Kentucky State Income Tax

When it comes to personal finances and understanding the various tax systems in the United States, one crucial aspect to consider is state-level income taxation. Kentucky, known for its rich history, diverse economy, and vibrant culture, has its own unique approach to taxing its residents' income. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Kentucky's state income tax system, exploring its rates, brackets, deductions, and other essential components.
Unraveling the Kentucky Income Tax Structure

Kentucky operates on a progressive income tax system, which means that as your income increases, so does the tax rate applied to your earnings. This progressive structure aims to ensure fairness and contribute to the state’s overall revenue. Let’s break down the key elements of Kentucky’s income tax system.
Tax Rates and Brackets
The Kentucky income tax system consists of six tax brackets, each with its own tax rate. These brackets are designed to accommodate different income levels, providing a balanced approach to taxation. Here’s a detailed look at the tax rates and the corresponding income brackets for the 2023 tax year:
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate | Income Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2% | 0 - 3,100 |
| 2 | 3% | 3,101 - 4,400 |
| 3 | 4% | 4,401 - 5,700 |
| 4 | 5% | 5,701 - 7,000 |
| 5 | 5.5% | 7,001 - 8,300 |
| 6 | 6% | $8,301 and above |
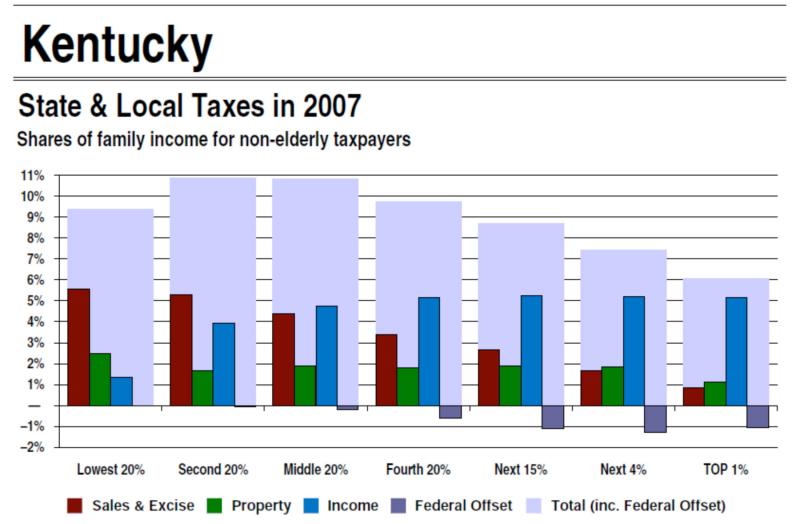
These tax rates are applicable to both single filers and married couples filing jointly. Kentucky's progressive tax system ensures that those with higher incomes contribute a larger portion of their earnings to state revenue, promoting economic fairness.
Taxable Income and Exemptions
Kentucky follows a comprehensive approach to determining taxable income. All sources of income, including wages, salaries, bonuses, commissions, self-employment earnings, and investment income, are generally subject to state income tax. However, certain exemptions and deductions can reduce your taxable income, providing some relief.
One notable exemption is for Social Security benefits. In Kentucky, a portion of Social Security benefits is exempt from state income tax, which can provide significant savings for retirees. The state also offers tax credits and deductions for various expenses, such as education costs, medical expenses, and charitable contributions, which can further reduce your taxable income.
Filing Status and Joint Returns
Kentucky recognizes three filing statuses: single, married filing jointly, and married filing separately. Each status has its own set of rules and considerations when it comes to tax liability. Married couples in Kentucky often benefit from filing jointly, as it can lead to a lower overall tax burden due to the progressive nature of the tax brackets.
For those who are married but choose to file separately, Kentucky treats each spouse as a single filer, applying the single tax rates to their respective incomes. This option may be beneficial in certain situations, such as when one spouse has significantly higher income or when there are complex tax situations involved.
Deductions and Credits
Kentucky offers a range of deductions and credits to help reduce the tax burden on its residents. One of the most significant deductions is the standard deduction, which allows taxpayers to subtract a fixed amount from their taxable income. The standard deduction amount varies based on filing status, and taxpayers can choose between the standard deduction and itemized deductions.
Itemized deductions, on the other hand, allow taxpayers to deduct specific expenses, such as mortgage interest, state and local taxes, charitable contributions, and medical expenses. These deductions can be particularly beneficial for those with significant expenses in these categories.
In addition to deductions, Kentucky provides various tax credits to encourage specific behaviors or support certain populations. For example, the state offers a low-income tax credit, which provides a refund to low-income earners, helping to alleviate the tax burden on those with limited means.
Estimated Tax Payments
If you have substantial income from self-employment, investments, or other sources, you may be required to make estimated tax payments throughout the year. These payments ensure that you are meeting your tax obligations in a timely manner. Kentucky provides guidelines and resources to help taxpayers calculate and make these estimated payments accurately.
Tax Filing and Deadlines
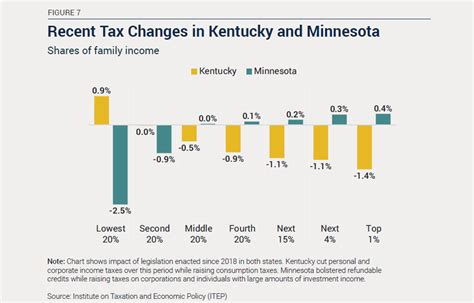
Understanding the tax filing process and deadlines is crucial to ensure compliance with Kentucky’s income tax laws. Here’s a brief overview of the key dates and requirements:
Tax Year and Filing Deadline
The Kentucky tax year aligns with the federal tax year, running from January 1st to December 31st. The deadline for filing your Kentucky income tax return typically aligns with the federal deadline, which is usually April 15th of the following year. However, it’s essential to stay updated with any changes or extensions announced by the Kentucky Department of Revenue.
Electronic Filing and Paper Returns
Kentucky encourages electronic filing of tax returns, as it is more efficient and reduces the risk of errors. The state provides an online filing system, making it convenient for taxpayers to submit their returns digitally. However, if you prefer to file a paper return, Kentucky also accepts traditional mail-in submissions.
Extensions and Payment Plans
In certain circumstances, taxpayers may request an extension to file their Kentucky income tax return. An extension provides additional time to gather necessary information and complete the filing process. However, it’s important to note that an extension to file does not extend the deadline for paying any taxes owed.
If you are unable to pay your entire tax liability by the deadline, Kentucky offers payment plans to help taxpayers manage their obligations. These plans allow for installment payments, providing flexibility and ensuring that taxpayers can fulfill their tax responsibilities over time.
Tax Refunds and Amended Returns
Kentucky aims to process tax refunds promptly, typically within a few weeks of receiving a complete and accurate return. If you are due a refund, you can choose to receive it through direct deposit or by check. It’s essential to ensure that your banking information is accurate to avoid any delays in receiving your refund.
In the event that you need to make changes to a previously filed tax return, you can submit an amended return. Kentucky allows taxpayers to correct errors or update information on their returns, ensuring that your tax liability is accurately calculated.
Future Implications and Tax Reforms
Kentucky’s income tax system is subject to ongoing evaluation and potential reforms. As economic conditions change and new policies are proposed, the state may adjust its tax rates, brackets, or deductions to align with its fiscal goals. Staying informed about these potential changes is crucial for taxpayers to understand how they may impact their future tax obligations.
One notable trend in Kentucky's tax landscape is the discussion surrounding tax reform and simplification. Efforts to streamline the tax code and reduce complexity have been proposed, aiming to make the tax system more efficient and user-friendly. These reforms could impact everything from tax rates to filing processes, so it's essential to stay updated on any significant developments.
Expert Insights and Tax Planning

Conclusion
Understanding Kentucky’s state income tax system is a crucial step in managing your personal finances and ensuring compliance with state laws. By familiarizing yourself with the tax rates, brackets, deductions, and filing requirements, you can navigate the process with confidence. Remember, seeking professional advice and staying updated on tax reforms can further enhance your tax planning efforts.
What is the tax rate for the highest income bracket in Kentucky?
+The highest income bracket in Kentucky for the 2023 tax year is taxed at a rate of 6% for incomes above $8,300.
Are there any special tax credits available in Kentucky for low-income earners?
+Yes, Kentucky offers a low-income tax credit to provide relief to low-income earners. This credit can result in a refund, helping to reduce the tax burden on those with limited means.
Can I file my Kentucky income tax return electronically, and what are the benefits?
+Yes, Kentucky encourages electronic filing of tax returns. Electronic filing is more efficient, reduces the risk of errors, and typically results in faster processing and refund times.
What are the consequences of not paying my Kentucky income taxes on time?
+Failure to pay your Kentucky income taxes on time can result in penalties and interest charges. It’s important to manage your tax obligations to avoid these additional costs and maintain compliance with state laws.
Are there any tax incentives or deductions for investing in Kentucky’s economy?
+Kentucky offers various tax incentives and deductions to encourage investment and economic growth. These may include tax credits for business investments, research and development, and job creation. It’s worth exploring these incentives to optimize your tax strategy.



