Is Severance Taxed

Severance pay, also known as termination pay or redundancy pay, is a common practice in employment contracts, particularly in certain industries and regions. It is a financial compensation provided to employees when their employment ends, typically due to circumstances beyond their control, such as company downsizing, restructuring, or layoff. While severance pay can be a welcome financial buffer during a period of transition, it's essential to understand its tax implications to ensure compliance and optimize financial planning.
Understanding Severance Pay and Taxation

Severance pay is a monetary benefit offered by employers to departing employees as a means of compensation for the loss of their job. It is often a negotiated or predetermined amount outlined in employment contracts or labor laws, and its purpose is to provide financial support during the transition period. The tax treatment of severance pay varies depending on the jurisdiction and the specific circumstances surrounding the termination.
In many countries, severance pay is considered taxable income, just like regular wages or salaries. However, the tax treatment can be more complex, and it's crucial to understand the specific rules and regulations in your jurisdiction to avoid any unexpected tax surprises.
Tax Treatment by Jurisdiction
The tax implications of severance pay can differ significantly between countries and even within different states or provinces of a country. Here’s an overview of how severance pay is taxed in some major jurisdictions:
United States
In the United States, severance pay is generally subject to federal income tax, as well as Social Security and Medicare taxes (FICA). It is considered wages for tax purposes and is reported on a W-2 form by the employer. The amount of tax withheld depends on the employee’s overall income and tax bracket. However, certain states, like California and New York, have additional state-level tax considerations for severance pay.
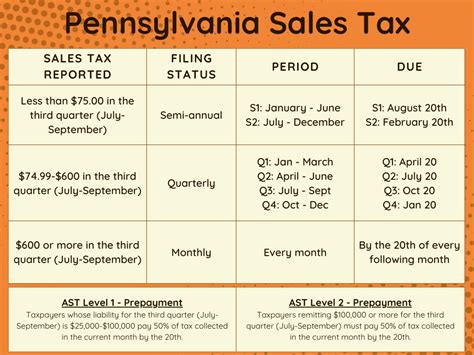
| State | Tax Treatment |
|---|---|
| California | Severance pay is taxable up to a certain threshold, after which it is exempt. The threshold varies based on the length of employment and the employee's age. |
| New York | Severance pay is taxable and must be included in the employee's state income tax return. The tax rate depends on the employee's overall state taxable income. |

Canada
In Canada, severance pay is generally taxable at the federal and provincial levels. It is considered employment income and is subject to income tax deductions. The amount of tax withheld depends on the province and the employee’s income level. Some provinces, like Ontario, have specific rules for calculating taxes on severance pay, including the use of a Severance Pay Tax Calculator to determine the tax liability.
| Province | Tax Treatment |
|---|---|
| Ontario | Severance pay is taxable and included in the employee's annual income. The tax rate varies based on the total income and the applicable provincial tax rates. |
| Quebec | Severance pay is taxable and subject to both federal and provincial income taxes. Quebec has its own income tax system, and the tax rates differ from other provinces. |
United Kingdom
In the UK, severance pay is generally taxable as earnings. It is subject to Income Tax and National Insurance Contributions (NICs). The amount of tax owed depends on the employee’s income and the applicable tax brackets. The tax treatment can be more complex if the severance pay exceeds a certain threshold, as it may be subject to additional tax rules, such as the Taxable Pay Arising from Employment (PAYE) regulations.
Australia
In Australia, severance pay, known as redundancy pay, is generally taxable. It is included in the employee’s assessable income and is subject to income tax. The tax rate depends on the total taxable income and the applicable tax scales. However, there are certain tax concessions available for redundancy payments, such as the Redundancy Concession, which allows a portion of the payment to be tax-free under specific conditions.
Factors Affecting Taxability of Severance Pay
The tax treatment of severance pay can be influenced by various factors, including the reason for termination, the amount of the severance package, and the employee’s overall financial situation. Here are some key considerations:
- Reason for Termination: The circumstances surrounding the termination can impact the tax treatment. For instance, if the termination is due to a redundancy or downsizing, the tax implications may differ from a voluntary resignation or a termination for cause.
- Severance Package Amount: The size of the severance package can affect the tax liability. In some cases, a larger package may trigger additional tax obligations or require special tax calculations.
- Employment Duration: The length of employment can influence the tax treatment, especially in jurisdictions where there are thresholds or exemptions based on the duration of the employment relationship.
- Income Level: The employee's overall income level can impact the tax rate applied to the severance pay. In progressive tax systems, higher income levels may result in a higher tax rate.
Tax Planning and Strategies for Severance Pay
When facing a potential severance package, it’s essential to consider the tax implications and develop a tax planning strategy. Here are some strategies to optimize the tax treatment of severance pay:
- Review Tax Guidelines: Familiarize yourself with the tax guidelines and regulations specific to your jurisdiction. This includes understanding the tax rates, thresholds, and any applicable exemptions or concessions.
- Consult a Tax Professional: Consider seeking advice from a qualified tax advisor or accountant who can provide personalized guidance based on your circumstances. They can help navigate the complexities of severance pay taxation and ensure compliance.
- Negotiate Severance Terms: During the negotiation process, consider the tax implications of different severance package structures. For instance, you may opt for a combination of salary continuation and a lump-sum payment to optimize tax efficiency.
- Utilize Tax Calculators: Take advantage of tax calculators and tools specifically designed for severance pay. These can help estimate your tax liability and provide a clearer picture of your financial obligations.
- Plan for Tax Payments: Understand the timing of tax payments and plan accordingly. Ensure you have the necessary funds set aside to cover any tax obligations, especially if you expect a significant tax liability.
- Consider Investment Strategies: Depending on your financial goals, you may want to explore investment opportunities with your severance pay. Consult a financial advisor to discuss tax-efficient investment options that align with your risk tolerance and financial objectives.
Conclusion
Severance pay is an essential aspect of employment termination, providing financial support during a period of transition. However, it’s crucial to understand the tax implications to avoid any surprises and optimize your financial planning. By familiarizing yourself with the tax regulations in your jurisdiction, seeking professional advice, and implementing tax-efficient strategies, you can navigate the tax landscape of severance pay with confidence and make the most of your financial situation.
Frequently Asked Questions

Is severance pay always taxable?
+In most jurisdictions, severance pay is taxable, as it is considered income. However, there may be exceptions or tax concessions available based on the specific circumstances and the laws of your country or state.
How is severance pay taxed in the United States?
+Severance pay in the US is generally subject to federal income tax, as well as Social Security and Medicare taxes (FICA). It is reported on a W-2 form, and the tax withholding depends on the employee’s tax bracket and overall income.
Are there any tax benefits or deductions available for severance pay?
+Some jurisdictions offer tax benefits or deductions for severance pay, such as the Redundancy Concession in Australia or the tax exemption threshold in California. It’s essential to consult the tax guidelines of your specific jurisdiction to understand any available tax advantages.
Can I negotiate the tax treatment of my severance pay?
+The tax treatment of severance pay is typically governed by tax laws and regulations, and it may not be negotiable in most cases. However, during the severance negotiation process, you can discuss the tax implications with your employer and seek guidance from a tax professional to optimize the tax efficiency of your package.
What should I do if I receive a large severance payment and have significant tax obligations?
+If you anticipate a large tax liability due to a significant severance payment, it’s crucial to plan ahead. Consult a tax professional to understand your obligations and explore strategies to manage the tax burden effectively. This may include adjusting your tax withholding, making estimated tax payments, or considering investment options to optimize your financial situation.