
Simplification and Harmonization of Tax Laws
The complex and diverse nature of remittance taxation across countries has led to calls for simplification and harmonization of tax laws. International organizations and financial institutions are advocating for more uniform tax regulations to facilitate cross-border transactions and reduce the administrative burden on individuals and businesses.
Efforts are being made to develop international standards for remittance taxation, particularly within regional economic blocs like the European Union and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). These initiatives aim to streamline the process, making it more accessible and less costly for individuals and businesses to send and receive funds internationally.
Conclusion: Embracing a New Era of Remittance Taxation
The world of remittance taxation is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and the evolving needs of global citizens. As we move forward, it is essential to stay informed about the latest developments and trends in this field.
By staying abreast of these changes and seeking expert advice when needed, individuals and businesses can navigate the complexities of remittance taxation with confidence. The future of remittances holds the promise of greater efficiency, transparency, and accessibility, making it an exciting time for those engaged in international financial transactions.
How are remittance taxes calculated and applied in different countries?
+The calculation and application of remittance taxes vary widely across countries. In some countries, a flat rate is applied to all remittances, while others use progressive tax rates based on the amount transferred. Additionally, certain jurisdictions offer tax exemptions or reductions for specific types of remittances, such as educational expenses or humanitarian aid.
What are the potential consequences of non-compliance with remittance tax laws?
+Non-compliance with remittance tax laws can lead to severe consequences, including substantial fines, penalties, and even criminal charges. In some cases, individuals or businesses may be required to pay back taxes with interest, and they could also face legal action, especially if the non-compliance is deemed intentional or fraudulent.
How can individuals and businesses stay updated with the latest changes in remittance tax laws and regulations?
+Keeping up with the latest changes in remittance tax laws can be challenging due to their complexity and frequent updates. It is advisable to consult tax professionals or subscribe to reliable sources of tax information, such as government websites, industry publications, or reputable tax advisory firms. These sources provide timely updates and analysis on tax law changes, ensuring individuals and businesses remain compliant.