Schedule C Tax

Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of the intricacies of Schedule C tax, a critical component of the US tax system for small business owners and the self-employed. Schedule C is a crucial form used to report income and expenses related to a business operated as a sole proprietorship or single-member LLC. This guide will delve into the specifics of Schedule C, its purpose, how to complete it, and its implications for your business's financial health.
Understanding Schedule C: The Basics
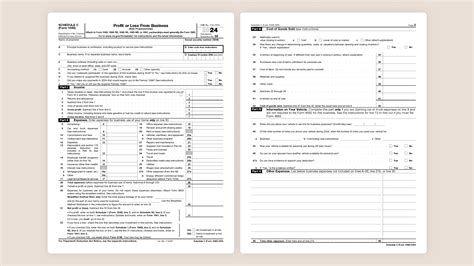
Schedule C, officially known as the “Profit or Loss From Business (Sole Proprietorship)” form, is an integral part of the Internal Revenue Service’s (IRS) tax documentation. It is designed to capture the financial performance of a business, providing a detailed overview of its revenue, expenses, and net profit or loss.
Every self-employed individual or sole proprietor must complete and file Schedule C along with their annual income tax return (Form 1040). This form is the foundation for understanding the financial health and tax obligations of a small business.
Here's a step-by-step breakdown of what Schedule C entails:
- Revenue Reporting: Begin by listing all sources of income generated by your business, including sales, services provided, and any other revenue streams.
- Expense Accounting: Next, you'll itemize all expenses incurred in the course of running your business. This includes everything from office supplies and rent to insurance and vehicle expenses.
- Calculating Profit or Loss: By subtracting your total expenses from your total revenue, you arrive at your net profit (or loss) for the tax year. This figure is a critical indicator of your business's financial performance.
The Importance of Schedule C
Schedule C serves as a financial benchmark for your business, allowing you to track its performance and make informed decisions. It’s also essential for tax purposes, as it determines your business’s tax liability and eligibility for various tax deductions and credits.
Moreover, Schedule C data can be used to apply for loans, secure investments, or negotiate with suppliers and clients. It provides a clear picture of your business's financial standing, which is invaluable when seeking external support or partnerships.
Completing Schedule C: A Step-by-Step Guide

Completing Schedule C accurately is essential to ensure you pay the correct amount of taxes and maintain compliance with IRS regulations. Here’s a detailed guide to help you navigate the process:
Step 1: Gather Your Documents
Before you begin, ensure you have all the necessary documentation. This includes records of your business income, such as sales receipts, invoices, and bank statements. Similarly, gather all expense receipts and records to ensure you can accurately account for all costs associated with your business.
Step 2: Calculate Your Revenue
Start by calculating your total business income. This involves adding up all sources of revenue, including sales, services, interest, and any other income streams directly related to your business operations.
| Revenue Source | Amount |
|---|---|
| Sales Revenue | $[Revenue Amount] |
| Service Income | $[Income Amount] |
| Interest Income | $[Interest Amount] |
| Other Income | $[Other Income Amount] |
| Total Revenue | $[Total Revenue] |
Step 3: Itemize Your Expenses
Now, it’s time to list all your business expenses. This step is critical to ensuring you maximize your tax deductions and minimize your tax liability.
| Expense Category | Amount |
|---|---|
| Office Supplies | $[Office Supplies Amount] |
| Rent/Lease | $[Rent/Lease Amount] |
| Insurance | $[Insurance Amount] |
| Advertising/Marketing | $[Marketing Amount] |
| Utilities | $[Utilities Amount] |
| Vehicle Expenses | $[Vehicle Expenses Amount] |
| Travel/Meals | $[Travel/Meals Amount] |
| Depreciation | $[Depreciation Amount] |
| Other Expenses | $[Other Expenses Amount] |
| Total Expenses | $[Total Expenses] |
Step 4: Calculate Your Net Profit or Loss
Subtract your total expenses from your total revenue to determine your net profit or loss. If your expenses exceed your revenue, you have a net loss. Conversely, if your revenue exceeds expenses, you have a net profit.
Net Profit or Loss: $[Net Profit/Loss]
Step 5: Transfer Data to Form 1040
Once you’ve calculated your net profit or loss, transfer this figure to your Form 1040. Schedule C is an integral part of your tax return, and this step ensures your business income and expenses are accurately reflected in your overall tax liability.
Common Mistakes and Pitfalls to Avoid
Completing Schedule C can be complex, and there are several common mistakes that business owners should be aware of to avoid potential penalties or audits.
Inaccurate Record-Keeping
Maintaining meticulous records is crucial. Inaccurate or incomplete records can lead to errors in your revenue and expense calculations, which may result in underreporting income or overstating expenses.
Failure to Itemize Expenses
Failing to account for all eligible expenses is a common oversight. Every legitimate business expense can be deducted, so ensure you capture all relevant costs, from office supplies to travel expenses.
Mixing Personal and Business Expenses
It’s essential to keep personal and business finances separate. Mixing these expenses can lead to complications when filing Schedule C. Ensure you have a clear understanding of which expenses are strictly business-related and which are personal.
Overlooking Special Deductions
The IRS offers various deductions and credits specifically for small businesses. These can significantly reduce your tax liability. Some common deductions include the home office deduction, vehicle expenses, and healthcare costs.
Maximizing Your Deductions and Credits
Understanding how to maximize your deductions and credits is key to minimizing your tax liability. Here are some strategies to consider:
Home Office Deduction
If you operate your business from a dedicated home office, you may be eligible for the home office deduction. This deduction allows you to deduct a portion of your home expenses, such as rent, mortgage interest, utilities, and maintenance, based on the percentage of your home used for business purposes.
Vehicle Expenses
If you use a vehicle for business purposes, you can deduct expenses related to its operation and maintenance. This includes fuel, repairs, insurance, and depreciation. Keep detailed records of your business mileage to accurately calculate these deductions.
Healthcare Costs
Healthcare expenses related to your business, such as health insurance premiums, can be deducted. This can be a significant tax savings, especially for self-employed individuals.
Other Deductions and Credits
Explore other deductions and credits specific to your industry or business activities. These may include research and development credits, startup costs, and certain business investments.
Conclusion: Schedule C and Your Business Strategy

Schedule C is more than just a tax form; it’s a vital tool for understanding and managing your business’s financial health. By accurately completing Schedule C, you gain valuable insights into your business’s performance and can make informed decisions to improve its financial standing.
Furthermore, Schedule C plays a critical role in your tax strategy. By maximizing deductions and credits, you can significantly reduce your tax liability, freeing up resources for business growth and expansion. Remember, every business is unique, so consult with a tax professional to ensure you're taking full advantage of the deductions and credits available to you.
FAQ
Can I deduct personal expenses on Schedule C?
+No, you should not deduct personal expenses on Schedule C. Schedule C is specifically for business-related expenses. Mixing personal and business expenses can lead to complications and potential audits. Keep your finances separate to avoid any issues.
What if I have a net loss on Schedule C?
+A net loss on Schedule C means your business expenses exceeded your revenue for the year. This can have tax implications, as you may be able to carry over the loss to offset future profits. Consult a tax professional to understand how to handle a net loss and its potential benefits.
Can I deduct startup costs on Schedule C?
+Yes, certain startup costs can be deducted on Schedule C. These include expenses incurred while setting up your business, such as legal fees, business licenses, and marketing costs. However, there are specific rules and limits for deducting startup costs, so consult a tax advisor for guidance.
Do I need to attach Schedule C to my tax return?
+Yes, you must attach Schedule C to your tax return (Form 1040). Schedule C is an integral part of your tax documentation, providing a detailed breakdown of your business income and expenses. Ensure you complete Schedule C accurately and attach it to your tax return to avoid any issues.
Can I e-file Schedule C with my tax return?
+Yes, you can e-file Schedule C along with your tax return. Many tax preparation software programs allow you to complete and e-file Schedule C directly. This can save time and reduce the risk of errors compared to manual filing. However, always review your return carefully before submitting it.