Overtime Tax Free

In the complex world of employment and taxation, understanding the concept of overtime and its potential tax implications is crucial for both employees and employers. The treatment of overtime pay varies across jurisdictions, and one of the key considerations is whether or not it is subject to tax deductions.
This comprehensive article aims to delve into the intricacies of overtime pay that remains tax-free, exploring the legal frameworks, eligibility criteria, and practical implications. By examining real-world examples and providing expert insights, we will navigate the nuances of this topic, ensuring a clear understanding for all readers.
Understanding Overtime and Its Tax Treatment

Overtime work occurs when employees exceed their standard working hours, as defined by their employment contracts or relevant labor laws. This additional work often arises due to increased demand, project deadlines, or unexpected circumstances within the workplace.
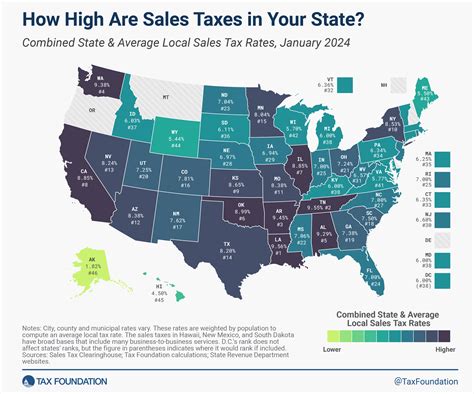
From a taxation perspective, overtime pay is typically treated as regular income, subject to income tax, social security contributions, and other applicable deductions. However, in certain scenarios, specific types of overtime pay may be exempt from these taxes, offering financial benefits to employees and employers alike.
Tax-Free Overtime: A Closer Look
Tax-free overtime is a concept that allows individuals to earn additional income without incurring income tax or certain other deductions. This exemption is usually granted under specific conditions and varies depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the overtime work.
For instance, in some countries, overtime pay is exempt from income tax if it is earned during certain periods of the year or if it falls within a specific income threshold. This incentive aims to encourage employees to take on additional work and boost their earnings, while also providing employers with a means to reward their staff without increasing their tax burden.
| Jurisdiction | Tax-Free Overtime Conditions |
|---|---|
| Country A | Overtime pay up to $500 per month is exempt from income tax. |
| Country B | Overtime worked during the holiday season is tax-free. |
| Region X | Tax exemption for overtime pay if it's part of a shift work arrangement. |

It's important to note that the eligibility for tax-free overtime often comes with certain criteria, such as the employee's regular income level, the number of overtime hours worked, and the type of work performed. These conditions can be quite detailed and may require careful consideration to ensure compliance with the relevant tax laws.
Eligibility and Conditions for Tax-Free Overtime

Determining eligibility for tax-free overtime involves a careful examination of various factors. Here are some key aspects to consider:
Income Level and Thresholds
Many jurisdictions implement income thresholds to determine whether an employee qualifies for tax-free overtime. For instance, an individual's regular income might need to fall below a certain amount to be eligible for the exemption. This threshold can vary based on factors like the individual's marital status, number of dependents, and the tax year.
Let's take a hypothetical example. In Country Z, an individual earning below $30,000 annually may be eligible for tax-free overtime if they work a certain number of hours. However, as their income increases, the exemption may phase out, ensuring that higher-income earners do not benefit disproportionately.
Overtime Hour Limitations
The number of overtime hours worked is often a crucial factor in determining tax-free status. Jurisdictions may impose a maximum number of overtime hours that qualify for the exemption. For example, an employee might be eligible for tax-free overtime for the first 10 hours worked beyond their standard workweek, but any additional hours may be subject to regular taxation.
This limitation helps prevent abuse of the tax-free overtime provision and ensures that it remains a benefit for employees who genuinely need the additional income, rather than a loophole for excessive overtime work.
Type of Work and Employment Status
The nature of the work performed can also influence the tax treatment of overtime pay. Certain types of work, such as shift work or work performed in hazardous conditions, may be more likely to qualify for tax-free status. Additionally, an employee's employment status, whether they are full-time, part-time, or contract-based, can impact their eligibility.
For instance, a full-time employee in a manufacturing plant might be eligible for tax-free overtime if they work night shifts, as this type of work often comes with additional challenges and potential health risks.
Practical Considerations and Real-World Examples
Understanding the theoretical aspects of tax-free overtime is one thing, but real-world examples can provide a more tangible understanding of how this concept plays out in practice.
Case Study: Tax-Free Overtime in the Retail Sector
During the holiday season, many retail stores experience a surge in customer traffic, leading to increased demand for staff. In such scenarios, employers often incentivize their employees to work additional hours by offering tax-free overtime pay.
For example, let's consider a retail store in a busy urban area. To meet the holiday rush, the store offers its employees the opportunity to work up to 10 additional hours per week, with the promise that this overtime pay will be tax-free. This incentive not only helps the store manage its staffing needs but also provides a financial boost to its employees during a typically expensive time of year.
Impact on Employee Retention and Motivation
Tax-free overtime can have a significant impact on employee retention and motivation. When employees see the financial benefits of working additional hours without the burden of increased tax deductions, they are more likely to be motivated to take on this extra work.
Furthermore, employers can use tax-free overtime as a strategic tool to retain their top performers. By offering this benefit selectively to high-performing employees, employers can create a culture of recognition and appreciation, leading to increased job satisfaction and reduced turnover.
Navigating the Complexities: Expert Insights
While the concept of tax-free overtime seems straightforward, it can become quite complex when dealing with the nuances of tax laws and employment regulations. To navigate these complexities, it's essential to seek expert advice and stay informed about the latest developments.
Staying Informed: Tax Law Updates and Changes
Tax laws are not static; they can change frequently, and these changes can significantly impact the eligibility and conditions for tax-free overtime. It's crucial for both employees and employers to stay updated on any amendments to tax regulations that might affect their circumstances.
For instance, a recent change in a country's tax code might introduce a new income threshold for tax-free overtime eligibility, or it might alter the conditions under which certain types of work qualify for the exemption. Being aware of these changes can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions about their financial strategies.
Future Outlook and Potential Implications

As the global workforce evolves, so too will the landscape of overtime work and its tax treatment. Several trends and factors are likely to shape the future of tax-free overtime, impacting both employees and employers.
Remote Work and Its Impact
The rise of remote work, accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic, has introduced new complexities to the concept of overtime and its taxation. With employees working from various locations, the determination of tax-free overtime eligibility becomes more intricate, especially when considering the varying tax laws across different jurisdictions.
As remote work continues to gain traction, employers and employees will need to navigate these challenges, potentially leading to the development of new tax policies and practices to accommodate this shift in the workplace.
Technological Advancements and Automation
Advancements in technology and automation are already reshaping the nature of work, and this trend is expected to continue. As certain tasks become automated, the demand for human labor may shift, impacting the need for overtime work.
However, the introduction of new technologies can also lead to increased productivity, which might result in a higher demand for overtime work in specific sectors. The interplay between technology, productivity, and overtime will be a key factor in determining the future of tax-free overtime provisions.
Changing Attitudes Towards Work-Life Balance
Society's evolving attitudes towards work-life balance can also influence the future of tax-free overtime. As employees prioritize their well-being and personal time, the demand for tax-free overtime may decrease, especially if it is seen as a disincentive to maintain a healthy work-life balance.
Employers, in turn, may need to adapt their strategies, offering alternative incentives or flexible work arrangements to attract and retain talent in a competitive job market.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of tax-free overtime is essential for both employees and employers, as it can significantly impact their financial strategies and overall work experience. By exploring the legal frameworks, eligibility criteria, and practical implications, this article has provided a comprehensive guide to navigating the world of tax-free overtime.
As we've seen, the concept of tax-free overtime is multifaceted, with numerous factors influencing its application. From income levels and overtime hour limitations to the type of work and employment status, each element plays a crucial role in determining eligibility.
With the ever-evolving landscape of work and tax laws, staying informed and seeking expert advice is crucial. As we look to the future, the impact of remote work, technological advancements, and changing attitudes towards work-life balance will continue to shape the landscape of tax-free overtime, offering both challenges and opportunities for employees and employers alike.
Can all types of overtime work be considered tax-free?
+No, not all overtime work is eligible for tax-free status. The eligibility often depends on factors like income level, number of overtime hours, and the nature of the work. Certain types of work, like shift work or work in hazardous conditions, may be more likely to qualify.
Are there any income thresholds for tax-free overtime eligibility?
+Yes, many jurisdictions implement income thresholds to determine eligibility. For example, an individual’s regular income might need to fall below a certain amount to qualify for tax-free overtime.
How does remote work impact the eligibility for tax-free overtime?
+Remote work introduces complexities, as tax-free overtime eligibility may depend on the jurisdiction from which the employee is working. Employers and employees need to navigate these challenges, potentially leading to new tax policies.