Seattle Taxes
In the bustling city of Seattle, Washington, taxes play a significant role in shaping the local economy and influencing the lives of its residents. From property taxes to sales taxes, and income taxes, understanding the tax landscape is crucial for individuals, businesses, and investors alike. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricacies of Seattle's tax system, offering an in-depth analysis of its structure, rates, and implications.
The Seattle Tax System: An Overview

Seattle, like many other cities, has a multi-faceted tax system designed to generate revenue for the city’s operations, infrastructure development, and public services. This section provides a high-level overview of the key tax components that make up Seattle’s fiscal framework.
Property Taxes: A Foundation of Revenue
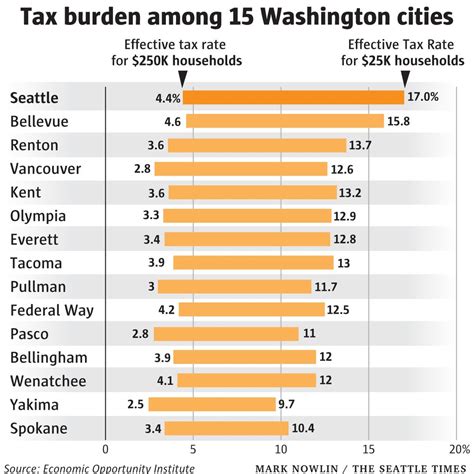
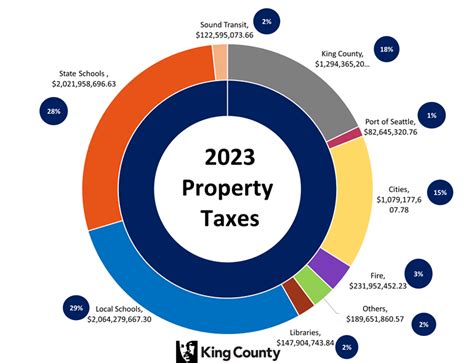
Property taxes are a cornerstone of Seattle’s tax structure, contributing significantly to the city’s revenue stream. These taxes are levied on both real estate and personal property, with rates varying based on the assessed value of the property and its classification.
The City of Seattle utilizes a millage rate system for property taxation. A millage rate, or mill rate, represents the amount per dollar of assessed value that a property owner pays in taxes. For instance, a mill rate of 10 mills would mean that for every 1,000 of assessed value, a property owner would pay 10 in taxes. This rate is determined annually by the city and can vary from one year to the next.
Assessed values are determined through a combination of factors, including the property’s market value, its location, and its use. Properties are reassessed periodically to ensure that the assessed value remains current and reflective of market conditions.
| Property Type | Assessment Ratio | Millage Rate (FY 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Residential | 12% | 6.30 |
| Commercial/Industrial | 12% | 10.00 |
| Timberland | 12% | 3.50 |
Sales and Use Taxes: Capturing Consumer Spending
Sales and use taxes are another crucial component of Seattle’s tax revenue. These taxes are applied to the sale of goods and services, as well as the use or consumption of certain products within the city limits.
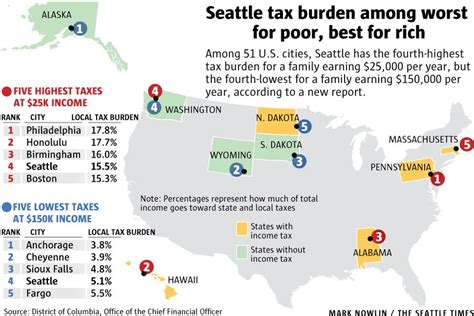
Seattle imposes a combined sales tax rate that includes both state and local taxes. As of 2024, the total sales tax rate in Seattle is 10.1%, which is made up of a 6.5% state tax and a 3.6% local tax. This rate applies to most retail sales, including clothing, electronics, and many services.
Additionally, Seattle levies a Business and Occupation (B&O) tax on businesses operating within the city. This tax is based on the gross receipts or income generated by the business and varies depending on the industry and business type. For example, wholesale businesses pay a rate of 0.484%, while service businesses pay a rate of 0.968% on their gross receipts.
Income Taxes: A Progressive Approach
Seattle, unlike many other states, has its own income tax system, separate from the federal and state levels. This system is designed to be progressive, meaning that higher income earners pay a larger proportion of their income in taxes.
The city’s income tax is structured with four tax brackets, each with its own tax rate. As of 2024, these brackets and rates are as follows:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to 12,000</td> <td>1.1%</td> </tr> <tr> <td>12,001 - 24,000</td> <td>2.2%</td> </tr> <tr> <td>24,001 - 55,000</td> <td>3.3%</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Over 55,000 | 3.9% |
These rates apply to individuals, estates, and trusts. Partnerships and limited liability companies (LLCs) are subject to a flat rate of 2.1% on their net income.
Tax Incentives and Exemptions: Supporting Local Growth
To encourage economic development and support specific industries, Seattle offers a range of tax incentives and exemptions. These initiatives aim to attract businesses, create jobs, and foster innovation within the city.
Business Tax Incentives
Seattle provides various tax incentives to businesses, particularly those in targeted industries or located in designated areas. These incentives can take the form of tax credits, abatements, or deferrals, and are designed to offset certain tax liabilities.
For instance, the Seattle Jobs Initiative offers tax credits to businesses that create new jobs within the city. The program provides a 2,000 credit</strong> for each new full-time job, with a maximum credit of <strong>10,000 per business. This initiative is aimed at encouraging businesses to hire locally and invest in Seattle’s workforce.
Additionally, the Family and Education Levy provides tax incentives for businesses that offer family-friendly benefits to their employees. These benefits can include childcare assistance, dependent care, and education assistance. Businesses that implement such programs are eligible for a tax credit of up to 0.50 per hour worked by an eligible employee</strong>, up to a maximum of <strong>2,000 per year.
Property Tax Exemptions
Seattle also offers property tax exemptions to certain property types or organizations. These exemptions can significantly reduce the tax burden for eligible entities.
One notable exemption is the Exemption for Senior Citizens and Disabled Persons. This exemption reduces or eliminates property taxes for eligible seniors and individuals with disabilities. To qualify, individuals must meet certain income and age criteria, and their primary residence must be located within Seattle city limits.
Additionally, non-profit organizations, such as charities, religious institutions, and educational facilities, may be eligible for a full or partial exemption from property taxes. These exemptions are designed to support the vital work of these organizations and ensure their long-term viability.
The Impact of Seattle’s Tax System
Seattle’s tax system has a profound impact on the city’s economy and its residents. Understanding these effects is crucial for individuals and businesses alike, as it influences financial planning, investment decisions, and overall economic stability.
Economic Growth and Development
Seattle’s tax structure, particularly its progressive income tax and targeted business incentives, has been instrumental in fostering economic growth and development. The city’s ability to attract and retain businesses, especially in tech and innovation sectors, has led to a thriving economy with a diverse range of industries.
The income tax system, with its higher rates for higher earners, ensures that those with greater financial means contribute proportionally more to the city’s revenue. This helps to address income inequality and provides resources for public services and infrastructure improvements that benefit all residents.
Furthermore, the targeted business tax incentives encourage investment in specific industries, such as clean technology, biotechnology, and aerospace, which are key sectors for Seattle’s economic future. These incentives create a competitive advantage for the city, making it an attractive location for businesses seeking to innovate and expand.
Residential Affordability and Equity
Seattle’s tax system also plays a role in addressing residential affordability and equity issues. The city’s property tax system, while providing a significant source of revenue, can also be a burden for homeowners, particularly those on fixed incomes or facing rising property values.
To mitigate this, Seattle offers various property tax relief programs and exemptions, such as the Senior Citizen and Disabled Persons Exemption mentioned earlier. These initiatives help ensure that long-term residents can remain in their homes, even as property values rise. Additionally, the city’s commitment to affordable housing development is partly funded through dedicated property tax levies.
The income tax system also contributes to equity by ensuring that higher-income earners contribute more to the city’s revenue. This revenue is then used to fund social services, affordable housing initiatives, and other programs that support low- and moderate-income residents.
Impact on Businesses
For businesses operating in Seattle, the tax landscape is a critical consideration. The city’s sales and use taxes, while contributing to revenue, can also impact consumer behavior and business profitability.
The progressive nature of Seattle’s income tax system can be both a benefit and a challenge for businesses. On one hand, it ensures that high-income earners, often found in successful businesses, contribute proportionally more to the city’s revenue. On the other hand, it can impact the decision-making process for business owners, particularly when considering expansion or relocation.
However, Seattle’s targeted tax incentives and abatements can be a significant draw for businesses. These incentives provide a competitive advantage, helping businesses offset costs and improve their bottom line. For instance, the Seattle Jobs Initiative encourages businesses to create new jobs, while the Family and Education Levy supports businesses that offer family-friendly benefits, enhancing employee retention and satisfaction.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes
As with any tax system, Seattle’s framework is subject to change based on a variety of factors, including economic conditions, political shifts, and societal needs. Understanding potential future developments is crucial for individuals and businesses looking to plan for the long term.
Potential Tax Reforms
In recent years, there have been discussions and proposals for tax reforms in Seattle, aimed at addressing various issues, such as income inequality, housing affordability, and revenue generation.
One proposed reform is the implementation of a wealth tax, which would tax individuals based on their net worth rather than their income. This could potentially impact high-net-worth individuals and could generate significant revenue for the city, which could be used to address social and economic disparities.
Another proposed reform is the extension of the income tax to capital gains, which are currently not taxed at the city level. This could bring in additional revenue and create a more balanced tax system, as capital gains are often realized by higher-income individuals.
Economic and Social Factors
The economic landscape of Seattle, like any major city, is subject to fluctuations and external influences. Economic downturns or recessions can impact tax revenue, leading to potential budget constraints and adjustments to the tax system.
Additionally, societal needs and priorities can drive changes to the tax system. For instance, if there is a growing demand for affordable housing or improved public transportation, the city may consider implementing dedicated taxes or levies to fund these initiatives.
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has also had a significant impact on Seattle’s economy and tax revenue. As the city continues to recover, the tax system may need to adapt to support businesses and residents affected by the pandemic.
Political Influences
Political dynamics and leadership can greatly influence the direction of Seattle’s tax system. Changes in city leadership or shifts in political ideologies can lead to different priorities and potential tax reforms.
For example, a new administration may prioritize certain social or environmental initiatives, which could result in new taxes or levies to fund these projects. Conversely, a shift towards a more conservative approach could lead to tax cuts or simplified tax structures.
It’s important for residents and businesses to stay informed about political developments and their potential impact on the tax system, as these changes can have significant financial implications.
Conclusion: Navigating Seattle’s Tax Landscape

Seattle’s tax system is a complex and dynamic framework that plays a pivotal role in the city’s economy and the lives of its residents. From property taxes to sales taxes and income taxes, each component contributes to the city’s revenue and influences economic growth, residential affordability, and business operations.
Understanding Seattle’s tax system is crucial for individuals and businesses alike, as it impacts financial planning, investment decisions, and overall economic stability. By staying informed about the city’s tax landscape, residents and businesses can make more informed choices and better navigate the opportunities and challenges that arise.
As Seattle continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic, social, and political landscapes, its tax system will undoubtedly undergo transformations. Staying attuned to these changes will be essential for all stakeholders in the city’s vibrant and ever-evolving economy.
What is the current sales tax rate in Seattle?
+The total sales tax rate in Seattle as of 2024 is 10.1%, which includes a 6.5% state tax and a 3.6% local tax.
Are there any property tax exemptions in Seattle for seniors or veterans?
+Yes, Seattle offers an exemption for senior citizens and disabled persons. To qualify, individuals must meet certain income and age criteria, and their primary residence must be within Seattle city limits.
How does Seattle’s income tax system differ from the state and federal systems?
+Seattle has its own income tax system separate from the state and federal levels. It is structured with four tax brackets, each with its own rate, and offers a partial tax credit for residents who also pay state income tax to reduce potential double taxation.
What are some of the tax incentives available for businesses in Seattle?
+Seattle offers tax incentives to businesses, including the Seattle Jobs Initiative, which provides tax credits for new jobs created, and the Family and Education Levy, which supports businesses offering family-friendly benefits.