Indiana State Tax Rate

The state of Indiana, located in the Midwest region of the United States, employs a flat income tax rate structure for individual taxpayers. This means that regardless of a taxpayer's income level, the same tax rate is applied to their taxable income. As of my last update in January 2023, Indiana's state income tax rate stands at 3.23% for the 2022 tax year. This rate is applicable to all taxable income earned within the state, including wages, salaries, and other forms of income.
Understanding Indiana’s Flat Tax Rate

Indiana’s flat tax rate system is straightforward and easy to understand for taxpayers. The 3.23% tax rate is applied to the entire taxable income, with no differentiation based on income brackets. This means that whether you earn 50,000 or 500,000, the same tax rate will be applied. This system is in contrast to many other states that have progressive tax rates, where higher income levels are taxed at higher rates.
The flat tax rate in Indiana is beneficial for taxpayers as it provides simplicity and predictability when it comes to calculating their state tax liability. It also ensures that taxpayers with lower incomes are not disproportionately taxed compared to those with higher incomes. However, it's important to note that this flat rate may not always be the most advantageous for high-income earners, as some states offer more favorable tax rates for higher incomes.
Taxable Income and Exemptions in Indiana
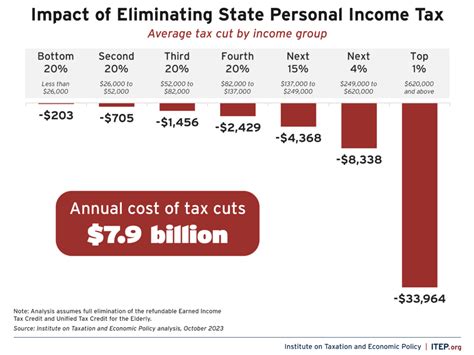
While Indiana has a flat tax rate, it’s essential to understand that not all income is taxable at the state level. Certain types of income are exempt from Indiana state income tax. These exemptions can significantly impact the overall tax liability of a taxpayer.
Income Exemptions
- Interest and dividends from certain government bonds.
- Certain retirement income, including Social Security benefits.
- Some types of farm income.
- Gains from the sale of a principal residence.
- Income from life insurance policies.
It's crucial to consult with a tax professional or refer to the official Indiana Department of Revenue website for a comprehensive list of income exemptions to ensure you are not paying taxes on non-taxable income.
Tax Credits and Deductions
In addition to exemptions, Indiana offers various tax credits and deductions that can reduce the taxable income and, consequently, the tax liability. These credits and deductions can provide significant savings for taxpayers and should be carefully considered when preparing tax returns.
- Standard Deduction: All Indiana taxpayers are eligible for a standard deduction, which reduces the taxable income by a fixed amount. The standard deduction amount varies based on filing status.
- Itemized Deductions: Taxpayers can choose to itemize their deductions instead of claiming the standard deduction. This allows for the deduction of specific expenses, such as medical costs, charitable contributions, and certain taxes paid.
- Credits for Specific Situations: Indiana offers various tax credits for specific situations, including credits for research and development, credits for rehabilitation of historic structures, and credits for employing individuals with disabilities.
Exploring these credits and deductions can help taxpayers minimize their tax liability and maximize their refunds.
Indiana’s Tax System: Pros and Cons
Indiana’s flat tax rate system has its advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a closer look at some of the key aspects:
Pros
- Simplicity: The flat tax rate is easy to understand and calculate, making tax filing less complex for taxpayers.
- Equitable Distribution: The flat tax rate ensures that all taxpayers, regardless of income level, contribute equally to the state’s tax revenue. This promotes fairness and avoids penalizing higher-income earners.
- Stable Revenue: With a flat tax rate, Indiana can predict its tax revenue more accurately, as the rate remains consistent across all income levels.
Cons
- Lack of Progressivity: Some argue that a flat tax rate does not take into account the ability-to-pay principle, as higher-income earners pay the same rate as lower-income individuals. This can result in a less progressive tax system.
- Limited Revenue Potential: While the flat tax rate provides stability, it may limit the state’s ability to generate additional revenue during times of economic growth, as higher incomes are not taxed at higher rates.
- Dependence on Other Revenue Sources: With a flat tax rate, Indiana may need to rely more heavily on other revenue sources, such as sales tax or property tax, to fund state programs and services.
Overall, Indiana's flat tax rate system has both positive and negative aspects, and it's important for taxpayers and policymakers to consider these when evaluating the state's tax structure.
Comparing Indiana’s Tax Rate with Other States
Indiana’s 3.23% flat tax rate places it in the lower range of state income tax rates across the United States. Many states have progressive tax systems with multiple tax brackets, resulting in higher tax rates for higher incomes. However, some states, like Indiana, have chosen a flat tax rate system, while others have no state income tax at all.
Here's a comparison of Indiana's tax rate with a few neighboring states:
| State | Tax Rate | Number of Tax Brackets |
|---|---|---|
| Indiana | 3.23% (flat) | 1 |
| Ohio | 2.8% - 4.799% | 3 |
| Kentucky | 5% | 1 |
| Illinois | 4.95% - 4.99% | 2 |

As shown in the table, Indiana's flat tax rate of 3.23% is lower than Kentucky's flat rate of 5%, but higher than Ohio's top tax rate of 4.799% and Illinois' top rate of 4.99%. It's important to note that these rates may have changed since my last update, so it's always advisable to refer to official state government websites for the most current information.
Indiana’s Tax Climate and Economic Impact

Indiana’s tax system, including its flat income tax rate, plays a significant role in shaping the state’s economic landscape. A competitive tax climate can attract businesses and investors, leading to job creation and economic growth. Here’s a deeper look at Indiana’s tax climate and its potential impact on the state’s economy.
Attracting Businesses and Investment
A flat tax rate can make Indiana an attractive destination for businesses, especially when compared to states with higher tax rates or more complex tax structures. Businesses often consider tax rates when deciding where to locate or expand, and a competitive tax rate can be a significant factor in their decision-making process.
Additionally, a flat tax rate can encourage business owners and entrepreneurs to start or grow their ventures in Indiana, as they can predict their tax liability with ease. This can lead to increased economic activity, job creation, and overall economic growth for the state.
Impact on Personal Finance
For individuals, Indiana’s flat tax rate can have both positive and negative implications. On the one hand, the simplicity of the flat rate can make tax filing less burdensome and reduce the need for complex tax planning. On the other hand, those with higher incomes may feel that they are not receiving the same tax benefits as those with lower incomes, especially when compared to states with progressive tax systems.
However, it's important to remember that Indiana's tax system includes various deductions, credits, and exemptions that can significantly impact an individual's tax liability. By taking advantage of these provisions, taxpayers can reduce their taxable income and minimize their state tax burden.
Potential for Economic Growth
A competitive tax climate, including a flat tax rate, can contribute to Indiana’s economic growth and development. By attracting businesses and investors, the state can create a vibrant economic ecosystem that fosters innovation and job opportunities. This, in turn, can lead to increased tax revenue for the state, allowing for investments in infrastructure, education, and other public services.
Furthermore, a thriving economy can benefit taxpayers directly through improved job prospects, higher incomes, and a higher standard of living. As such, Indiana's flat tax rate, when combined with other economic factors, can play a crucial role in the state's long-term economic prosperity.
Future Implications and Considerations
Indiana’s flat tax rate system has served the state well, providing a stable and predictable tax revenue stream. However, as the state’s economy and population continue to evolve, there may be considerations for potential changes to the tax system to better meet the needs of the 21st century.
Modernizing the Tax System
In an era of rapid technological advancement and changing economic landscapes, some argue that Indiana’s tax system could benefit from modernization. This could involve exploring new revenue sources, such as digital services taxes or remote work taxes, to adapt to the evolving nature of the digital economy.
Additionally, while the flat tax rate has its advantages, some policymakers and economists suggest that a more progressive tax system could be considered to better address income inequality and provide additional revenue for critical state programs and services.
Tax Reform Initiatives
Indiana has seen various tax reform initiatives in recent years, aimed at improving the efficiency and fairness of the tax system. These initiatives often involve comprehensive reviews of the tax code, identifying areas for simplification, and exploring ways to reduce the tax burden on individuals and businesses.
For example, the state has implemented tax credits for certain industries, such as manufacturing and technology, to encourage economic development in these sectors. Additionally, efforts have been made to streamline the tax filing process and improve taxpayer services, making it easier for individuals and businesses to comply with tax obligations.
Staying Competitive
As other states continue to explore and implement tax reforms, Indiana must remain competitive to attract and retain businesses and taxpayers. This may involve regularly reviewing and adjusting the tax system to ensure it remains fair, efficient, and responsive to the needs of the state’s residents and businesses.
By staying agile and adapting to changing economic conditions, Indiana can maintain its position as a desirable state for businesses and individuals, fostering continued economic growth and prosperity.
Conclusion
Indiana’s flat tax rate of 3.23% provides a stable and straightforward tax system for its residents and businesses. While this system has its advantages, it’s essential to consider the evolving needs of the state’s economy and population when evaluating the long-term effectiveness of the tax structure. As Indiana continues to adapt and thrive in a dynamic economic landscape, the state’s tax system will play a crucial role in shaping its future prosperity.
What is Indiana’s state income tax rate for the 2022 tax year?
+Indiana’s state income tax rate for the 2022 tax year is 3.23%.
How does Indiana’s flat tax rate compare to other states?
+Indiana’s flat tax rate of 3.23% is lower than some neighboring states like Kentucky (5%) and Illinois (4.95% - 4.99%), but higher than Ohio’s top tax rate of 4.799%.
What are some income exemptions in Indiana’s tax system?
+Indiana exempts certain types of income from state income tax, including interest and dividends from government bonds, some retirement income, farm income, gains from selling a principal residence, and life insurance income.
How can taxpayers reduce their tax liability in Indiana?
+Taxpayers can reduce their tax liability by taking advantage of various tax credits and deductions, such as the standard deduction, itemized deductions, and specific tax credits offered by the state.
What are some potential future considerations for Indiana’s tax system?
+Future considerations may include modernizing the tax system to adapt to the digital economy, exploring more progressive tax structures, and regularly reviewing and adjusting the tax code to stay competitive and responsive to the state’s needs.



