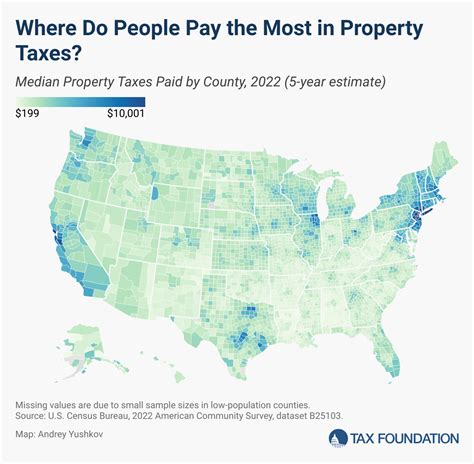
Indiana State Income Tax Rate

The state of Indiana, located in the Midwest region of the United States, has a progressive income tax system, which means that the tax rate applied to your income depends on your earnings. This system ensures that individuals and businesses contribute to the state's revenue in a manner that reflects their ability to pay. Indiana's income tax rates are set by the state government and are an essential part of the state's financial framework, contributing to various public services and infrastructure.
Understanding Indiana’s Income Tax Structure
Indiana’s income tax system consists of three distinct tax brackets, each with its own rate. This progressive structure ensures that higher incomes are taxed at a higher rate, promoting fairness and economic stability. The state’s Department of Revenue is responsible for administering and collecting these taxes, which are then allocated to support vital state services and initiatives.
Tax Brackets and Rates
Indiana’s income tax brackets are divided as follows:
- 3.23% Tax Rate: This rate applies to taxable income up to 25,000 for individuals and 50,000 for married couples filing jointly. This bracket accounts for a significant portion of the state’s taxpayers, particularly those with lower to moderate incomes.
- 3.38% Tax Rate: Taxable income between 25,000 and 110,750 for individuals and 50,000 to 221,500 for married couples falls into this bracket. This category represents a larger portion of the state’s income earners, including many middle-class families.
- 3.46% Tax Rate: The highest tax bracket, this rate applies to taxable income over 110,750 for individuals and 221,500 for married couples filing jointly. This category typically includes high-income earners and businesses, contributing a substantial portion of the state’s tax revenue.
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate | Applicable Income Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.23% | Up to $25,000 (individual) / $50,000 (married filing jointly) |
| 2 | 3.38% | $25,001 - $110,750 (individual) / $50,001 - $221,500 (married filing jointly) |
| 3 | 3.46% | Over $110,750 (individual) / Over $221,500 (married filing jointly) |
Income Tax Calculation and Filing
To calculate your Indiana state income tax, you’ll need to determine your taxable income and apply the appropriate tax rate based on the bracket your income falls into. Taxable income is calculated after deductions and exemptions are applied to your gross income. Various deductions, such as those for charitable contributions, medical expenses, and mortgage interest, can reduce your taxable income, potentially moving you into a lower tax bracket.
Filing Options and Deadlines
Indiana offers several options for filing state income taxes, including online filing through the Department of Revenue’s website, by mail, or in person at a designated office. The state generally aligns its tax filing deadlines with the federal deadline, which is typically April 15th of each year. However, it’s essential to verify the exact deadline for the relevant tax year to ensure timely filing and avoid penalties.
Tax Forms and Resources
The Indiana Department of Revenue provides a range of resources and forms to assist taxpayers in filing their state income taxes accurately. These include the IT-40 form for individual taxpayers, the IT-40EX form for exemptions, and various schedules for reporting income from different sources. The department’s website also offers guidance on deductions, credits, and other tax-related matters.
Tax Relief and Credits
Indiana provides several tax relief measures and credits to support certain taxpayers. These include:
- Hoosier Circuit Breaker Credit: This credit provides tax relief for low-income Hoosiers, particularly seniors and those with disabilities, by reducing their state income tax liability.
- Property Tax Deduction and Credit: Indiana offers a property tax deduction for homeowners and a property tax credit for renters, helping to alleviate the burden of property taxes on residents.
- Child and Dependent Care Tax Credit: Eligible taxpayers can claim this credit for expenses related to child and dependent care, providing financial support for working families.
Economic Impact and Revenue Allocation
Indiana’s state income tax plays a crucial role in the state’s economy, providing a significant source of revenue for the government. This revenue is allocated to various public services, including education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and public safety. The progressive tax structure ensures that the state’s tax burden is distributed equitably, with higher-income earners contributing a larger share.
Revenue Allocation by Sector
A substantial portion of Indiana’s state income tax revenue is directed towards education, supporting the state’s schools, universities, and vocational training programs. Other significant allocations include healthcare services, transportation infrastructure, and law enforcement. The state’s budget process ensures that these vital public services receive the necessary funding, with income tax revenue playing a critical role in this allocation.
Comparison with Other States

Compared to other states, Indiana’s income tax rates are relatively moderate. Some states have higher tax rates, particularly for higher incomes, while others have a flat tax rate or no income tax at all. This variability in state tax structures reflects the diverse economic and social landscapes across the United States.
State-by-State Comparison
For example, California has some of the highest income tax rates in the nation, with a top rate of 13.3%, while states like Florida and Texas have no income tax. Indiana’s progressive structure and moderate rates position it as a balanced approach, ensuring fairness and economic sustainability.
Future Implications and Tax Policy
The future of Indiana’s income tax rates and policy is an ongoing discussion among policymakers, economists, and taxpayers. The state’s economic growth, population trends, and budget requirements are key factors that influence tax policy decisions. Changes in tax rates or structures can have significant impacts on the state’s economy and residents’ financial well-being, so these decisions are made with careful consideration and public input.
Potential Tax Reforms
Proposed reforms could include adjustments to tax brackets, rates, or the introduction of new tax credits and deductions. These changes aim to address evolving economic conditions, promote fairness, and support the state’s long-term financial stability. Regular reviews of tax policies ensure that Indiana’s tax system remains effective and responsive to the needs of its residents and businesses.
Conclusion
Indiana’s state income tax system is a vital component of the state’s fiscal framework, contributing to its economic stability and the provision of essential public services. The progressive tax structure ensures that the tax burden is distributed equitably, with higher incomes contributing a larger share. Understanding the state’s tax rates, brackets, and the various credits and deductions available is crucial for taxpayers to navigate the system effectively and optimize their tax liabilities.
When is the deadline for filing Indiana state income taxes?
+
The deadline for filing Indiana state income taxes typically aligns with the federal deadline, which is usually April 15th of each year. However, it’s important to verify the exact deadline for the relevant tax year to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
What are the penalties for late filing or non-payment of Indiana state income taxes?
+
Late filing or non-payment of Indiana state income taxes can result in penalties and interest charges. The penalties can vary based on the amount owed and the duration of the delay. It’s important to note that the state offers payment plans and other options for taxpayers who are unable to pay their taxes in full by the deadline.
Are there any tax credits or deductions available for Indiana taxpayers?
+
Yes, Indiana offers several tax credits and deductions to support taxpayers. These include the Hoosier Circuit Breaker Credit, which provides tax relief for low-income Hoosiers, the Property Tax Deduction and Credit for homeowners and renters, and the Child and Dependent Care Tax Credit for eligible taxpayers.