What Is Tax Designation

Tax designation is a critical aspect of the financial landscape, serving as the backbone of fiscal policy and revenue generation for governments worldwide. It involves the classification and categorization of various entities, activities, and transactions for tax purposes, ensuring that the right individuals and organizations are taxed appropriately. This intricate system of designations plays a pivotal role in maintaining economic stability and funding public services, infrastructure, and social programs.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of tax designation, exploring its definition, purpose, and the diverse categories it encompasses. We will also analyze the implications of tax designation on individuals, businesses, and the broader economy, highlighting its impact on financial planning, investment strategies, and overall economic growth.
Understanding Tax Designation: Definition and Purpose

Tax designation is the process by which governments classify entities and transactions to determine the applicable tax rates and obligations. It serves as a fundamental tool for tax authorities to enforce compliance, prevent tax evasion, and ensure equitable tax collection. By assigning specific designations to taxpayers, governments can tailor tax policies to meet their revenue goals and promote economic fairness.
The primary purpose of tax designation is to establish a systematic and transparent framework for tax assessment and collection. It enables tax authorities to identify the appropriate tax treatment for different entities, such as individuals, businesses, and organizations, based on their unique characteristics and activities. This classification process ensures that taxpayers are aware of their tax obligations and facilitates efficient tax administration.
Moreover, tax designation plays a crucial role in promoting economic efficiency and growth. By distinguishing between different types of taxpayers and transactions, governments can implement targeted tax incentives and policies to stimulate investment, encourage innovation, and support specific sectors of the economy. For instance, tax designations can be used to encourage entrepreneurship, promote sustainable practices, or support industries vital to national development.
Tax Designation Categories: A Comprehensive Overview
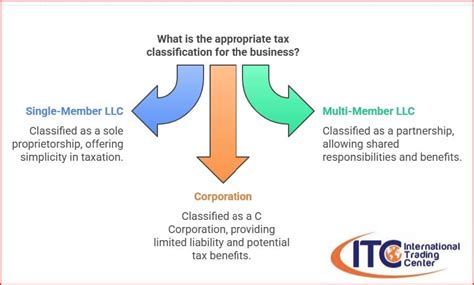
Tax designation encompasses a wide range of categories, each with its own set of rules and regulations. Understanding these categories is essential for taxpayers to navigate the complex world of taxation and ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Individual Tax Designation
Individual tax designation focuses on the classification of individuals based on their income, residence, and personal circumstances. This category includes various tax brackets, tax credits, and deductions that individuals can claim to reduce their taxable income. For instance, taxpayers may be classified as single, married filing jointly, head of household, or qualifying widow(er), each with its own tax rates and benefits.
| Tax Designation | Description |
|---|---|
| Single | Individuals who are not married or do not qualify for other filing statuses. |
| Married Filing Jointly | Spouses filing a joint tax return, combining their incomes and deductions. |
| Head of Household | Unmarried individuals who maintain a household and provide financial support for a qualifying dependent. |
| Qualifying Widow(er) | Taxpayers who have lost their spouse and are eligible for certain tax benefits. |

Additionally, individual tax designation includes classifications based on residency. For example, taxpayers may be considered residents of a particular state or country, which determines their tax obligations at the local or international level. Residency status can also impact the tax treatment of foreign income and assets.
Business Tax Designation
Business tax designation involves classifying businesses based on their legal structure, size, and industry. This category includes sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and limited liability companies (LLCs), each with its own tax implications.
| Business Type | Tax Treatment |
|---|---|
| Sole Proprietorship | Business income is taxed as personal income, and the owner is personally liable for business debts. |
| Partnership | Partners report their share of profits and losses on their personal tax returns, but the partnership itself is not taxed. |
| Corporation | Corporations are taxed separately from their owners, and profits are taxed twice (once at the corporate level and again when distributed as dividends to shareholders) |
| Limited Liability Company (LLC) | LLCs offer flexibility in tax treatment, allowing them to be taxed as sole proprietorships, partnerships, or corporations. |
Business tax designation also considers industry-specific factors, such as tax incentives for research and development, renewable energy, or manufacturing. Additionally, businesses may be classified based on their size, with different tax rules and benefits for small, medium, and large enterprises.
Other Tax Designation Categories
Beyond individual and business tax designation, several other categories exist to address specific situations and entities. These include:
- Trusts and Estates: Tax designation for trusts and estates involves classifying these entities based on their purpose, beneficiaries, and the assets they hold. This category includes tax implications for income, capital gains, and estate planning.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Nonprofit organizations are designated based on their mission, structure, and activities. This classification determines their tax-exempt status and eligibility for various tax benefits.
- International Tax Designation: This category covers the classification of individuals and businesses with cross-border activities, including residency, tax treaties, and transfer pricing regulations.
- Special Tax Designations: Certain entities or activities may be subject to special tax designations, such as tax-favored savings accounts (e.g., IRAs, 401(k)s), education savings plans (e.g., 529 plans), or renewable energy incentives.
The Impact of Tax Designation on Financial Planning and Investment Strategies
Tax designation has a significant influence on financial planning and investment strategies for both individuals and businesses. Understanding the applicable tax designations and their implications is crucial for optimizing tax efficiency and achieving financial goals.
Individual Financial Planning
For individuals, tax designation plays a pivotal role in determining the most advantageous tax strategies. By understanding their tax bracket, credits, and deductions, individuals can make informed decisions about income management, savings, and investments. For example, individuals may choose to maximize contributions to tax-advantaged retirement accounts, such as IRAs or 401(k)s, to reduce their taxable income and grow their savings tax-efficiently.
Additionally, tax designation can impact investment choices. For instance, individuals may opt for tax-efficient investment vehicles, such as municipal bonds or tax-free savings accounts, to minimize the tax burden on their investment returns. Understanding capital gains tax rates and long-term investment strategies can also help individuals optimize their portfolio performance and tax obligations.
Business Financial Planning and Investment Strategies
Businesses face unique tax considerations based on their legal structure and industry. Tax designation influences their financial planning and investment decisions, affecting their overall profitability and growth prospects.
For instance, corporations may consider the tax implications of different financing options, such as debt or equity financing, to minimize their tax burden. They may also explore tax-efficient investment strategies, such as research and development tax credits or investment in renewable energy projects, to reduce their tax liability and enhance their competitive position.
Furthermore, business tax designation can impact strategic decisions, such as mergers and acquisitions, expansions into new markets, or changes in business structure. By understanding the tax implications of these moves, businesses can make informed choices that align with their financial goals and minimize potential tax liabilities.
The Role of Tax Designation in Economic Growth and Development
Tax designation is not merely a regulatory mechanism but also a powerful tool for economic growth and development. Governments use tax designations to shape economic policies, encourage investment, and support specific industries or initiatives.
Tax Incentives and Economic Development
Tax designation allows governments to implement targeted tax incentives to stimulate economic activity. For example, tax credits or deductions may be offered to encourage investment in research and development, renewable energy, or infrastructure projects. These incentives can attract businesses and investors, fostering economic growth and job creation.
Additionally, tax designation can be used to support specific industries or regions. Governments may offer tax breaks or incentives to promote manufacturing, agriculture, or technology sectors, helping to diversify the economy and create sustainable growth.
International Tax Designation and Global Economic Integration
In an increasingly globalized economy, international tax designation plays a critical role in facilitating cross-border trade and investment. Tax treaties and agreements between countries establish rules for taxing income earned in foreign jurisdictions, preventing double taxation, and promoting economic integration.
By establishing clear tax rules for international businesses and investors, governments can attract foreign investment, support international trade, and foster economic cooperation. This integration enhances global economic growth and promotes the exchange of goods, services, and capital across borders.
The Future of Tax Designation: Technological Advancements and Digital Taxation
As technology continues to evolve, tax designation is also experiencing significant transformations. The rise of digital economies, e-commerce, and remote work has presented new challenges and opportunities for tax authorities. Governments are adapting their tax systems to accommodate these changes and ensure that digital activities are taxed appropriately.
One key development is the emergence of digital taxation, which focuses on taxing the digital economy, including online transactions, digital services, and data-driven businesses. This involves addressing issues such as tax avoidance, ensuring a level playing field for traditional and digital businesses, and promoting fair taxation in the digital age.
Furthermore, technological advancements are revolutionizing tax administration. Tax authorities are leveraging data analytics, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technology to enhance tax compliance, streamline tax processes, and improve taxpayer services. These innovations enable more efficient tax collection, reduce administrative burdens, and promote transparency and fairness in taxation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)

How often do tax designations change, and what are the key factors that trigger these changes?
+Tax designations can change periodically due to various factors, including legislative changes, economic conditions, and shifts in tax policies. Key triggers for tax designation changes include amendments to tax laws, adjustments to tax rates, and modifications in tax regulations. Additionally, changes in the economic landscape, such as shifts in industry trends or technological advancements, can also prompt tax authorities to revise tax designations to maintain fairness and efficiency.
What are the potential consequences of misclassifying tax designations for individuals or businesses?
+Misclassifying tax designations can have significant consequences for individuals and businesses. Incorrect tax classification can lead to overpayment or underpayment of taxes, resulting in financial penalties, interest charges, or even legal repercussions. Moreover, misclassification can impact financial planning, investment strategies, and business operations, potentially hindering growth and profitability.
How can individuals and businesses stay updated on the latest tax designation changes and their implications?
+Staying informed about tax designation changes is crucial for individuals and businesses. They can subscribe to tax authority newsletters or alerts, consult with tax professionals or advisors, and regularly review tax regulations and updates provided by government websites or reputable tax resources. Additionally, attending tax seminars, workshops, or webinars can provide valuable insights into the latest tax developments and their implications.
What role do tax advisors or professionals play in assisting individuals and businesses with tax designation-related matters?
+Tax advisors or professionals play a vital role in guiding individuals and businesses through the complex world of tax designation. They possess expert knowledge of tax laws, regulations, and designations, helping clients navigate the tax landscape and make informed decisions. Tax advisors can provide strategic tax planning, assist with tax compliance, and offer advice on tax-efficient financial strategies tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of their clients.
How do tax authorities ensure compliance and enforce tax designation regulations?
+Tax authorities employ various strategies to ensure compliance with tax designation regulations. They conduct audits, investigations, and examinations to verify the accuracy of tax returns and compliance with tax laws. Additionally, tax authorities may impose penalties, interest charges, or legal actions for non-compliance. To promote voluntary compliance, tax authorities also provide educational resources, guidance, and support to taxpayers.
In conclusion, tax designation is a multifaceted and dynamic aspect of the financial landscape, impacting individuals, businesses, and the broader economy. By understanding the intricacies of tax designation and its implications, taxpayers can make informed decisions, optimize their financial strategies, and contribute to economic growth and development. As tax systems continue to evolve, staying informed and adapting to changes is essential for successful financial management and compliance.



