Does Nc Have A State Income Tax
The state of North Carolina has a progressive income tax system, which means that its residents pay taxes on their earned income based on different tax brackets and rates. Understanding the state's tax structure is crucial for individuals and businesses operating within North Carolina, as it directly impacts their financial planning and obligations.
North Carolina’s Income Tax Structure

North Carolina imposes an income tax on its residents’ earnings, including wages, salaries, bonuses, commissions, and other forms of compensation. The state’s tax system is designed to ensure that individuals and businesses contribute to the state’s revenue while maintaining a competitive business environment.
The income tax rates in North Carolina are divided into six tax brackets, each with its own marginal tax rate. As of 2023, these tax brackets and rates are as follows:
| Tax Bracket (Income Range) | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to $11,800 | 5.25% |
| $11,801 to $23,600 | 5.45% |
| $23,601 to $47,200 | 5.75% |
| $47,201 to $94,400 | 5.95% |
| $94,401 to $220,000 | 6.04% |
| Over $220,000 | 6.95% |

It's important to note that these tax rates are subject to change, and individuals should refer to the latest tax guidelines and regulations provided by the North Carolina Department of Revenue for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Taxable Income and Deductions
When calculating their income tax liability, North Carolina residents can take advantage of various deductions and credits. The state offers standard deductions, which vary based on filing status, and residents can also choose to itemize their deductions if it results in a lower taxable income.
Common itemized deductions include medical expenses, charitable contributions, mortgage interest, state and local taxes, and certain business-related expenses. Additionally, North Carolina allows taxpayers to claim personal exemptions for themselves, their spouses, and qualifying dependents.
Taxable Entities and Exemptions
While North Carolina imposes an income tax on individuals, the state also has provisions for taxing businesses and certain entities. Corporations, limited liability companies (LLCs), partnerships, and other business entities are subject to North Carolina’s corporate income tax, which is separate from the individual income tax.
However, not all income is taxable in North Carolina. Certain types of income, such as capital gains from the sale of a personal residence, may be exempt from taxation. Additionally, North Carolina offers tax incentives and credits to attract businesses and promote economic development, so it's essential for entities to understand these opportunities.
Filing and Payment Requirements
North Carolina residents and businesses must file their income tax returns and pay their taxes by the annual deadline, which is typically April 15th. The state provides various options for filing, including electronic filing and paper returns. Late filing and payment may result in penalties and interest charges.
For individuals who are unable to pay their tax liability in full by the deadline, North Carolina offers payment plans and options for resolving tax debts. It's crucial to stay informed about these options and communicate with the state's tax authorities to avoid any unnecessary complications.
Impact and Considerations

The presence of a state income tax can have significant implications for individuals and businesses in North Carolina. For residents, the income tax affects their disposable income and financial planning, influencing decisions related to savings, investments, and overall financial management.
Businesses, on the other hand, must consider the impact of North Carolina's income tax on their profitability and operational costs. The tax structure can influence business expansion plans, investment strategies, and overall financial projections. It's essential for businesses to thoroughly understand the tax implications and explore potential tax-saving opportunities to optimize their financial performance.
Comparative Analysis
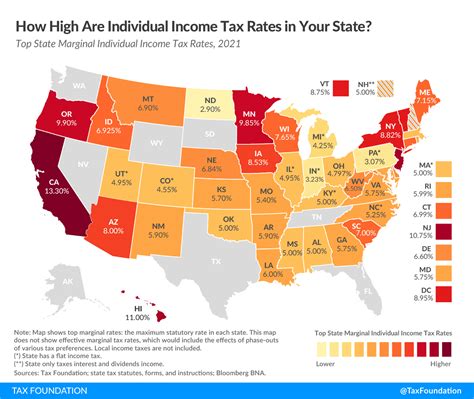
When comparing North Carolina’s income tax system to other states, it’s evident that the Tar Heel State’s tax rates are generally competitive. North Carolina’s tax brackets and rates are relatively moderate compared to some neighboring states, which can make it an attractive destination for individuals and businesses seeking a balanced tax environment.
However, it's important to consider the overall tax burden, which includes not only income taxes but also sales taxes, property taxes, and other state-level levies. A comprehensive analysis of the tax landscape is crucial for individuals and businesses making relocation or expansion decisions.
Tax Planning and Strategies
Given the complexity of tax regulations, individuals and businesses in North Carolina should consider seeking professional tax advice to ensure compliance and optimize their tax positions. Tax planning strategies can help minimize tax liabilities, maximize deductions, and take advantage of available tax credits and incentives.
Whether it's utilizing tax-efficient investment vehicles, structuring business operations to minimize tax impact, or simply understanding the nuances of North Carolina's tax laws, having a solid tax strategy is essential for long-term financial success.
Future Outlook
The future of North Carolina’s income tax system is subject to ongoing debates and policy changes. While the state’s current tax structure provides a stable revenue source, there are ongoing discussions about tax reform and potential adjustments to rates and brackets.
As the state's economy evolves and new industries emerge, policymakers will need to carefully consider the impact of tax policies on economic growth, job creation, and the overall well-being of North Carolina's residents and businesses. Balancing the need for revenue with the desire to maintain a competitive business environment will continue to be a key challenge for the state's leaders.
Conclusion
North Carolina’s income tax system plays a vital role in the state’s economy, providing a source of revenue for essential services and infrastructure. While the progressive tax structure ensures fairness, individuals and businesses must remain vigilant about their tax obligations and explore opportunities to optimize their tax positions.
By understanding the intricacies of North Carolina's tax laws, residents and businesses can make informed financial decisions, contributing to the state's economic prosperity while achieving their own financial goals. Staying informed about tax regulations and seeking professional advice when needed is key to navigating the complex world of state income taxes.
What are the tax filing deadlines in North Carolina?
+The tax filing deadline in North Carolina is typically April 15th, aligning with the federal tax deadline. However, it’s important to note that in years when April 15th falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline may be extended to the next business day. It’s always advisable to check the official guidelines provided by the North Carolina Department of Revenue for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Are there any tax incentives or credits available in North Carolina for businesses?
+Yes, North Carolina offers a range of tax incentives and credits to attract businesses and promote economic development. These incentives can include tax credits for job creation, research and development, and investment in certain industries. Businesses should consult with tax professionals or refer to the state’s official resources to explore the available options and eligibility criteria.
How can I calculate my North Carolina income tax liability?
+Calculating your North Carolina income tax liability involves determining your taxable income, which is your total income minus any applicable deductions and exemptions. You can then use the tax brackets and rates provided by the state to calculate your tax liability. It’s recommended to use official tax calculators or consult with tax professionals for accurate calculations.
Are there any tax exemptions for certain types of income in North Carolina?
+Yes, North Carolina offers tax exemptions for certain types of income. For example, capital gains from the sale of a personal residence are generally exempt from taxation. Additionally, the state provides exemptions for military personnel, veterans, and individuals with certain disabilities. It’s important to review the specific exemptions and requirements to determine eligibility.
What happens if I owe taxes but cannot pay by the deadline?
+If you are unable to pay your North Carolina income taxes by the deadline, it’s crucial to take proactive steps to address the situation. The state offers payment plans and options for resolving tax debts. Contacting the North Carolina Department of Revenue and explaining your circumstances can help you explore available options and avoid penalties and interest charges.