Does Michigan Tax Social Security
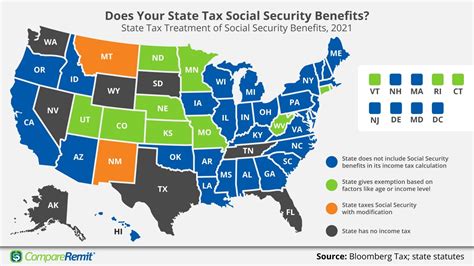
In the state of Michigan, the taxation of Social Security benefits is a topic that has evolved over the years, and understanding the current regulations is crucial for retirees and those planning for retirement. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to the taxation of Social Security in Michigan, offering insights into the state's policies and how they impact individuals' financial planning.
Understanding Michigan’s Tax Landscape
Michigan, like many other states, has its own set of tax regulations that differ from federal guidelines. While the federal government has specific rules for taxing Social Security benefits, states can choose to follow, modify, or exclude these rules. Michigan’s approach to Social Security taxation is unique and can have significant implications for retirees.
The Michigan Tax Exemption
One of the notable features of Michigan’s tax system is its partial exemption for Social Security benefits. Unlike some states that fully exempt Social Security income from taxation, Michigan has implemented a graduated exemption system. This means that a portion of an individual’s Social Security benefits may be exempt from state income tax, depending on their income level and marital status.
| Income Level | Exemption Amount |
|---|---|
| Single Filers | $20,000 or less: $20,000 exemption $20,001 - $50,000: $14,000 exemption $50,001 - $75,000: $7,000 exemption Over $75,000: No exemption |
| Married Filing Jointly | $40,000 or less: $20,000 exemption per person $40,001 - $100,000: $14,000 exemption per person $100,001 - $150,000: $7,000 exemption per person Over $150,000: No exemption |
Calculating Taxable Benefits
To determine the taxable portion of your Social Security benefits in Michigan, you must first calculate your total income. This includes not only Social Security benefits but also other sources such as pensions, interest, dividends, and earnings from work. Once your total income is established, you can apply the exemption amounts based on your filing status.
For example, a single filer with a total income of $30,000, including $18,000 in Social Security benefits, would be eligible for a $14,000 exemption. This means only $4,000 of their Social Security benefits would be subject to Michigan state income tax.
Federal vs. State Taxation
It’s important to note that Michigan’s tax exemption for Social Security benefits does not apply to federal taxation. The federal government has its own rules for taxing Social Security benefits, which are based on an individual’s provisional income. Provisional income includes half of your Social Security benefits, plus any other taxable income.
If your provisional income exceeds certain thresholds, a portion of your Social Security benefits may become taxable at the federal level. These thresholds are adjusted annually and are based on your filing status.
Financial Planning Considerations

Understanding Michigan’s tax policies on Social Security benefits is crucial for financial planning. Here are some key considerations for retirees and those approaching retirement age:
- Maximizing Exemptions: Retirees with lower incomes can benefit significantly from Michigan's graduated exemption system. Planning retirement income to stay within the exemption thresholds can help minimize state tax liabilities.
- Taxable Income Sources: Other income sources, such as pensions or investment earnings, can push you into a higher tax bracket and reduce your Social Security exemption. Strategic financial planning can help manage these sources to stay within exemption limits.
- Federal Taxation: Federal taxation of Social Security benefits is a separate consideration. Understanding how your provisional income affects federal taxation is essential for comprehensive financial planning.
Expert Insights and Tips
As a financial advisor with extensive experience in Michigan, here are some practical tips for retirees and those planning for retirement:
- Review Your Income Sources: Carefully review all your income sources and how they interact with Michigan's tax system. This includes not only Social Security benefits but also pensions, investments, and any other earnings.
- Optimize Income Streams: Consider strategies to optimize your income streams to maximize the benefit of Michigan's graduated exemption. This might involve adjusting the timing of income or using tax-efficient investment strategies.
- Consult a Professional: The tax landscape can be complex, especially when dealing with multiple income sources. Consulting a financial advisor or tax professional can provide personalized guidance based on your unique financial situation.
Future Implications
While Michigan’s current tax policies provide a favorable environment for retirees, it’s essential to consider potential future changes. Tax laws can evolve over time, and keeping abreast of any proposed or enacted changes is crucial for long-term financial planning.
Additionally, the impact of inflation and rising healthcare costs should be considered when planning for retirement. These factors can influence the purchasing power of your retirement income and the overall cost of living, affecting your tax liability and financial well-being.
Conclusion
In summary, Michigan’s approach to taxing Social Security benefits offers a graduated exemption system that benefits low- to moderate-income retirees. Understanding this system and how it interacts with your unique financial situation is essential for effective financial planning. By staying informed and seeking professional guidance, retirees can navigate Michigan’s tax landscape with confidence and ensure their retirement income is optimized.
How does Michigan’s graduated exemption system benefit retirees?
+Michigan’s graduated exemption system provides a higher tax exemption for low- to moderate-income retirees. This means that a larger portion of their Social Security benefits is exempt from state income tax, reducing their overall tax liability.
What happens if my income exceeds the exemption thresholds?
+If your income exceeds the exemption thresholds, a portion of your Social Security benefits may become taxable. The exact amount will depend on your total income and filing status. It’s advisable to consult a tax professional to understand the implications.
Are there any strategies to minimize state tax liabilities for Social Security benefits?
+Yes, strategic financial planning can help minimize state tax liabilities. This may involve adjusting the timing of income streams, optimizing investment strategies, or utilizing tax-efficient retirement accounts. Consulting a financial advisor can provide personalized strategies.