Delinquent Property Taxes

Delinquent property taxes are a complex issue that can have significant financial implications for both property owners and local governments. When property owners fail to pay their taxes on time, it can lead to a cascade of consequences, including penalties, legal actions, and potential loss of ownership. This article aims to delve into the world of delinquent property taxes, exploring the causes, consequences, and strategies to navigate this challenging situation.
Understanding Delinquent Property Taxes
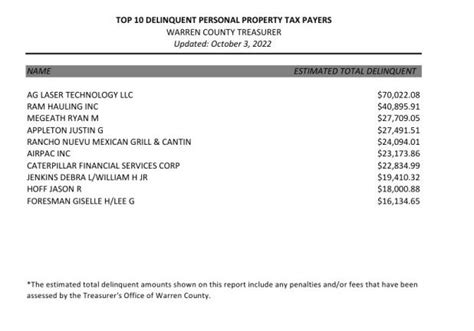
Delinquent property taxes refer to the non-payment or late payment of taxes owed on real estate properties. These taxes are typically levied by local governments and are an essential source of revenue for municipalities, counties, and other governing bodies. Property taxes contribute to the funding of various public services and infrastructure, such as schools, roads, emergency services, and local amenities.
When property owners fail to meet their tax obligations, it not only affects their personal financial standing but also impacts the community as a whole. Delinquent taxes can disrupt the flow of revenue needed to maintain essential services and can lead to budget constraints for local governments.
Causes of Delinquent Property Taxes
Understanding the reasons behind delinquent property taxes is crucial for both property owners and authorities. Here are some common factors that contribute to this issue:
- Financial Hardship: Economic challenges, such as job loss, reduced income, or unexpected expenses, can make it difficult for property owners to meet their tax obligations. In such cases, property taxes may become a lower priority compared to other essential expenses.
- Lack of Awareness: Some property owners may be unaware of their tax responsibilities or the consequences of non-payment. This lack of knowledge can lead to unintentional delinquency.
- Complex Tax Systems: Property tax systems can vary widely across different jurisdictions, and understanding the assessment process and payment schedules may be challenging for property owners, especially those with multiple properties or those new to a particular area.
- Intentional Non-Payment: In some cases, property owners may deliberately choose not to pay their taxes due to disagreements with local authorities, protest against government policies, or as a strategic move in complex legal or financial situations.
- Administrative Issues: Delinquency can also arise from administrative errors, such as incorrect billing addresses, miscommunication between property owners and tax authorities, or delays in processing payments.
Consequences and Implications
The consequences of delinquent property taxes can be far-reaching and impact various aspects of both personal and community life.
- Financial Penalties: Local governments often impose penalties and interest on late tax payments. These additional charges can quickly accumulate, making it even more challenging for property owners to catch up on their tax obligations.
- Legal Actions: In severe cases of delinquency, local authorities may take legal action against property owners. This can include tax liens, which are legal claims on the property to secure payment, or even foreclosure proceedings, resulting in the loss of ownership.
- Impact on Credit: Delinquent property taxes can negatively affect an individual's credit score. Late payments or liens may be reported to credit bureaus, making it difficult for property owners to access future financing or obtain favorable interest rates.
- Community Services: Delinquent taxes can disrupt the funding of essential community services. When local governments face budget shortfalls due to non-payment, they may have to cut back on services or increase taxes for compliant property owners, creating a ripple effect throughout the community.
- Property Value: Unpaid taxes can also impact the value of the property. Potential buyers may be deterred by the presence of tax liens or the uncertainty surrounding the property's ownership status, leading to a decrease in market value.
Navigating Delinquent Property Taxes

Dealing with delinquent property taxes requires a proactive and informed approach. Here are some strategies for property owners and local governments to navigate this challenging situation:
Strategies for Property Owners
- Stay Informed: Understand the property tax assessment process, payment schedules, and any changes in tax rates or policies in your jurisdiction. Stay updated on tax-related communications from local authorities.
- Plan and Budget: Create a financial plan that accounts for property taxes. Include tax payments as a priority expense and consider setting aside funds specifically for this purpose.
- Seek Assistance: If financial hardship is the reason for delinquency, explore options such as tax relief programs, payment plans, or assistance from local non-profit organizations. Many jurisdictions offer relief for low-income homeowners or those facing exceptional circumstances.
- Communicate: If you anticipate difficulties in meeting your tax obligations, reach out to the tax authority early on. Honest communication can lead to potential resolutions or arrangements to avoid penalties.
- Consider Professional Advice: In complex situations, consult with tax professionals or legal experts who can provide guidance tailored to your specific circumstances.
Strategies for Local Governments
- Clear Communication: Ensure that property owners are well-informed about tax obligations, payment schedules, and the consequences of delinquency. Provide clear and accessible information through various channels, including online platforms and community outreach programs.
- Flexible Payment Options: Offer diverse payment methods and consider implementing installment plans or online payment portals to make it easier for property owners to meet their tax commitments.
- Early Intervention: Identify delinquent taxpayers early and reach out proactively. Offering assistance and guidance can help prevent situations from escalating into legal actions.
- Collaborate with Community Partners: Work with local non-profits, financial institutions, and community organizations to raise awareness about property taxes and provide support to property owners facing financial challenges.
- Consider Alternative Revenue Sources: Explore additional revenue streams to reduce the reliance on property taxes alone. This can help alleviate the burden on property owners and provide a more diverse funding base for local services.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
To illustrate the impact and potential solutions for delinquent property taxes, let’s explore some real-world scenarios:
Case Study: Economic Downturn and Delinquency
During the 2008 financial crisis, many property owners in the United States faced significant financial challenges. A study by the National Association of Realtors found that delinquent property taxes increased sharply in areas heavily impacted by the recession. However, jurisdictions that implemented proactive outreach programs and flexible payment plans saw a reduction in delinquency rates, highlighting the importance of timely intervention.
| Jurisdiction | Delinquency Rate Before Intervention | Delinquency Rate After Intervention |
|---|---|---|
| City A | 8.2% | 4.1% |
| County B | 12.5% | 6.7% |
| Town C | 10.3% | 3.9% |
Case Study: Delinquency in Commercial Properties
Delinquency is not limited to residential properties; commercial properties can also face challenges. A report by Commercial Property Tax Insights highlights the impact of delinquent taxes on commercial real estate. In a major city, a significant number of commercial properties were delinquent, leading to a strain on the local economy and a reduction in tax revenue for essential services.
To address this issue, the city implemented a comprehensive outreach program, offering personalized assistance to commercial property owners. By providing tax consultants and streamlined payment processes, the city was able to reduce delinquency rates and improve tax compliance among businesses.
International Perspective: Property Tax Systems
Property tax systems vary widely across different countries. For instance, in Country X, property taxes are assessed based on the value of the property, while in Country Y, they are calculated based on the rental income generated by the property. Understanding these variations is crucial for property owners and investors operating in multiple jurisdictions.
Future Implications and Potential Solutions
As the landscape of property ownership and taxation evolves, several key trends and potential solutions emerge to address delinquent property taxes:
Technology-Driven Solutions
- Digital Payment Platforms: Implementing user-friendly online payment portals can simplify the tax payment process, making it more convenient for property owners to meet their obligations.
- Tax Assessment Automation: Advanced data analytics and machine learning can improve the accuracy and efficiency of tax assessments, reducing administrative errors and potential disputes.
Community Engagement and Education
- Taxpayer Education Programs: Investing in educational initiatives can empower property owners with the knowledge and tools to navigate the tax system effectively.
- Community Forums: Hosting community events and forums where property owners can interact with tax officials and share experiences can foster a sense of collective responsibility and understanding.
Policy Reform and Tax Incentives
- Progressive Tax Structures: Exploring progressive tax systems that consider the ability to pay can reduce the burden on low-income homeowners and encourage compliance.
- Tax Relief Programs: Expanding tax relief initiatives for specific groups, such as veterans, seniors, or those with disabilities, can provide much-needed support and alleviate financial stress.
Conclusion

Delinquent property taxes are a complex issue with far-reaching consequences. By understanding the causes, consequences, and potential solutions, both property owners and local governments can work together to navigate this challenge effectively. Through proactive communication, education, and innovative approaches, a balanced and sustainable tax system can be achieved, ensuring the well-being of communities and the stability of local governments.
What happens if I can’t pay my property taxes on time due to financial hardship?
+If you’re facing financial hardship, it’s important to reach out to your local tax authority. Many jurisdictions offer payment plans or tax relief programs for those in challenging circumstances. Being proactive and communicating your situation can lead to potential solutions and prevent further penalties.
Can I lose my property if I fail to pay property taxes?
+Yes, in severe cases of delinquent property taxes, local governments may take legal action, including placing a tax lien on your property. If the situation remains unresolved, foreclosure proceedings could result in the loss of ownership. It’s crucial to address delinquent taxes promptly to avoid such consequences.
Are there any tax relief programs for senior citizens or low-income homeowners?
+Yes, many jurisdictions offer tax relief programs specifically designed to assist senior citizens, low-income homeowners, and individuals with disabilities. These programs can provide reduced tax rates or exemptions, helping these groups manage their property tax obligations more affordably. Check with your local tax authority to explore these options.
How can I stay informed about property tax changes and deadlines?
+Staying informed is crucial. Keep an eye on official government websites, subscribe to tax-related newsletters, and follow local news sources. Many jurisdictions also offer tax alerts or notification services to keep taxpayers updated on important changes and deadlines.