Tax Vs Tariff
Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of the often-misunderstood and highly influential concepts of taxes and tariffs. These two economic instruments play a pivotal role in shaping the financial landscape of nations and can significantly impact businesses and individuals alike. In this article, we will delve deep into the intricacies of taxes and tariffs, offering a nuanced understanding of their definitions, applications, and implications.
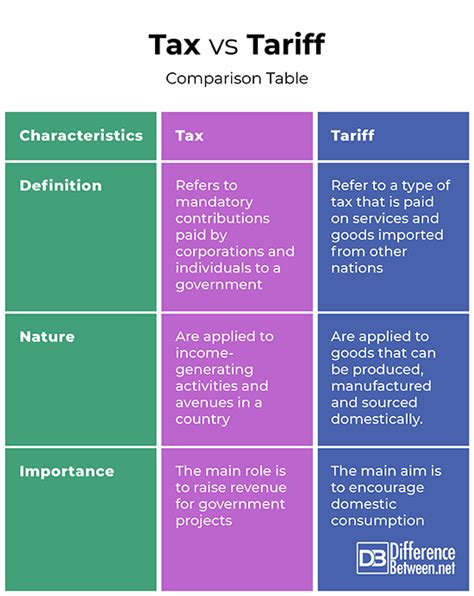
Taxes: The Backbone of Modern Economies

Taxes are mandatory financial charges imposed by a governing body on its citizens or entities within its jurisdiction. These charges are levied on income, goods, services, transactions, and various other economic activities. Taxes are the lifeblood of modern governments, providing the necessary revenue to fund public services, infrastructure development, defense, and social welfare programs. The efficient and equitable collection of taxes is a cornerstone of a functioning economy.
Types of Taxes
Taxes can be categorized into several types, each serving a specific purpose and targeting different economic aspects:
- Income Tax: Perhaps the most well-known, income tax is levied on an individual’s or corporation’s income, including wages, salaries, investments, and business profits. It is a progressive tax, meaning the tax rate increases with higher income levels.
- Sales Tax: Applied to the sale of goods and services, sales tax is typically calculated as a percentage of the transaction value. It is often used to generate revenue for local governments and can be imposed at different rates for different items.
- Property Tax: Imposed on the value of real estate or personal property, property tax is a significant source of revenue for local governments. It is commonly used to fund public services such as education, law enforcement, and infrastructure maintenance.
- Excise Tax: Applied to specific goods or services, such as tobacco, alcohol, gasoline, and luxury items, excise taxes are often used to discourage consumption of certain products or to generate additional revenue.
- Value Added Tax (VAT): A type of consumption tax, VAT is added at each stage of the production and distribution process, with the final consumer bearing the full tax burden. It is widely used in Europe and many other countries.
Tax Administration and Compliance
Tax administration is a complex process involving the creation and enforcement of tax laws, the collection of taxes, and the provision of taxpayer services. Tax authorities, such as the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States, play a critical role in ensuring compliance and enforcing tax regulations. Non-compliance with tax laws can result in penalties, interest charges, and even criminal prosecution.
The Impact of Taxes on Businesses
For businesses, taxes can significantly affect profitability and operational strategies. Corporate tax rates, for instance, can influence investment decisions and the competitiveness of a business in the global market. Additionally, taxes on goods and services can impact pricing strategies and the overall cost structure of a business.
| Tax Category | Average Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Corporate Income Tax | 21 |
| Individual Income Tax (Top Bracket) | 37 |
| Sales Tax (Average) | 7 |
Tariffs: Protecting Industries and Managing Trade

Unlike taxes, which are primarily used to fund government operations, tariffs are a type of tax specifically imposed on imported goods and services. Tariffs are a key tool in international trade, often used to protect domestic industries, generate revenue, and regulate the flow of goods and services across borders.
Types of Tariffs
Tariffs can be classified into two main categories:
- Ad Valorem Tariffs: These tariffs are levied as a percentage of the value of the imported goods. They are the most common type and are easy to administer, as the value of the goods is readily available.
- Specific Tariffs: These tariffs are imposed as a fixed amount per unit of the imported good, regardless of its value. They are often used for goods with stable prices, such as agricultural products.
The Purpose of Tariffs
Tariffs serve several purposes in the global trade landscape:
- Protectionism: By imposing tariffs on imported goods, governments can protect domestic industries from foreign competition, especially when foreign producers have a cost advantage. This can help nurture and support local industries and jobs.
- Revenue Generation: Tariffs are a significant source of revenue for many governments, particularly for developing countries. The revenue collected can be used to fund public services and infrastructure projects.
- Trade Negotiations: Tariffs can be a powerful tool in international trade negotiations. Governments may use the threat of imposing tariffs as a bargaining chip to secure favorable trade agreements or address trade imbalances.
- Quality Control: In some cases, tariffs are imposed to discourage the import of low-quality or unsafe goods, ensuring that only high-quality products enter the domestic market.
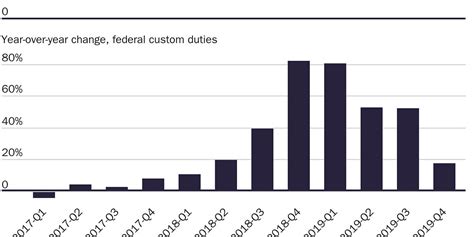
The Impact of Tariffs on Global Trade
The imposition of tariffs can have significant consequences for global trade dynamics. While they can protect domestic industries, they can also lead to retaliatory measures from trading partners, resulting in a cycle of escalating tariffs and potential trade wars. This can disrupt supply chains, increase prices for consumers, and negatively impact economic growth.
| Country | Average Tariff Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| United States | 1.6 |
| European Union | 3.2 |
| China | 4.2 |
The Interplay Between Taxes and Tariffs
While taxes and tariffs are distinct concepts, they are not mutually exclusive. In fact, they often work hand in hand to shape a country’s economic landscape. For instance, a government may use taxes to fund social programs that benefit its citizens while using tariffs to protect domestic industries and manage trade relations.
Tax and Tariff Policies in Action
Consider the case of the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), which replaced the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). The USMCA includes provisions for the auto industry, requiring a certain percentage of a vehicle’s components to be made in North America to qualify for tariff-free status. This not only protects domestic auto industries but also incentivizes investment and job creation in the region.
The Future of Taxes and Tariffs
The landscape of taxes and tariffs is constantly evolving. With the rise of digital economies and the increasing complexity of global supply chains, tax authorities are facing new challenges in ensuring fair and efficient taxation. Similarly, the ongoing negotiations and agreements in the realm of international trade will continue to shape the use and impact of tariffs.
In conclusion, taxes and tariffs are powerful tools that governments use to manage their economies and international relations. Understanding their intricacies is essential for businesses, policymakers, and individuals alike. By navigating the complex world of taxes and tariffs, we can better grasp the economic forces that shape our world.
How do taxes impact economic growth?
+Taxes can impact economic growth positively or negatively. A well-structured tax system can incentivize investment and innovation, leading to job creation and economic expansion. However, excessive or complex tax regimes can hinder growth by increasing compliance costs and discouraging investment.
What are the potential consequences of a trade war sparked by tariffs?
+A trade war can have severe consequences, including disrupted supply chains, increased prices for consumers, and a decline in economic growth. It can also lead to geopolitical tensions and hinder international cooperation.
How do taxes and tariffs affect consumers?
+Taxes and tariffs can increase the cost of goods and services for consumers. For instance, higher taxes on income can reduce disposable income, while tariffs on imported goods can raise the prices of those products.