7 Key Facts About Sales Tax in Miami You Need to Know
Miami's vibrant economy and bustling retail landscape make understanding sales tax crucial for both consumers and businesses. As a hub for tourism, commerce, and cultural diversity, Miami’s sales tax policies reflect its economic dynamism and local government strategies. Whether you're a business owner navigating compliance or a visitor trying to budget accurately, having a thorough grasp of the key facts surrounding Miami’s sales tax system is essential. This article embarks on a detailed exploration of these critical points, grounded in the latest legal frameworks, economic data, and practical considerations, to empower stakeholders with expert knowledge and actionable insights.
Comprehensive Overview of Miami’s Sales Tax System
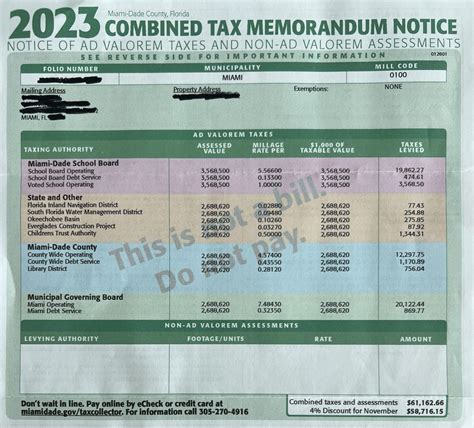
Miami, part of Miami-Dade County, operates within the broader fiscal context of Florida, which sets the foundational state sales tax rate. However, local jurisdictions like Miami-Dade County have the authority to impose additional sales taxes, resulting in distinctive tax rates that reflect local revenue needs and policy priorities. The confluence of state and local taxes creates a layered structure that impacts retail prices, compliance obligations, and economic planning.
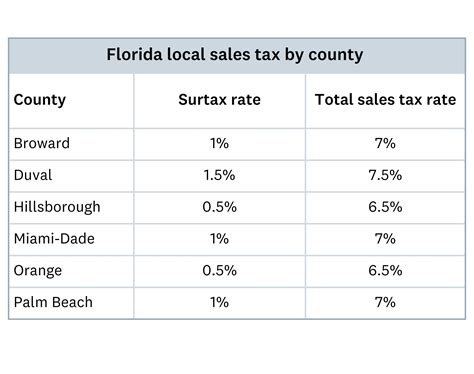
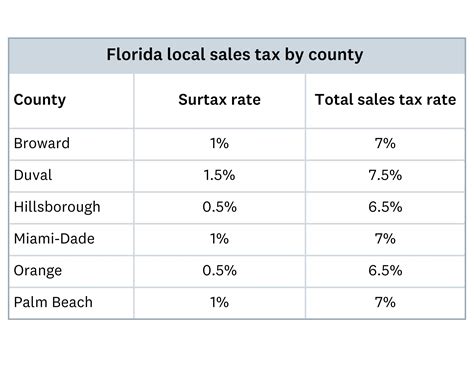
Florida’s statutory baseline sales tax rate is currently 6%, but in Miami-Dade County, the total rate can rise to approximately 7.5% when combining state, county, and discretionary sales surtaxes. This nuanced rate structure exemplifies the importance of localized tax policies in shaping economic activity. Accurate knowledge of these rates is vital, particularly given the rapid growth of Miami’s tourism and service sectors, which are heavily influenced by sales tax regulations.
The process of establishing and modifying sales tax rates involves legislative processes at both the state and county levels, with public input and economic assessments guiding each change. Notably, Miami’s sales tax policies are periodically reviewed to adapt to economic shifts and infrastructure projects. This dynamic environment underscores the importance of staying current with legal updates, as even minor rate adjustments can significantly impact retail margins and consumer spending patterns.
Key Facts About Miami’s Sales Tax Rate and Jurisdictional Variations
Understanding the Official Sales Tax Rate in Miami
The nominal sales tax rate in Miami is approximately 7.5%, blending Florida’s base 6% with local surtaxes designed to fund specific community projects and infrastructure. This composite rate is among the higher figures in Florida, reflecting Miami’s status as a major metropolitan and economic center. Retailers must ensure accurate application at the point of sale, considering both state and local component rates.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| State sales tax rate | 6.00%, applied statewide |
| Miami-Dade county surtax | 1.50%, designated for local projects |
| Total combined rate | Approximately 7.5% in Miami |

Jurisdictional Nuances and Special Tax Districts
Miami’s local taxation extends beyond broad county surtaxes, encompassing specific districts aimed at funding transit, tourism promotion, and community development. For instance, the Miami Beach Special Taxing District imposes additional charges on select hospitality services, reflecting a strategic approach to taxation that targets revenue sources linked directly to tourism-driven sectors.
Moreover, certain retail sectors, such as alcohol and tobacco sales, may attract additional excise taxes or special local levies. Businesses engaged in these sectors must stay acutely aware of these jurisdictional nuances, which can vary even within Miami-Dade County, affecting pricing strategies and profit margins.
Legal Framework Governing Sales Tax Collection and Remittance in Miami
The legal underpinnings for sales tax collection in Miami are embedded in Florida statutes and local ordinances. The Florida Department of Revenue (FDOR) provides comprehensive guidelines and enforces compliance, with specific registration, reporting, and remittance procedures designed to streamline tax collection and reduce errors. Miami’s local tax authorities often coordinate with the FDOR but retain authority over enforcement within their jurisdictions.
Generally, all retail businesses selling tangible personal property or certain digital goods must register for a sales tax permit with the FDOR. Once registered, they are responsible for collecting the relevant sales tax at the time of each transaction, maintaining accurate records, and submitting payments on a scheduled basis—monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on their volume of sales.
Critical legal considerations include understanding taxable items, exemptions, and proper documentation. For example, certain food items, prescription medications, and educational materials may be exempt from some or all sales taxes in Miami, necessitating precise application to avoid penalties or audits.
Impacts of Sales Tax on Miami’s Business Ecosystem and Consumer Behavior
Economic Impacts on Local Retail and Hospitality Sectors
The cumulative sales tax rate directly influences pricing strategies, profit margins, and shopper behavior. In Miami’s competitive hospitality and retail markets, small fluctuations in tax rates can tilt consumer preferences, especially in price-sensitive segments like souvenirs, dining, and apparel. High tax rates can sometimes dampen spontaneous purchases but can be offset by targeted marketing and value-added services.
For business owners, strategic location choices—such as operating in districts with lower tax rates or leveraging tax exemptions—are increasingly relevant. Additionally, understanding the tax implications of online sales, particularly with the growth of e-commerce, is vital, as remote sellers must navigate sales tax nexus issues and establish compliance accordingly.
Consumer Spending Patterns and Tax-Driven Budgeting
On the consumer side, awareness of Miami’s sales tax impacts their purchasing decisions. Tourists, in particular, often underestimate local taxes, leading to budget miscalculations. Therefore, accurate knowledge and clear communication about total costs—including taxes—are vital for retailers to build trust and ensure satisfaction.
Research indicates that the presence of higher sales taxes can influence spending behavior, prompting some consumers to delay purchases or seek alternatives in jurisdictions with lower rates. This behavior underscores the strategic importance of regulatory clarity and transparent pricing for maintaining Miami’s commercial vitality.
Recent Trends and Future Outlook for Miami’s Sales Tax Policies

Miami’s fiscal policies are subject to ongoing review, influenced by economic growth, demographic shifts, and infrastructural investments. Recent initiatives include proposals for increased surtaxes to fund transportation upgrades and affordable housing programs—an indication of the region’s commitment to sustainable urban development.
Looking ahead, the trend suggests a cautious calibration of tax rates to balance revenue needs against economic competitiveness. Local governments are increasingly exploring digital platforms to enhance tax collection efficiency, leveraging technology to reduce evasion and streamline reporting processes.
Moreover, with the expansion of Miami’s tourism and international trade sectors, the sales tax system may evolve to accommodate new services and digital goods, requiring continuous adaptation by businesses and policymakers alike. Such developments highlight the importance of staying informed through reliable sources and professional advisement.
Key Points
- Miami’s combined sales tax rate averages around 7.5%, integrating state and local surtaxes.
- Jurisdictional nuances create diverse tax implications across districts, influencing pricing and compliance strategies.
- Legal frameworks mandate meticulous registration, collection, and remittance processes for retailers.
- Sales tax rates shape consumer behavior and strategic decisions within Miami’s bustling economy.
- Future policy shifts rely on economic conditions and infrastructural priorities, emphasizing ongoing regulatory vigilance.
What is the current sales tax rate in Miami?
+The total sales tax rate in Miami is approximately 7.5%, combining Florida’s 6% state rate with a 1.5% county surtax specific to Miami-Dade County.
Are there any specific exemptions in Miami’s sales tax system?
+Yes, certain items such as prescription medications, groceries, and educational materials may be exempt from sales tax. Businesses should consult Florida’s guidelines and local ordinances to identify specific exemptions.
How do local districts influence Miami’s sales tax?
+Local districts, including tourism promotion and infrastructure enhancement zones, impose additional levies that increase the overall sales tax rate for specific sectors or areas, impacting retail pricing and visitor expenditure.
What are the responsibilities of businesses regarding sales tax in Miami?
+Businesses are required to register with the Florida Department of Revenue, collect the correct amount of sales tax on taxable sales, maintain detailed records, and remit taxes according to the scheduled periods to ensure legal compliance.
How might Miami’s sales tax policies evolve in the future?
+Future developments could include increased surtaxes for infrastructure projects, digital service taxation, and adjustments influenced by economic growth. Policymakers are actively considering these actions to fund urban development while maintaining economic competitiveness.