State Of Alabama Sales Tax
The State of Alabama, located in the southeastern region of the United States, implements a sales tax system that plays a significant role in its revenue generation and economic landscape. Understanding the intricacies of Alabama's sales tax is crucial for businesses operating within the state and for individuals interested in the state's economic policies.
Overview of Alabama Sales Tax
Alabama’s sales tax is a consumption tax imposed on the sale of tangible personal property and certain services within the state. It is a crucial source of revenue for the state government, funding various public services and infrastructure projects. The tax is administered by the Alabama Department of Revenue, which oversees its collection, distribution, and compliance.
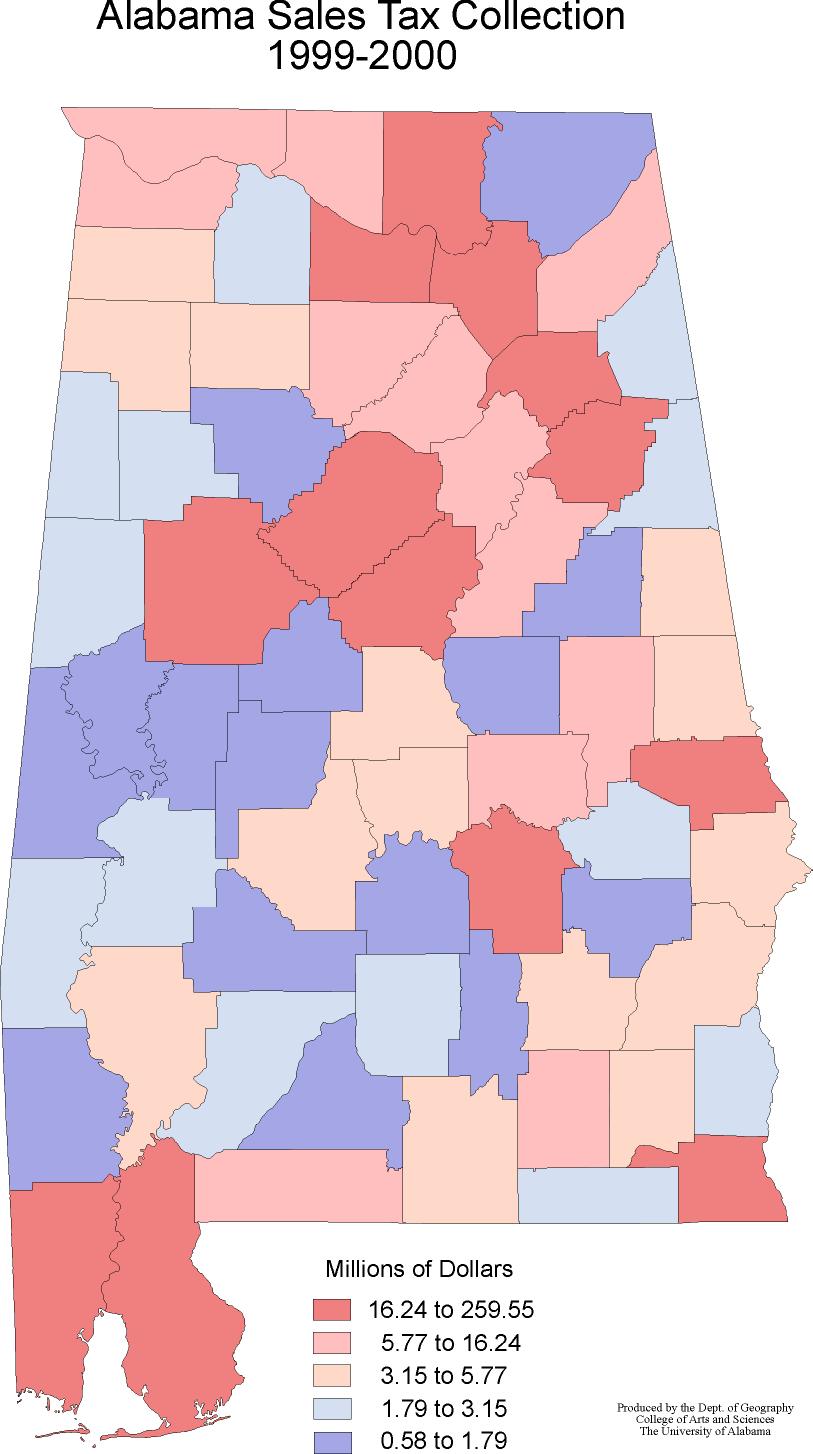
The state sales tax rate in Alabama is currently set at 4%, making it one of the lower state-level sales tax rates in the United States. However, it is important to note that local governments, counties, and municipalities can also levy their own sales taxes, resulting in a combined rate that varies across the state.
| State Sales Tax Rate | 4% |
|---|---|
| Combined Rate (State + Local) | Varies by Location |
Taxable Items and Exemptions
Alabama’s sales tax applies to a wide range of goods and services, including retail sales, leases, rentals, and certain services. Some common taxable items include clothing, electronics, groceries, restaurant meals, and admission fees. However, certain items are exempt from sales tax, such as most prescription medications, select medical devices, and some agricultural products.
Additionally, Alabama offers specific exemptions for certain industries and sectors. For instance, manufacturing and wholesale businesses may qualify for tax exemptions or reduced rates on certain purchases. These exemptions are designed to promote economic growth and support specific industries within the state.
Registration and Compliance
Businesses operating in Alabama are required to register with the Alabama Department of Revenue to obtain a sales tax permit. This permit allows businesses to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state. It is crucial for businesses to understand their sales tax obligations and to accurately calculate and remit the tax to avoid penalties and legal issues.
The Alabama Department of Revenue provides resources and guidelines to assist businesses in complying with sales tax regulations. This includes information on tax rates, filing deadlines, and record-keeping requirements. Businesses must maintain accurate records of sales transactions to facilitate accurate tax reporting and audits.
Sales Tax Distribution and Usage

The revenue generated from Alabama’s sales tax is distributed to various state funds and local governments. The state allocates a portion of the sales tax revenue to the Education Trust Fund, which supports public education in Alabama. This includes funding for schools, teacher salaries, and educational programs.
Local governments, such as counties and municipalities, also receive a share of the sales tax revenue. This funding is crucial for local infrastructure projects, public safety, and community development initiatives. The distribution of sales tax revenue to local governments helps ensure that essential services are provided to residents across the state.
Impact on Local Economies
Alabama’s sales tax system has a significant impact on local economies. The variation in combined sales tax rates across the state can influence consumer behavior and business decisions. Areas with lower combined rates may attract more businesses and consumers, leading to increased economic activity and job creation.
Additionally, sales tax revenue can drive local development projects. For example, a portion of the sales tax revenue may be earmarked for specific infrastructure improvements, such as road construction or public transportation upgrades. These investments can enhance the quality of life for residents and attract further economic growth.
Special Tax Districts
Alabama also utilizes special tax districts to support specific initiatives or projects. These districts are designated areas where an additional sales tax is imposed to fund particular endeavors. For instance, a sales tax increment district may be established to finance the redevelopment of a specific neighborhood or to support a major public project.
Special tax districts provide a targeted approach to funding and can help accelerate economic development in specific regions. However, it is essential for businesses operating within these districts to understand the additional tax obligations and how they contribute to the designated projects.
Future Outlook and Potential Reforms
As Alabama’s economy continues to evolve, there are ongoing discussions and proposals for sales tax reforms. One area of consideration is the potential expansion of sales tax to include additional services and digital products. With the growing digital economy, some advocate for extending the sales tax to online transactions to ensure a level playing field for brick-and-mortar businesses.
Additionally, there are proposals to streamline and simplify the sales tax system to reduce administrative burdens for businesses. This may involve harmonizing tax rates across the state or implementing a uniform tax rate with additional local option taxes for specific projects.
Potential Benefits and Challenges
Expanding the sales tax base to include more services and online transactions could provide a more stable revenue stream for the state. It would also help address the shifting consumer behavior towards digital purchases. However, implementing such reforms may face challenges, including resistance from businesses and consumers, as well as the need for updated infrastructure and systems to administer the expanded tax base.
Simplifying the sales tax system could benefit businesses by reducing compliance costs and complexity. It would also make it easier for consumers to understand and calculate their tax obligations. However, harmonizing tax rates or implementing uniform rates may require careful consideration to ensure that local governments and communities are not negatively impacted by reduced revenue streams.
Conclusion
Alabama’s sales tax system is a critical component of the state’s revenue generation and economic development. While the current system has its strengths and challenges, ongoing discussions and proposals for reform indicate a commitment to evolving the tax landscape to meet the changing needs of the state’s economy.
As Alabama continues to adapt to the digital age and navigate economic shifts, finding the right balance between generating sufficient revenue and supporting local economies will be crucial. The state's approach to sales tax reform will shape its economic future and influence the business environment for years to come.
What is the current state sales tax rate in Alabama?
+
The current state sales tax rate in Alabama is 4%.
How are sales tax rates determined in Alabama?
+
Sales tax rates in Alabama are determined at the state level and can vary at the local level. The state sales tax rate is set by the Alabama Legislature, while local governments, counties, and municipalities can impose additional sales taxes to fund specific projects or initiatives.
Are there any sales tax exemptions in Alabama?
+
Yes, Alabama offers specific sales tax exemptions for certain items and industries. Common exemptions include prescription medications, select medical devices, and agricultural products. Additionally, manufacturing and wholesale businesses may qualify for tax exemptions or reduced rates on certain purchases.
How can businesses comply with Alabama’s sales tax regulations?
+
Businesses operating in Alabama must register with the Alabama Department of Revenue to obtain a sales tax permit. This permit allows businesses to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state. Businesses should stay updated on tax rates, filing deadlines, and record-keeping requirements to ensure compliance. The Alabama Department of Revenue provides resources and guidelines to assist businesses in understanding their sales tax obligations.
How is Alabama’s sales tax revenue distributed and utilized?
+
Alabama’s sales tax revenue is distributed to various state funds and local governments. A portion of the revenue goes to the Education Trust Fund, supporting public education. Local governments also receive a share of the sales tax revenue, which is crucial for funding local infrastructure projects, public safety, and community development initiatives.