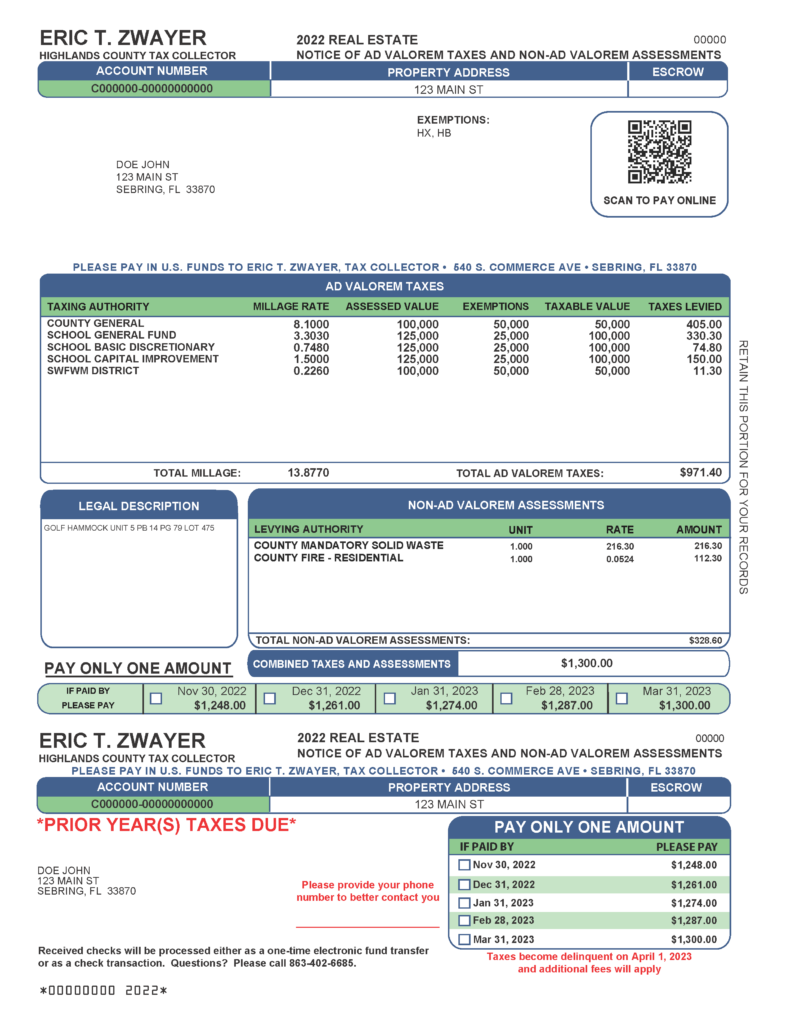
Do Previous Years Taxes

The process of filing taxes can often be a daunting task, especially when it comes to tackling previous years' tax returns. However, it is a necessary step to ensure compliance with tax laws and to potentially unlock any benefits or refunds you may be entitled to. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of doing previous years' taxes, providing you with the knowledge and tools to approach this task with confidence.
Understanding the Importance of Filing Previous Years’ Taxes

Filing taxes for previous years, also known as back taxes, is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures that you fulfill your legal obligation as a taxpayer. Tax laws require individuals and businesses to report their income and pay the corresponding taxes annually. Failing to do so can result in penalties, interest charges, and even legal consequences.
Additionally, filing back taxes provides an opportunity to claim any refunds or credits you may be eligible for. Many taxpayers discover that they are due a refund for prior years, and by filing these returns, they can reclaim that money. Moreover, accurate tax records are essential for financial planning and future tax strategies. They provide a comprehensive view of your financial history, which can be invaluable when making investment decisions or applying for loans.
Preparing for the Process: Gathering Essential Documents

Before you begin the process of filing previous years’ taxes, it is crucial to gather all the necessary documents. These documents will serve as the foundation for your tax returns and ensure accuracy in your filings.
Income Documents
Start by collecting all income-related documents for the years you intend to file. This includes:
- W-2 forms from your employer(s) for each year.
- 1099 forms if you received income from freelance work, investments, or other sources.
- Any other income statements, such as pension or retirement income, Social Security benefits, or unemployment compensation.
Expense Records
Next, gather records of any expenses that may be deductible. These could include:
- Medical and dental expenses.
- Charitable donations.
- Education expenses.
- Business-related expenses for freelancers or self-employed individuals.
- Home office expenses.
- Tax preparation fees from previous years.
Other Relevant Documents
Additionally, you’ll need the following:
- Social Security numbers for yourself, your spouse (if applicable), and any dependents.
- A copy of your previous year’s tax return (if available) to ensure accuracy and to reference any changes in your financial situation.
- Any tax forms related to specific investments or transactions, such as stock sales or real estate transactions.
Filing Options: Choosing the Right Method
Once you have gathered all the necessary documents, it’s time to choose the method for filing your previous years’ taxes. There are several options available, each with its own advantages and considerations.
Online Tax Software
Online tax software has become increasingly popular due to its convenience and user-friendly interfaces. These platforms guide you through the tax filing process, offering step-by-step instructions and calculations. They are particularly useful for individuals with straightforward tax situations, such as those with W-2 income and a few deductions.
Some popular online tax software options include:
- TurboTax
- H&R Block
- TaxAct
Professional Tax Preparation Services
For more complex tax situations or if you prefer a personalized approach, professional tax preparation services can be invaluable. Certified Public Accountants (CPAs) and Enrolled Agents (EAs) are experts in tax law and can provide tailored advice and assistance. They can help you navigate intricate tax regulations, optimize your deductions, and ensure compliance with all relevant tax laws.
Paper Returns
While less common in today’s digital age, paper returns are still an option for filing previous years’ taxes. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides tax forms and instructions that you can download or order by mail. However, it’s important to note that paper returns can be more time-consuming and may require additional research to ensure accuracy.
Step-by-Step Guide to Filing Previous Years’ Taxes
Now, let’s delve into the step-by-step process of filing previous years’ taxes, regardless of the method you choose.
Step 1: Choose the Right Tax Year
Determine which tax year(s) you need to file. Generally, tax years correspond to the calendar year, so if you’re filing for 2021, you would select the “2021 tax year” option. However, some individuals may need to file for specific quarters or months, so be sure to select the correct timeframe.
Step 2: Gather All Necessary Information
As mentioned earlier, gather all the relevant documents and information for the chosen tax year(s). This includes income statements, expense records, and any other tax-related documents.
Step 3: Select Your Filing Status
Choose your filing status, which determines your tax rate and any applicable deductions or credits. The common filing statuses include:
- Single: If you are unmarried and have no qualifying dependents.
- Married Filing Jointly: If you are married and you and your spouse are filing a joint return.
- Married Filing Separately: If you are married but choose to file separate returns.
- Head of Household: If you are unmarried, have a qualifying dependent, and pay more than half the cost of maintaining your home.
- Qualifying Widow(er): If your spouse has passed away and you have a dependent child.
Step 4: Calculate Your Income
Accurately report all sources of income for the tax year. This includes wages, salaries, tips, dividends, capital gains, and any other taxable income.
Step 5: Itemize Deductions (if applicable)
If your itemized deductions exceed the standard deduction amount, you may choose to itemize. Itemized deductions can include medical expenses, state and local taxes, mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and more. Calculate and list these deductions to reduce your taxable income.
Step 6: Calculate Taxable Income and Tax Liability
Subtract any deductions and exemptions from your total income to determine your taxable income. Apply the appropriate tax rates and brackets to calculate your tax liability for the year.
Step 7: Apply Credits and Refunds
If you are eligible for tax credits, such as the Child Tax Credit or the Earned Income Tax Credit, apply them to reduce your tax liability. Calculate any overpayments and determine if you are due a refund.
Step 8: Sign and Submit Your Return
Review your tax return for accuracy and completeness. Sign and submit your return electronically or by mail, depending on your chosen filing method.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filing Previous Years’ Taxes
While filing previous years’ taxes can be complex, there are several common mistakes that taxpayers often make. Being aware of these pitfalls can help you avoid potential issues and ensure a smooth filing process.
Mistake 1: Forgetting to File
The most common mistake is simply forgetting to file. It’s crucial to stay on top of your tax obligations and file your returns within the designated deadlines. Late filing can result in penalties and interest charges.
Mistake 2: Misreporting Income or Deductions
Accurate reporting of income and deductions is essential. Misreporting can lead to discrepancies, which may trigger an audit by the IRS. Take the time to carefully review and verify all income and expense records.
Mistake 3: Not Claiming All Eligible Deductions or Credits
Many taxpayers fail to claim all the deductions and credits they are entitled to. It’s important to research and understand the various deductions and credits available to ensure you maximize your tax benefits.
Mistake 4: Failing to Keep Records
Maintaining accurate and organized records is crucial for tax filing. Without proper documentation, it can be challenging to support your claims or defend yourself in the event of an audit.
Conclusion: Benefits and Peace of Mind
Filing previous years’ taxes may seem like a daunting task, but with the right preparation and guidance, it can be a straightforward process. By understanding the importance of filing back taxes, gathering essential documents, and choosing the right filing method, you can ensure compliance with tax laws and potentially unlock financial benefits.
Remember, accurate tax filing provides peace of mind and sets a solid foundation for your financial future. So, take the time to tackle your previous years' taxes, and you'll be rewarded with a sense of accomplishment and the knowledge that your finances are in order.
How far back can I file my taxes?
+You can generally file tax returns for the past three tax years. However, it’s important to note that there may be specific circumstances or exceptions, so it’s advisable to consult with a tax professional or refer to official tax guidelines for accurate information.
Are there any penalties for filing previous years’ taxes late?
+Yes, filing your taxes late can result in penalties and interest charges. The IRS imposes a failure-to-file penalty and a failure-to-pay penalty, which can accumulate over time. It’s important to file your taxes as soon as possible to minimize these penalties.
Can I still file previous years’ taxes if I don’t have all the necessary documents?
+While it’s ideal to have all the necessary documents, you can still file previous years’ taxes even if some documents are missing. In such cases, it’s recommended to contact the relevant institutions or employers to obtain missing forms or information. Additionally, you can estimate values based on available data and update your return once you have the complete information.