Local Income Tax Pa

Local Income Tax (LIT) in Pennsylvania is a vital aspect of the state's tax system, impacting residents and businesses alike. Understanding how this tax works and its implications is crucial for financial planning and compliance. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Local Income Tax in PA, exploring its history, current regulations, and potential future developments.
The Evolution of Local Income Tax in Pennsylvania
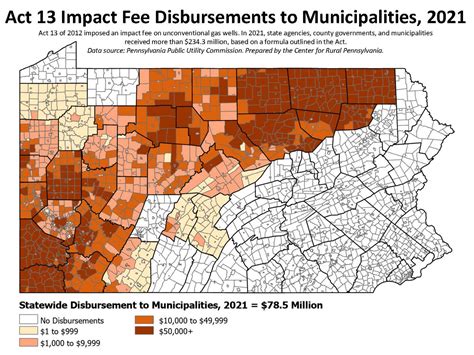
Local Income Tax has a rich history in Pennsylvania, dating back to the mid-20th century. It was introduced as a means to provide a stable revenue stream for local governments and municipalities, allowing them to fund essential services and infrastructure projects.
The origins of LIT can be traced to the Local Tax Enabling Act of 1965, which empowered local authorities to levy taxes on individuals and businesses within their jurisdictions. This marked a significant shift in the state’s tax landscape, decentralizing the tax collection process and granting more financial autonomy to local governments.
Over the years, Local Income Tax has undergone several iterations and amendments, adapting to the changing economic and political climate. Key milestones include the Local Tax Reform Act of 1997, which streamlined the tax collection process and introduced uniformity in tax rates across different localities. This act aimed to reduce administrative burdens and ensure fairness in taxation.
More recently, the Local Taxpayer Protection Act of 2015 brought further reforms, emphasizing transparency and accountability in LIT. This act mandated clearer communication of tax rates and provided safeguards against excessive taxation, protecting the interests of Pennsylvania's residents and businesses.
Understanding Local Income Tax Rates and Structures
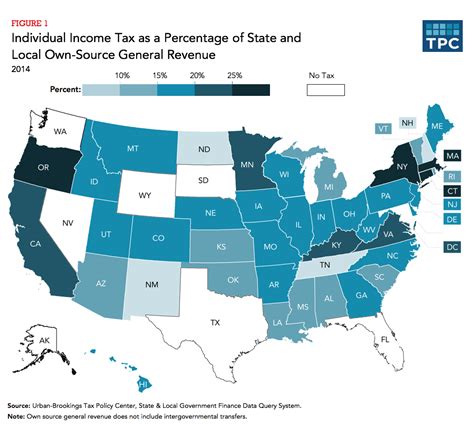
Local Income Tax rates and structures vary significantly across Pennsylvania’s diverse municipalities. While the state provides a framework for LIT, local governments have the authority to set their own tax rates, often reflecting the unique financial needs and challenges of their communities.
In general, Local Income Tax is levied as a percentage of an individual's or business's taxable income. The taxable income is typically calculated by subtracting certain deductions and exemptions from the gross income, resulting in the income subject to taxation.
For individuals, LIT is often calculated based on factors such as residency status, income level, and the number of dependents. Residents may be subject to LIT in their primary municipality of residence, as well as in other localities where they own property or conduct business.
Businesses, on the other hand, face a more complex LIT landscape. They may be required to pay LIT in multiple jurisdictions, depending on their physical presence, sales activities, or other factors. The tax rates for businesses can vary significantly, with some localities offering incentives or reduced rates to attract and retain businesses.
To illustrate the diversity of LIT rates, consider the following table, showcasing a sample of Pennsylvania municipalities and their respective LIT rates for individuals and businesses:
| Municipality | Individual Rate (%) | Business Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Philadelphia | 3.876 | 6.35 |
| Pittsburgh | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| Harrisburg | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Allentown | 1.32 | 1.32 |
| Erie | 1.0 | 1.0 |

It's important to note that these rates are subject to change and may not reflect the most current tax information. Residents and businesses are encouraged to consult official sources, such as the Pennsylvania Department of Revenue or local tax authorities, for the most accurate and up-to-date LIT rates and regulations.
The Impact of Local Income Tax on Residents and Businesses
Local Income Tax has far-reaching implications for both individuals and businesses in Pennsylvania. For residents, LIT can significantly impact their disposable income and overall financial well-being. Higher LIT rates may reduce the funds available for savings, investments, or discretionary spending, affecting economic growth and consumer confidence.
Businesses, on the other hand, face a complex web of LIT regulations and obligations. While some localities offer attractive tax rates and incentives to businesses, others may impose higher taxes, impacting their profitability and competitive position. The need to navigate multiple LIT jurisdictions can be a significant administrative burden, requiring dedicated resources for tax compliance and planning.
To illustrate the impact of LIT on businesses, let's consider a hypothetical scenario. Imagine a small business operating in two different municipalities with varying LIT rates. The business generates an annual profit of $500,000 and operates in Municipality A, with a LIT rate of 2%, and Municipality B, with a LIT rate of 4%.
In Municipality A, the business would owe $10,000 in LIT (2% of $500,000). However, in Municipality B, the tax liability would be $20,000 (4% of $500,000). This difference in tax rates can significantly impact the business's bottom line, affecting its ability to invest, expand, or offer competitive pricing.
Furthermore, the administrative burden of managing multiple LIT obligations can be substantial. The business would need to ensure accurate record-keeping, timely tax payments, and compliance with different filing requirements, which may require additional staff or external tax professionals.
Navigating the Complexities of Local Income Tax Compliance
Ensuring compliance with Local Income Tax regulations is a critical aspect of financial management for both individuals and businesses. The complex nature of LIT, with its varying rates and jurisdictions, demands a thorough understanding of the tax landscape and a proactive approach to tax planning.
For individuals, staying informed about their LIT obligations is essential. This includes understanding the tax rates in their primary municipality of residence, as well as any additional LIT obligations arising from property ownership or business activities in other localities. Keeping track of changes in tax rates and regulations is crucial to avoid surprises during tax season.
Businesses, particularly those operating across multiple jurisdictions, face a more intricate challenge. They must establish robust tax compliance systems, ensuring accurate record-keeping and timely tax payments. This may involve implementing dedicated tax software or engaging the services of tax professionals who specialize in LIT compliance.
Regular reviews of LIT obligations and potential changes in tax rates are critical for businesses. Staying informed about local tax initiatives, economic developments, and legislative updates can help businesses anticipate and adapt to changing tax landscapes. This proactive approach can minimize the risk of non-compliance and potential penalties.
The Future of Local Income Tax: Trends and Potential Developments
As Pennsylvania’s economy and tax landscape continue to evolve, Local Income Tax is likely to undergo further transformations. Understanding potential future developments is crucial for individuals and businesses to stay ahead of the curve and adapt their financial strategies accordingly.
One key trend to watch is the increasing emphasis on tax fairness and transparency. The Local Taxpayer Protection Act has already set a precedent for greater transparency in LIT, and further initiatives may aim to ensure that tax rates are reasonable and consistently applied across different localities.
Additionally, there may be growing scrutiny on the administrative burdens associated with LIT compliance. Efforts to streamline the tax collection process and reduce compliance costs could be on the horizon, benefiting both taxpayers and local governments by improving efficiency and reducing administrative overhead.
Another potential development is the exploration of alternative tax structures. While Local Income Tax has been a staple of Pennsylvania's tax system, there may be discussions and proposals for alternative revenue-generating mechanisms, such as increased reliance on property taxes or sales taxes, which could impact the future of LIT.
Moreover, the digital transformation of tax systems and the increasing use of technology for tax administration may also shape the future of LIT. Online filing systems, real-time tax data analytics, and blockchain-based tax solutions could revolutionize the way LIT is collected and managed, enhancing efficiency and security.
Finally, the impact of economic trends and policy changes at the federal and state levels cannot be overlooked. Shifts in economic growth, inflation rates, and tax policies can indirectly influence Local Income Tax rates and structures, requiring taxpayers to stay agile and responsive to changing economic conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Local Tax Enabling Act of 1965, and how does it relate to Local Income Tax in Pennsylvania?
+
The Local Tax Enabling Act of 1965 was a pivotal piece of legislation that granted local governments in Pennsylvania the authority to levy taxes, including Local Income Tax (LIT), on individuals and businesses within their jurisdictions. This act decentralized the tax collection process, allowing local authorities to generate revenue for essential services and infrastructure projects.
How often are Local Income Tax rates updated or changed in Pennsylvania?
+
Local Income Tax rates in Pennsylvania can be subject to periodic updates or changes, typically driven by local economic conditions, budgetary needs, or legislative initiatives. While some localities may review and adjust their tax rates annually, others may make changes less frequently. It’s essential for taxpayers to stay informed about any changes in LIT rates by consulting official sources or local tax authorities.
Are there any tax breaks or incentives available for businesses related to Local Income Tax in Pennsylvania?
+
Yes, certain localities in Pennsylvania offer tax breaks or incentives to businesses as a means to attract and retain economic activity. These incentives can take various forms, such as reduced Local Income Tax rates, tax credits, or other financial incentives. Businesses should explore the specific tax programs offered by their localities to determine if they qualify for any tax breaks or incentives.
How can individuals and businesses stay informed about changes in Local Income Tax regulations and rates in Pennsylvania?
+
Staying informed about changes in Local Income Tax regulations and rates is crucial for both individuals and businesses. Official sources, such as the Pennsylvania Department of Revenue’s website, often provide up-to-date information on tax rates and regulations. Additionally, local tax authorities and professional tax advisors can offer valuable insights and guidance on the latest developments in LIT.
What are the potential implications of the Local Taxpayer Protection Act of 2015 for taxpayers in Pennsylvania?
+
The Local Taxpayer Protection Act of 2015 aimed to enhance transparency and accountability in Local Income Tax (LIT) collection. For taxpayers, this act provides greater clarity on tax rates and ensures safeguards against excessive taxation. It mandates clearer communication of tax rates and provides mechanisms for taxpayers to voice concerns or disputes, contributing to a more equitable and fair tax system.
In conclusion, Local Income Tax in Pennsylvania is a dynamic and multifaceted aspect of the state’s tax system. From its historical evolution to its current complexities and future potential, LIT continues to shape the financial landscape for residents and businesses alike. By staying informed, proactive, and engaged with the ever-changing tax landscape, individuals and businesses can effectively navigate the challenges and opportunities presented by Local Income Tax.