San Bernardino Sales Tax

San Bernardino, a vibrant city nestled in the Inland Empire region of Southern California, is a hub of economic activity and a popular destination for businesses and residents alike. One aspect that plays a significant role in the city's economic landscape is its sales tax. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricacies of San Bernardino's sales tax, exploring its history, rates, and impact on the local economy. From its evolution over the years to its current implications, we aim to provide a detailed understanding of this essential revenue stream for the city.
A Historical Perspective on San Bernardino’s Sales Tax

The sales tax in San Bernardino, like many other cities, has a rich history that reflects the city’s growth and economic development. It serves as a critical source of revenue for the city, funding various public services and infrastructure projects. Let’s trace the evolution of this tax and understand its significance in the context of San Bernardino’s financial landscape.
The Early Days: Laying the Foundation
San Bernardino’s sales tax journey began in the mid-20th century, mirroring the broader trend of cities adopting sales taxes to augment their revenue streams. Initially, the tax was implemented at a relatively low rate, primarily to fund essential city services such as police and fire departments, as well as basic infrastructure maintenance.
During this early period, the tax rate was set at 2.5%, which was in line with the state sales tax rate at the time. This meant that for every dollar spent on taxable goods or services within the city limits, consumers paid an additional 2.5 cents in tax. While this may seem negligible, it provided a substantial financial boost to the city's coffers, especially as the city's population and economic activity grew.
Expansion and Growth: The 1970s and Beyond
As San Bernardino continued to thrive and expand, so did the need for additional revenue to support the city’s growing infrastructure and public service demands. In response, the city incrementally increased its sales tax rate over the years. By the late 1970s, the rate had risen to 4%, providing a more substantial revenue stream to fund critical city projects.
This increase in sales tax not only helped maintain and improve existing city services but also played a pivotal role in funding new initiatives. For instance, a portion of the increased revenue was dedicated to enhancing public transportation, a move that not only benefited residents but also attracted more businesses to the city, further boosting economic activity.
Moreover, the additional revenue allowed the city to invest in cultural and recreational amenities, enhancing the overall quality of life for its residents. This strategic use of sales tax revenue positioned San Bernardino as an attractive destination for both businesses and individuals, fostering continued economic growth.
The Current Landscape: San Bernardino’s Sales Tax Today
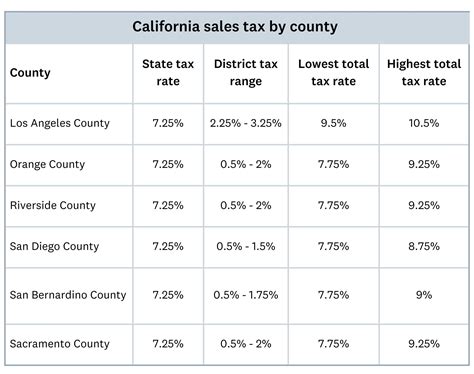
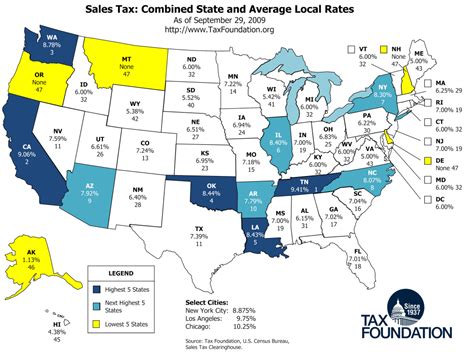
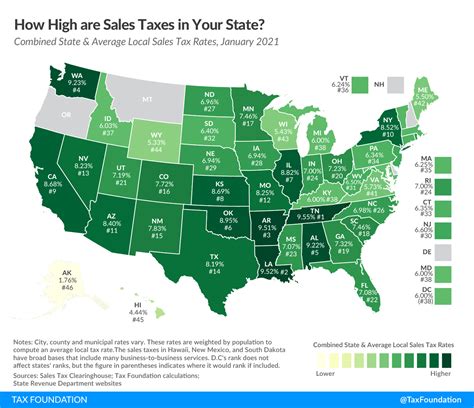
Fast forward to the present, and San Bernardino’s sales tax landscape has evolved significantly. Today, the city’s sales tax rate stands at 9.5%, comprising both state and local components. This rate is one of the highest in the region, reflecting the city’s commitment to providing top-notch public services and maintaining its infrastructure.
Breaking Down the Components
San Bernardino’s sales tax rate is composed of several components, each serving a specific purpose and contributing to the overall revenue stream. Let’s dissect these components to understand their individual roles and significance.
| Tax Component | Rate | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| State Sales Tax | 6% | Funds various state-wide programs and services, including education, healthcare, and transportation infrastructure. |
| Local Sales Tax | 3.5% | Directly benefits San Bernardino, supporting local initiatives such as public safety, community development, and infrastructure maintenance. |
The state sales tax, at 6%, is a standard rate across California and is used to fund essential state-wide services. This component ensures that the city contributes to the overall welfare of the state, while also benefiting from state-funded programs and infrastructure development.
The local sales tax, set at 3.5%, is where San Bernardino's revenue stream truly shines. This portion of the tax is solely dedicated to the city's needs, allowing it to invest in local priorities such as enhancing public safety measures, improving community facilities, and maintaining and developing vital infrastructure.
Impact on Local Businesses and Consumers
The higher sales tax rate in San Bernardino has both advantages and challenges for local businesses and consumers. For businesses, the increased tax burden can sometimes be a deterrent, especially for those operating on thin margins. However, the city’s vibrant economy and the benefits it offers, such as a skilled workforce and a thriving business environment, often outweigh this challenge.
For consumers, the higher sales tax means that they pay a slightly larger portion of their purchases as tax. While this may be a consideration in their purchasing decisions, the wide range of products and services available in the city, coupled with its vibrant culture and amenities, often make it a desirable place to live, work, and spend.
The Future of San Bernardino’s Sales Tax
Looking ahead, San Bernardino’s sales tax landscape is poised for continued evolution, shaped by economic trends, legislative decisions, and the city’s evolving needs. As the city continues to grow and adapt to changing circumstances, its sales tax policy will play a crucial role in sustaining its economic vitality and ensuring the well-being of its residents.
Potential Scenarios and Implications
One potential scenario is the possibility of a sales tax rate reduction, which could make San Bernardino a more attractive destination for businesses and consumers alike. A lower tax rate could stimulate economic activity, encouraging more businesses to set up shop and more consumers to spend within the city limits. However, such a move would also mean a reduction in revenue for the city, impacting its ability to fund public services and infrastructure development.
Conversely, the city might opt to maintain or even increase its sales tax rate, particularly if it aims to invest in ambitious infrastructure projects or enhance its public services significantly. While this could be a challenge for businesses and consumers in the short term, it could ultimately lead to a more robust and resilient economy in the long run.
Furthermore, the city might explore innovative ways to optimize its sales tax revenue, such as implementing targeted tax incentives for specific industries or promoting tourism through tax-free shopping periods. These strategies could help attract new businesses and consumers, boosting the city's economic growth and tax revenue without necessarily increasing the tax rate.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current sales tax rate in San Bernardino?
+
The current sales tax rate in San Bernardino is 9.5%, which includes both state and local components.
How does San Bernardino’s sales tax rate compare to other cities in California?
+
San Bernardino’s sales tax rate is relatively high compared to other cities in California. It is one of the highest in the region, reflecting the city’s commitment to funding public services and infrastructure.
What are the key components of San Bernardino’s sales tax rate?
+
San Bernardino’s sales tax rate is composed of a state sales tax of 6% and a local sales tax of 3.5%. The state tax funds various state-wide programs, while the local tax directly benefits the city.
How does San Bernardino’s sales tax revenue impact the city’s economy and residents?
+
The sales tax revenue plays a crucial role in funding public services, community development, and infrastructure maintenance in San Bernardino. It directly impacts the city’s economic vitality and the quality of life for its residents.
What are the potential future scenarios for San Bernardino’s sales tax policy?
+
The future of San Bernardino’s sales tax policy could involve scenarios such as a rate reduction to stimulate economic growth, maintaining the current rate for stability, or increasing the rate to fund ambitious projects. Innovative strategies like tax incentives or tax-free periods could also be explored.