Tax Exempt Interest Income
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of the intriguing concept of tax-exempt interest income, a topic that holds significant importance in the realm of personal finance and tax planning. As an individual or business entity, understanding the nuances of tax-exempt interest can unlock substantial savings and financial benefits. This comprehensive guide will unravel the complexities surrounding this income type, providing you with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions regarding your investments and tax strategies.
Understanding Tax-Exempt Interest Income

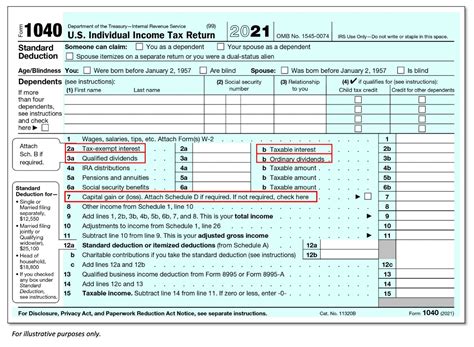
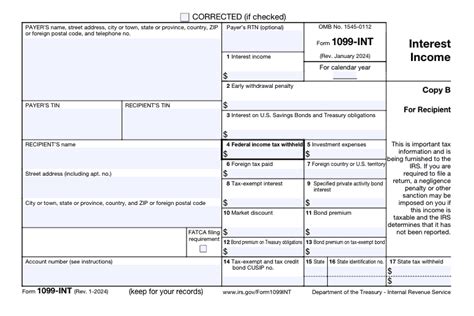
Tax-exempt interest income refers to the earnings generated from investments that are exempt from federal, state, or local taxes. These exemptions are granted by the government to promote specific economic or social objectives, such as supporting municipal infrastructure or encouraging investment in certain sectors. This unique feature makes tax-exempt interest an attractive proposition for investors seeking to maximize their returns while minimizing their tax liabilities.
The primary source of tax-exempt interest income for individuals is municipal bonds, also known as muni bonds. These bonds are issued by state and local governments, as well as their agencies and authorities, to finance various public projects like schools, highways, and public utilities. By investing in these bonds, individuals can enjoy the benefits of both a steady income stream and tax-free growth.
How Tax-Exempt Interest Works
When an investor purchases a municipal bond, they essentially lend money to the issuing government entity in exchange for regular interest payments and the eventual return of their principal investment. The key difference between municipal bonds and other types of bonds lies in the tax treatment of the interest earned. In the case of muni bonds, the interest is exempt from federal income tax, and often from state and local taxes as well, depending on the jurisdiction.
For instance, consider a hypothetical investor, Alice, who purchases a municipal bond issued by the city of New York to fund a new public transportation project. During the bond's term, Alice receives regular interest payments, typically semi-annually, and these payments are free from federal and state taxes. This tax-free status significantly enhances her overall returns, especially when compared to taxable bonds with similar interest rates.
Additionally, the tax-exempt nature of municipal bonds extends to capital gains. If Alice decides to sell her bond before its maturity date, any profits she makes from the sale are also exempt from federal and state taxes. This unique feature further amplifies the attractiveness of tax-exempt interest income for investors seeking to preserve their wealth and minimize their tax burden.
| Tax-Exempt vs. Taxable Interest | |
|---|---|
| Tax-Exempt Interest | Interest earned from investments exempt from federal, state, or local taxes. |
| Taxable Interest | Interest earned from investments subject to federal, state, and local taxes. |
The Benefits of Tax-Exempt Interest Income
The advantages of tax-exempt interest income are multifaceted and can have a profound impact on an investor’s financial portfolio. Here are some key benefits to consider:
Maximized Returns
Tax-exempt interest income offers investors the opportunity to maximize their returns by reducing their tax obligations. This means that a larger portion of their earnings can be reinvested or used for other financial goals, such as retirement planning or funding education expenses.
Stable Income Stream
Municipal bonds, a primary source of tax-exempt interest, are known for their reliability and stability. These bonds are typically backed by the full faith and credit of the issuing government entity, ensuring timely interest payments and principal repayment. This predictability makes tax-exempt interest an attractive option for investors seeking a consistent income stream.
Risk Mitigation
Investing in tax-exempt municipal bonds can provide a level of risk mitigation to an investor’s portfolio. Since these bonds are often backed by the creditworthiness of state and local governments, they are generally considered less volatile than other types of investments. This stability can be particularly beneficial for conservative investors or those seeking to preserve their wealth.
Wealth Preservation
The tax-exempt nature of interest income can play a crucial role in wealth preservation strategies. By avoiding taxes on interest earnings and capital gains, investors can retain a larger portion of their wealth, allowing for more effective estate planning and the preservation of assets for future generations.
Diversification
Tax-exempt interest income can be a valuable component of a well-diversified investment portfolio. By including municipal bonds, investors can reduce their overall portfolio risk while still maintaining a steady income stream. This diversification strategy can help protect against market fluctuations and provide a more stable long-term investment outlook.
Eligibility and Requirements
Not all investors are eligible for tax-exempt interest income, and there are certain requirements and restrictions to be aware of. Here are some key considerations:
Residency
The tax-exempt status of municipal bonds often extends to residents of the state or locality where the bonds are issued. For instance, a New York resident may enjoy tax-exempt status on New York municipal bonds, but the same may not apply to bonds issued by other states. This residency requirement can impact an investor’s eligibility for tax-exempt interest income.
Income Level
Tax-exempt interest income may be subject to limitations based on an investor’s income level. Some states and localities impose income restrictions on who can benefit from tax-exempt interest. For example, high-income earners may find that their tax-exempt status is reduced or eliminated altogether. It’s essential to understand the income thresholds and eligibility criteria in your specific jurisdiction.
Investment Minimums
Investing in municipal bonds often requires a minimum investment amount. These minimums can vary depending on the bond issuer and the type of bond. Investors should be aware of these thresholds to ensure they can meet the investment requirements for tax-exempt interest income.
Holding Period
To qualify for tax-exempt interest, investors may need to hold their municipal bonds for a minimum period. This holding period can vary, but it’s essential to understand the requirements to avoid potential tax consequences. Prematurely selling a municipal bond may result in the loss of tax-exempt status and the need to pay taxes on the interest earned.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While tax-exempt interest income offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to consider the potential risks and limitations associated with this investment strategy.
Limited Investment Options
The universe of tax-exempt investments is relatively limited compared to the broader investment landscape. This limitation can restrict an investor’s ability to diversify their portfolio and may impact their overall investment strategy.
Call Risk
Municipal bonds, like other bonds, are subject to call risk, which is the possibility that the bond issuer will redeem the bond before its maturity date. This can occur when interest rates fall, and the issuer seeks to refinance at a lower rate. Call risk can impact an investor’s expected income stream and capital gains, particularly if the bond is called at a time when market interest rates are low.
Default Risk
While municipal bonds are generally considered low-risk investments, there is still a possibility of default. If a bond issuer experiences financial difficulties or fails to make interest or principal payments, investors may lose some or all of their investment. It’s essential to conduct thorough research and assess the creditworthiness of the issuing government entity before investing.
Limited Liquidity
Municipal bonds, particularly those with longer maturities, may have limited liquidity. This means that it can be challenging to sell these bonds in the secondary market, especially during periods of market volatility. Investors should consider their liquidity needs and ensure that their investment strategy aligns with their financial goals and time horizons.
Tax Implications
While tax-exempt interest income provides significant tax advantages, there are still potential tax implications to consider. For instance, the tax-exempt status of municipal bonds may impact an investor’s eligibility for certain tax credits or deductions. Additionally, if an investor sells a municipal bond at a gain, they may incur capital gains taxes if the bond is not held for the required holding period.
Maximizing Tax-Exempt Interest Income
To make the most of tax-exempt interest income, investors should consider the following strategies and best practices:
Diversify Your Portfolio
While municipal bonds offer tax-exempt interest, it’s essential to maintain a diversified portfolio. Consider including a mix of taxable and tax-exempt investments to balance your overall risk and return profile. This diversification can help mitigate the impact of market fluctuations and provide a more stable investment strategy.
Research and Due Diligence
Conduct thorough research and due diligence before investing in municipal bonds. Assess the creditworthiness of the issuing government entity, understand the bond’s terms and conditions, and analyze the potential risks and returns. This research will help you make informed investment decisions and mitigate potential pitfalls.
Understand Your Tax Situation
Tax-exempt interest income can have a significant impact on your overall tax situation. Work with a qualified tax professional to understand how your tax-exempt investments fit into your broader financial plan. This expertise can help you optimize your tax strategy and ensure compliance with relevant tax laws and regulations.
Consider Bond Funds
Investing in municipal bond funds can provide a convenient and diversified approach to tax-exempt interest income. These funds pool investments from multiple bond issuers, offering a range of maturities and credit qualities. Bond funds can be an attractive option for investors seeking professional management and a more diversified exposure to the municipal bond market.
Stay Informed
Stay updated on the latest developments in the municipal bond market and the tax landscape. Tax laws and regulations can change, impacting the tax-exempt status of your investments. By staying informed, you can adjust your investment strategy as needed and ensure you’re taking advantage of the most current tax benefits.
The Future of Tax-Exempt Interest Income
The future of tax-exempt interest income is closely tied to the economic and political landscape. As governments seek to balance their budgets and meet the needs of their constituents, the tax treatment of municipal bonds may evolve. Here are some potential implications and considerations for the future:
Tax Reform
Tax reform initiatives at the federal, state, and local levels can impact the tax-exempt status of municipal bonds. For instance, proposals to limit or eliminate the tax-exempt status of municipal bonds have been discussed in the past. Investors should stay informed about potential tax reforms and their potential impact on tax-exempt interest income.
Economic Conditions
Economic conditions can influence the demand for municipal bonds and the availability of tax-exempt interest income. During periods of economic growth and low interest rates, municipal bonds may be in high demand, offering investors attractive yields and tax benefits. However, in times of economic downturn or rising interest rates, the appeal of tax-exempt interest may wane.
Alternative Investment Strategies
As the investment landscape evolves, investors may explore alternative strategies to tax-exempt interest income. These strategies could include investing in other asset classes, such as real estate or private equity, which offer different tax treatments and potential benefits. However, it’s essential to carefully assess the risks and returns of these alternatives before making any investment decisions.
Technological Innovations
Advancements in technology and digital platforms may impact the accessibility and efficiency of investing in tax-exempt interest income. Online platforms and robo-advisors, for example, can provide investors with convenient access to municipal bonds and tax-exempt investments. These innovations can streamline the investment process and make tax-exempt interest income more accessible to a broader range of investors.
What is the primary source of tax-exempt interest income for individuals?
+The primary source of tax-exempt interest income for individuals is municipal bonds, also known as muni bonds. These bonds are issued by state and local governments to finance public projects and offer tax-free interest to investors.
How does tax-exempt interest income benefit investors?
+Tax-exempt interest income benefits investors by reducing their tax obligations, maximizing returns, and providing a stable income stream. It also plays a role in wealth preservation and portfolio diversification.
Are there any risks associated with tax-exempt interest income?
+Yes, tax-exempt interest income comes with certain risks, including limited investment options, call risk, default risk, limited liquidity, and potential tax implications. Investors should carefully assess these risks before investing.
How can investors maximize their tax-exempt interest income?
+Investors can maximize their tax-exempt interest income by diversifying their portfolios, conducting thorough research, understanding their tax situation, considering bond funds, and staying informed about market developments and tax reforms.