Foreign Tax Exclusion

The Foreign Tax Exclusion is a vital provision in the U.S. tax code that offers significant relief to American citizens and residents who earn income abroad. This exclusion, officially known as the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE), is a powerful tool that helps expatriates reduce their tax liabilities when working or residing in foreign countries. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected, with professionals embracing international opportunities, understanding the intricacies of the Foreign Tax Exclusion becomes essential for anyone with global aspirations.
Understanding the Foreign Tax Exclusion

The Foreign Tax Exclusion is a mechanism designed to prevent double taxation for individuals earning income in foreign jurisdictions. Double taxation occurs when income is taxed by both the individual’s home country and the country where the income is earned. To mitigate this, the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allows eligible taxpayers to exclude a certain amount of their foreign-earned income from their U.S. taxable income, thus reducing their overall tax burden.
This exclusion is particularly beneficial for Americans living and working abroad, as it can significantly decrease their tax liabilities. However, it is crucial to note that the Foreign Tax Exclusion is not a blanket exemption; it has specific eligibility criteria and limitations that taxpayers must navigate to utilize it effectively.
Eligibility and Qualifications
To qualify for the Foreign Tax Exclusion, taxpayers must meet one of the following criteria:
- The bona fide residence test: This requires individuals to establish a tax home in a foreign country and reside there for an entire tax year. The IRS defines a “tax home” as the individual’s regular place of business or employment, and it must be located outside the United States.
- The physical presence test: This option is more flexible and allows taxpayers to be physically present in a foreign country for at least 330 full days during a 12-month period. This test provides an alternative for those who may not establish a permanent residence abroad but spend a significant amount of time working or living overseas.
It's important to note that the Foreign Tax Exclusion applies to earned income, including salaries, wages, bonuses, and self-employment income. It does not cover investment income, such as interest, dividends, or capital gains.
Exclusion Amount and Limitations
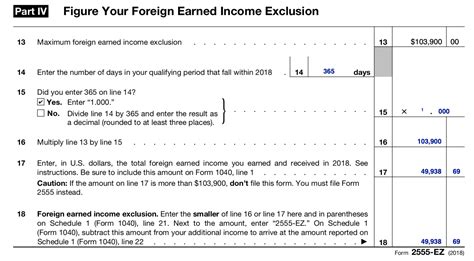
The amount of foreign-earned income that can be excluded under the FEIE varies annually and is adjusted by the IRS. For the tax year 2023, the exclusion limit is 112,000</strong>. This means that eligible taxpayers can exclude up to 112,000 of their foreign-earned income from their U.S. taxable income. Any income exceeding this limit is subject to U.S. taxation.
However, it's crucial to understand that the Foreign Tax Exclusion is not a simple deduction. It is a complex provision that requires careful consideration and planning. Taxpayers must ensure they meet the eligibility criteria and correctly calculate their exclusion amount to maximize the benefits while remaining compliant with IRS regulations.
Maximizing the Benefits of the Foreign Tax Exclusion

To make the most of the Foreign Tax Exclusion, expatriates should consider the following strategies and best practices:
1. Comprehensive Tax Planning
Effective tax planning is essential when dealing with international tax matters. Taxpayers should consult with tax professionals who specialize in international tax law to ensure they fully understand their obligations and rights. A tax expert can guide individuals through the complexities of the FEIE, helping them navigate the eligibility criteria and optimize their tax strategies.
2. Understanding the Tax Laws of Both Countries
Taxpayers must be well-versed in the tax laws of both their host country and the United States. Different countries have varying tax systems, rates, and requirements. By understanding these differences, expatriates can make informed decisions about their financial strategies, ensuring they comply with all applicable laws and maximize their tax advantages.
3. Maintaining Accurate Records
Accurate record-keeping is crucial when claiming the Foreign Tax Exclusion. Taxpayers should maintain detailed records of their time spent abroad, including travel dates, accommodation expenses, and income-related documentation. These records not only support their eligibility for the exclusion but also provide evidence in case of an IRS audit.
4. Exploring Additional Tax Benefits
The Foreign Tax Exclusion is just one of the tax benefits available to expatriates. Taxpayers should also explore other provisions, such as the Foreign Housing Exclusion or Deduction, which allows them to exclude or deduct certain housing-related expenses incurred while living abroad. Additionally, understanding tax treaties between the United States and their host country can further optimize their tax strategies.
| Year | Foreign Earned Income Exclusion Limit |
|---|---|
| 2023 | $112,000 |
| 2022 | $110,000 |
| 2021 | $108,700 |
Case Study: The Impact of the Foreign Tax Exclusion
Let’s consider a real-world example to illustrate the potential benefits of the Foreign Tax Exclusion. Imagine an American citizen, Jane, who takes a job as a consultant in a foreign country. Her annual income from this position is $150,000. Without the Foreign Tax Exclusion, Jane would be taxed on her entire income by both the United States and her host country, resulting in a significant tax burden.
However, by meeting the eligibility criteria and claiming the Foreign Tax Exclusion, Jane can exclude $112,000 (the current limit for 2023) of her income from U.S. taxation. This exclusion reduces her taxable income to $38,000, resulting in substantial tax savings. Additionally, by understanding the tax laws of her host country, Jane can further optimize her tax situation, potentially reducing her overall tax liability even further.
Future Implications and Considerations
The Foreign Tax Exclusion is a dynamic provision, and its impact on expatriates can be significant. As more individuals pursue international careers and opportunities, the FEIE becomes an increasingly important tool for managing their tax obligations. Here are some key considerations for the future:
1. Inflation Adjustments
The IRS typically adjusts the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion limit annually to account for inflation. This ensures that the exclusion remains relevant and provides adequate tax relief. Taxpayers should stay updated on these adjustments to maximize their benefits accurately.
2. Tax Treaty Negotiations
The United States negotiates tax treaties with various countries to prevent double taxation and promote international trade. These treaties often include provisions that align with or enhance the benefits of the Foreign Tax Exclusion. As these treaties evolve, expatriates should monitor the developments to take advantage of any additional tax advantages.
3. Compliance and Reporting
While the Foreign Tax Exclusion offers significant benefits, it also comes with increased compliance responsibilities. Taxpayers must accurately report their foreign income and comply with all relevant tax laws. Failure to do so can result in penalties and legal consequences. Therefore, staying informed and seeking professional advice is crucial to ensure compliance.
4. Expanding Global Opportunities
The Foreign Tax Exclusion encourages Americans to pursue international careers and explore global opportunities. As the world continues to globalize, the demand for skilled professionals with international experience grows. The FEIE plays a pivotal role in supporting this trend by providing tax relief that makes working abroad more financially viable.
Conclusion
The Foreign Tax Exclusion is a powerful tool for American expatriates, offering substantial tax relief and encouraging global engagement. By understanding the eligibility criteria, maximizing benefits, and staying informed about tax laws and treaties, individuals can effectively utilize this provision to manage their tax obligations while pursuing international opportunities. As the world becomes more interconnected, the FEIE will continue to play a vital role in shaping the financial landscape for expatriates, promoting global mobility, and fostering international cooperation.
How often is the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion limit adjusted for inflation?
+The IRS typically adjusts the FEIE limit annually, usually in the fall, to account for inflation. Taxpayers should refer to the IRS guidelines for the current tax year to ensure they have the most up-to-date information.
Can I claim the Foreign Tax Exclusion if I am a dual citizen?
+Yes, dual citizens who meet the eligibility criteria can claim the Foreign Tax Exclusion. However, they must still comply with the tax laws of both countries and may need to file tax returns in both jurisdictions.
What happens if I exceed the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion limit?
+If you exceed the FEIE limit, the excess income is subject to U.S. taxation. However, you may still be eligible for other tax benefits, such as the Foreign Housing Exclusion or Deduction, which can further reduce your taxable income.
Can I claim the Foreign Tax Exclusion if I work remotely for a U.S. company while living abroad?
+Yes, you can claim the Foreign Tax Exclusion if you meet the eligibility criteria, regardless of whether you work remotely for a U.S. company or are employed by a foreign entity. The key factor is your physical presence or residence in a foreign country.