Florida Retail Tax
Florida, known for its vibrant tourism industry and diverse retail landscape, has a unique tax system that impacts both residents and businesses. The Florida Retail Tax, often referred to as the sales tax, plays a crucial role in the state's economy and is a significant consideration for consumers and retailers alike. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Florida's retail tax, exploring its rates, exemptions, and the impact it has on various industries and consumer behavior.
Understanding the Florida Retail Tax Landscape

The Florida Retail Tax, a key component of the state’s revenue generation, is a consumption tax applied to the sale of goods and certain services. It is an essential revenue stream for the state, contributing to infrastructure development, education, and various public services. The tax structure in Florida is designed to be straightforward, with a uniform state sales tax rate applicable across the state.
However, it's important to note that Florida's tax system is not solely reliant on the state sales tax. The state also levies various other taxes, including a corporate income tax, an intangible personal property tax, and a tangible personal property tax, among others. These taxes, along with the sales tax, form a comprehensive tax structure that supports the state's financial needs.
Key Features of Florida’s Retail Tax System
Florida’s retail tax system is characterized by several key features that make it unique and impactful:
- Uniform State Sales Tax Rate: Florida maintains a single state sales tax rate, which is applicable to all counties and municipalities within the state. This uniformity simplifies tax calculations and compliance for both businesses and consumers.
- Local Sales Tax Options: While the state sales tax rate is standardized, local governments in Florida have the authority to impose additional sales taxes. These local taxes, often referred to as discretionary sales surtaxes, can vary across counties and even within municipalities, leading to varying tax rates for consumers depending on their location.
- Exemptions and Special Considerations: Florida’s retail tax system includes a range of exemptions and special provisions. These exemptions are designed to support specific industries, promote economic development, and provide relief to certain consumer groups. For example, some types of food, prescription drugs, and certain agricultural products are exempt from sales tax.
- Remote Seller Tax Collection: With the rise of e-commerce, Florida has implemented laws requiring remote sellers to collect and remit sales tax on transactions with Florida consumers. This ensures that online retailers, even those without a physical presence in the state, contribute to Florida’s tax revenue.
| Sales Tax Rate | 6% |
|---|---|
| Local Sales Tax Rates | Up to 1.5% (varies by county) |
| Total Tax Rate | 6% - 7.5% |

The table above provides a simplified overview of Florida's sales tax rates. It's important to note that the local sales tax rates can vary significantly, and certain areas may have additional taxes or surcharges. These variations make it crucial for businesses and consumers to stay informed about the specific tax rates applicable in their region.
Retail Tax Rates and Variations
Florida’s retail tax system is characterized by a combination of state and local sales taxes, which together form the total tax burden for consumers. Understanding these rates and variations is crucial for businesses and consumers alike.
State Sales Tax Rate
The state sales tax rate in Florida is a uniform 6%, which is applied to the sale of most goods and some services. This rate is set by the state legislature and remains consistent across the state, ensuring simplicity and predictability for businesses and consumers.
Local Sales Tax Rates
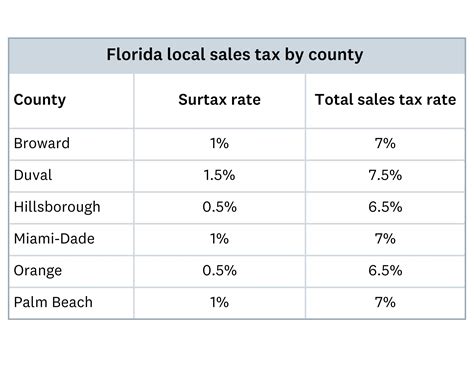
In addition to the state sales tax, local governments in Florida have the authority to impose discretionary sales surtaxes. These local sales taxes can vary significantly from one county to another, and even within municipalities. The purpose of these local taxes is to fund specific local projects, infrastructure development, and public services.
The local sales tax rates can range from 0% to 1.5%, with some counties opting for higher rates to support their unique needs. For example, certain counties with a higher cost of living or specific infrastructure requirements may choose to implement higher local sales taxes.
Total Tax Rates and Variations
When the state sales tax and local sales taxes are combined, the total tax rate can vary significantly across Florida. In areas with a 1.5% local sales tax rate, the total tax burden for consumers is 7.5% (6% state tax + 1.5% local tax). However, in counties with lower local tax rates, the total tax rate can be as low as 6%.
| Local Sales Tax Rate | Total Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 0% | 6% |
| 0.5% | 6.5% |
| 1.0% | 7% |
| 1.5% | 7.5% |
The table above provides a simplified illustration of how the local sales tax rate affects the total tax burden for consumers. It's important to note that these rates can vary significantly depending on the specific county and municipality, making it essential for businesses and consumers to be aware of the applicable tax rates in their area.
Impact on Industries and Consumer Behavior
Florida’s retail tax system has a significant impact on various industries and consumer behavior, shaping the state’s economic landscape.
Impact on Retailers
For retailers operating in Florida, the retail tax system presents both opportunities and challenges. On one hand, the relatively low state sales tax rate of 6% can be seen as advantageous, as it may encourage consumer spending and make the state an attractive destination for retail businesses. Additionally, the uniformity of the state sales tax rate simplifies tax compliance and makes it easier for retailers to manage their tax obligations.
However, the variability in local sales tax rates can create complexities for retailers. Businesses with multiple locations in different counties may need to navigate varying tax rates, which can impact their pricing strategies and tax collection processes. Moreover, the addition of local sales taxes can increase the overall tax burden for consumers, potentially affecting their purchasing decisions and retailer profitability.
Impact on Consumers
Florida’s retail tax system has a direct impact on consumer behavior and spending patterns. The uniform state sales tax rate of 6% provides consumers with a predictable and consistent tax burden when making purchases. This simplicity can make it easier for consumers to budget and plan their spending.
However, the addition of local sales taxes can lead to variations in the total tax rate across the state. Consumers living in areas with higher local sales tax rates may face a higher overall tax burden, potentially influencing their purchasing decisions. For example, consumers in counties with a 7.5% total tax rate may opt to shop in neighboring counties with lower tax rates, leading to shifts in consumer behavior and spending patterns.
Industry-Specific Considerations
The impact of Florida’s retail tax system extends beyond general retail. Certain industries and sectors have unique considerations and exemptions within the tax structure.
- Tourism and Hospitality: Florida's vibrant tourism industry benefits from a reduced sales tax rate of 6% for certain tourist-related services, such as hotel accommodations and car rentals. This reduced rate promotes tourism and makes Florida an attractive destination for travelers.
- Agriculture and Food: The state's agriculture sector and certain food items are exempt from sales tax. This exemption supports the agricultural industry and ensures that essential food items remain more affordable for consumers.
- E-commerce and Remote Sellers: With the rise of online shopping, Florida has implemented laws requiring remote sellers to collect and remit sales tax on transactions with Florida consumers. This ensures that e-commerce businesses contribute to the state's tax revenue, leveling the playing field for local retailers.
Future Implications and Potential Changes
Florida’s retail tax system is dynamic and subject to potential changes and reforms. As the state’s economy evolves and new challenges arise, the tax structure may need to adapt to meet changing needs.
Potential Tax Reform Proposals
In recent years, there have been discussions and proposals for tax reform in Florida. Some of these proposals aim to simplify the tax system, reduce the overall tax burden, or shift the tax burden away from certain sectors. For example, there have been proposals to reduce or eliminate the corporate income tax, which could have significant implications for businesses and the state’s revenue generation.
Additionally, there have been discussions about the potential for a state-wide reduction in the sales tax rate, which could make Florida more competitive in attracting businesses and consumers. However, such a reduction would require careful consideration of the state's revenue needs and the potential impact on public services.
Economic Impact and Revenue Considerations
Any changes to Florida’s retail tax system would have significant economic implications. A reduction in the sales tax rate, for instance, could stimulate consumer spending and boost economic growth. However, it would also reduce the state’s revenue stream, potentially impacting public services and infrastructure development.
On the other hand, an increase in the sales tax rate or the implementation of new taxes could generate additional revenue for the state, allowing for investments in critical areas such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. However, such changes could also face resistance from consumers and businesses, impacting their economic decisions and behavior.
Balancing Act
Florida’s policymakers face a delicate balancing act when considering changes to the retail tax system. On one hand, they must ensure that the tax structure remains competitive and attractive for businesses and consumers. On the other hand, they must generate sufficient revenue to support the state’s economic development and provide essential public services.
Finding the right balance between tax rates, exemptions, and incentives is crucial for Florida's economic growth and stability. It requires careful analysis of the state's revenue needs, the impact on various industries, and the potential behavioral responses of consumers and businesses.
Conclusion: Navigating Florida’s Retail Tax Landscape
Florida’s retail tax system is a complex and dynamic component of the state’s economic landscape. With a uniform state sales tax rate and varying local sales taxes, businesses and consumers must stay informed about the applicable tax rates in their region. The system offers both opportunities and challenges, impacting industries, consumer behavior, and the state’s economy as a whole.
As Florida continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic conditions, the retail tax system will likely undergo reforms and adjustments. Staying abreast of these changes is essential for businesses and consumers to make informed decisions and navigate the tax landscape effectively. By understanding the intricacies of Florida's retail tax, stakeholders can contribute to the state's economic growth and ensure a thriving business environment.
What is the current state sales tax rate in Florida?
+The current state sales tax rate in Florida is 6%.
Are there any counties in Florida with a higher total tax rate than 7.5%?
+No, currently, there are no counties in Florida with a total tax rate higher than 7.5%. However, it’s important to note that local tax rates can change, so it’s always advisable to check the latest information for your specific county.
How do I calculate the total tax rate in my county?
+To calculate the total tax rate in your county, you need to add the state sales tax rate (6%) to the local sales tax rate applicable in your county. You can find this information on the Florida Department of Revenue’s website or by contacting your local tax office.
Are there any tax-free shopping days in Florida?
+Yes, Florida offers tax-free shopping days, typically during back-to-school season. These tax-free days provide an opportunity for consumers to purchase certain items, such as clothing and school supplies, without paying sales tax. The dates for these tax-free periods vary each year, so it’s best to check the official announcements from the Florida Department of Revenue.
How do remote sellers collect and remit sales tax in Florida?
+Remote sellers are required to register with the Florida Department of Revenue and collect sales tax on transactions with Florida consumers. They must remit the collected tax to the state on a regular basis. The specific requirements and procedures for remote sellers can be found on the Department of Revenue’s website.



