Tax Manager Salary
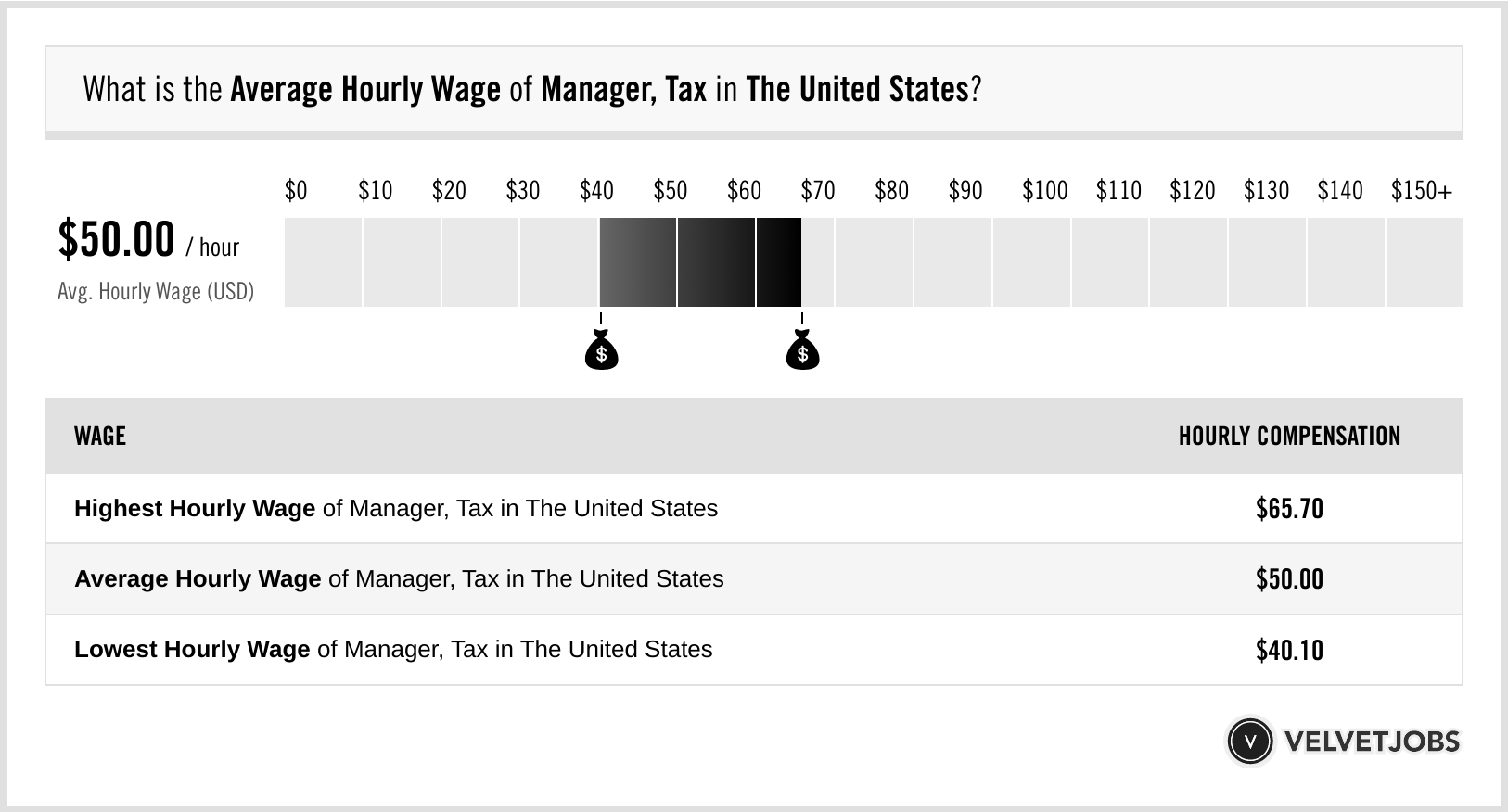
When discussing compensation in the field of tax management, it's important to delve into the intricate details of this specialized profession. Tax managers play a crucial role in businesses and organizations, overseeing complex tax strategies and compliance. Their expertise is highly valued, and their compensation reflects the critical nature of their work. In this article, we will explore the factors influencing tax manager salaries, provide real-world insights, and offer a comprehensive understanding of this aspect of the tax industry.
Understanding the Role of a Tax Manager
A tax manager is a seasoned professional responsible for the strategic management of an organization’s tax obligations. They possess extensive knowledge of tax laws, regulations, and best practices, ensuring that their clients or employers navigate the tax landscape effectively and efficiently. Tax managers are involved in various aspects of tax management, including tax planning, compliance, and advisory services.
In the ever-evolving world of taxation, their role demands a deep understanding of the latest tax reforms, international tax regulations, and industry-specific tax considerations. Tax managers often lead teams of tax professionals, providing guidance and oversight to ensure accurate and timely tax filings. Their expertise extends beyond basic compliance, as they offer strategic tax planning advice to optimize financial outcomes.
Factors Influencing Tax Manager Salaries
The compensation for tax managers can vary significantly based on several key factors. These factors contribute to the complexity of determining an exact salary range for this profession. Let’s explore some of the critical aspects that influence tax manager salaries.
Industry and Sector
The industry in which a tax manager operates plays a significant role in determining their compensation. Different industries have varying tax complexities and requirements. For instance, tax managers working in the finance or technology sectors may command higher salaries due to the intricate tax structures and regulations associated with these industries.
Additionally, the size and nature of the organization also impact tax manager salaries. Larger corporations with complex global operations often require more specialized tax expertise, leading to higher compensation packages. Conversely, smaller businesses or organizations with simpler tax structures may offer more modest salaries.
Experience and Expertise
Experience is a critical factor in tax manager salaries. Tax managers with extensive experience, particularly those who have navigated complex tax scenarios and demonstrated successful outcomes, are highly valued. Their expertise and ability to provide strategic tax advice can significantly impact an organization’s financial health, justifying higher compensation.
Furthermore, specialized knowledge in areas such as international tax, corporate restructuring, or tax litigation can further enhance a tax manager's earning potential. These niche skills are in high demand and often command premium salaries.
Location and Geographic Considerations
The geographic location of a tax manager’s role can have a substantial impact on their salary. Tax regulations and cost of living vary significantly across different regions and countries. For instance, tax managers working in major metropolitan areas or financial hubs may receive higher salaries to account for the higher cost of living and the increased demand for tax expertise in these locations.
Additionally, tax managers working in regions with more stringent tax laws or complex regulatory environments may earn higher salaries due to the specialized knowledge and compliance expertise required.
Employer and Organizational Structure
The type of employer and the organizational structure also influence tax manager salaries. Tax managers employed by large accounting firms or professional services firms may have access to more diverse projects and clients, leading to competitive compensation packages. These firms often have well-established salary structures and offer comprehensive benefits.
On the other hand, tax managers working for smaller boutique firms or consulting agencies may have more flexible compensation structures, often tied to performance and the value they bring to clients. In such cases, bonuses and incentives can be a significant portion of their overall earnings.
Education and Professional Credentials
The educational background and professional certifications of a tax manager can significantly impact their earning potential. Advanced degrees in taxation, accounting, or related fields can enhance their expertise and open doors to higher-paying positions. Additionally, holding professional designations such as Certified Public Accountant (CPA), Chartered Tax Advisor (CTA), or Chartered Accountant (CA) can further boost their salaries.
These credentials not only demonstrate a high level of competence but also signify a commitment to ongoing professional development, which is highly valued by employers.
Real-World Tax Manager Salaries
While the factors mentioned above provide a framework for understanding tax manager salaries, it’s essential to examine real-world data and insights. Below, we delve into specific salary ranges and examples to offer a more concrete understanding of compensation in this field.
Entry-Level Tax Managers
Entry-level tax managers, typically with 1-3 years of experience, can expect starting salaries ranging from 60,000 to 80,000 annually. This range may vary based on the factors discussed earlier, such as industry, location, and the size of the organization. Entry-level tax managers often work under the supervision of more senior professionals, gaining valuable experience and building their expertise.
| Industry | Starting Salary Range |
|---|---|
| Financial Services | $70,000 - $85,000 |
| Manufacturing | $65,000 - $75,000 |
| Retail | $60,000 - $70,000 |

Mid-Level Tax Managers
Mid-level tax managers, with 3-7 years of experience, typically command higher salaries due to their increased expertise and responsibility. Their compensation can range from 80,000 to 120,000 annually. At this stage, tax managers often lead teams, manage complex tax projects, and provide strategic tax planning advice.
| Sector | Mid-Level Salary Range |
|---|---|
| Technology | $90,000 - $110,000 |
| Healthcare | $85,000 - $105,000 |
| Energy | $80,000 - $120,000 |
Senior Tax Managers and Directors
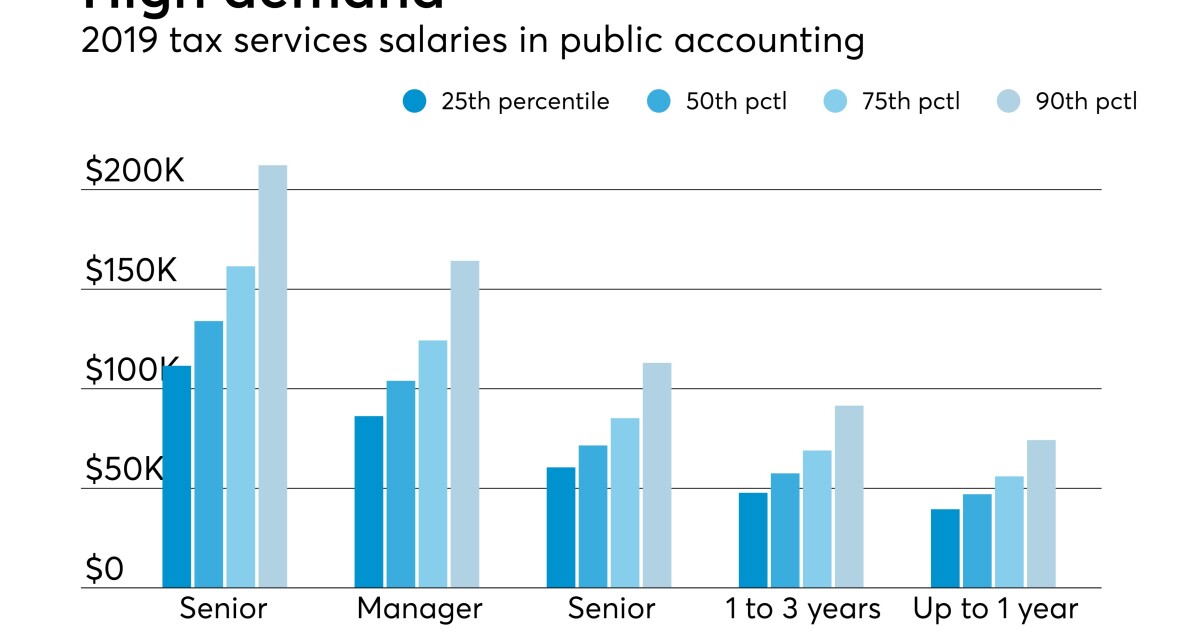
Senior tax managers and directors, with 7+ years of experience, are at the pinnacle of their careers and often oversee critical tax functions within organizations. Their salaries can range from 120,000 to 200,000 annually, with some earning even higher amounts depending on their expertise and the complexity of their roles.
| Position | Salary Range |
|---|---|
| Senior Tax Manager | $130,000 - $180,000 |
| Tax Director | $150,000 - $220,000 |
Performance-Based Compensation and Benefits
Tax managers, particularly those in mid- to senior-level positions, often have compensation packages that include performance-based incentives and benefits. These can include bonuses tied to individual or team performance, profit-sharing plans, and long-term incentive programs.
Additionally, tax managers may receive comprehensive benefit packages that cover healthcare, retirement plans, and other perks. These benefits contribute to the overall compensation package and can significantly enhance the value of their employment.
Future Outlook and Career Progression
The tax management profession is expected to remain in high demand, driven by the continuous evolution of tax laws and regulations. Tax managers with a strong foundation in tax knowledge and a commitment to ongoing professional development will continue to be valued assets for organizations.
Career progression in tax management often involves moving from a generalist role to a more specialized position. Tax managers may choose to focus on specific areas such as international tax, transfer pricing, or tax litigation, allowing them to command higher salaries and take on more complex assignments.
Furthermore, the increasing complexity of global tax landscapes and the rise of digital taxation may present new opportunities for tax managers to innovate and provide cutting-edge tax solutions. Staying abreast of these trends and acquiring relevant skills will be crucial for long-term career success.
Conclusion
Tax manager salaries are influenced by a myriad of factors, including industry, experience, location, and professional credentials. While it’s challenging to pinpoint an exact salary range, the insights and real-world data provided offer a comprehensive understanding of the compensation landscape in this specialized field. Tax managers play a vital role in organizations, and their expertise and strategic insights are highly valued, reflected in their earning potential.
As the tax landscape continues to evolve, tax managers who stay adaptable, acquire specialized knowledge, and provide innovative solutions will remain in high demand, ensuring their careers remain rewarding and lucrative.
How do tax managers stay updated with the ever-changing tax landscape?
+
Tax managers invest in continuous professional development, attending conferences, webinars, and workshops to stay abreast of tax law changes and industry trends. They also leverage technology and subscription services that provide real-time updates on tax regulations.
What skills are essential for tax managers to succeed in their roles?
+
Critical skills for tax managers include a deep understanding of tax laws, strong analytical abilities, excellent communication skills for client interactions, and the ability to stay organized and manage complex projects efficiently.
Are there opportunities for tax managers to work remotely or freelance?
+
Yes, with advancements in technology and the increasing demand for tax expertise, remote work and freelancing opportunities have become more prevalent in the tax management field. Tax managers can explore these options to enjoy flexibility while offering their services to a diverse range of clients.
How do tax managers handle ethical considerations in their practice?
+
Tax managers adhere to strict ethical guidelines and professional standards. They prioritize transparency, integrity, and compliance with tax laws. They also maintain confidentiality and ensure that their advice aligns with the best interests of their clients or employers.