Sales Tax Georgia

Sales tax in Georgia is a critical aspect of the state's fiscal landscape, influencing not only the financial obligations of its residents but also the broader economic dynamics and consumer behavior within the state. Understanding the nuances of Georgia's sales tax system is essential for businesses, consumers, and policymakers alike. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the complexities, providing an in-depth analysis of the rates, exemptions, collection processes, and economic implications of sales tax in Georgia.
Understanding the Basics of Sales Tax in Georgia

Sales tax in Georgia is a consumption tax levied on the sale of goods and certain services within the state. It is a crucial revenue stream for the state government, contributing significantly to its annual budget. The tax is typically added to the purchase price of taxable items at the point of sale, and it is the responsibility of the retailer to collect and remit this tax to the Georgia Department of Revenue.
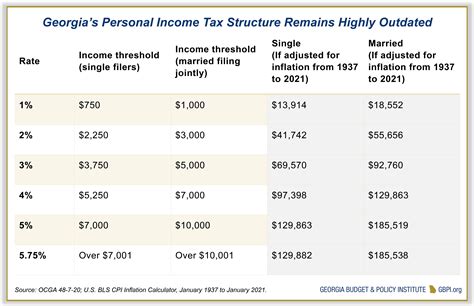
The current sales tax rate in Georgia is 4%, which is applied uniformly across the state. This rate is applicable to most retail sales, including tangible personal property and certain services. However, it is important to note that the total sales tax rate a consumer pays can vary depending on the location of the purchase, as counties and municipalities can impose additional local sales taxes on top of the state rate.
Local Sales Tax Variations
Georgia allows for the imposition of local option sales taxes, which can be added to the state sales tax rate. These local taxes are often used to fund specific projects or initiatives within a particular county or city. As a result, the total sales tax rate can differ significantly depending on the location of the purchase.
| Location | Local Sales Tax Rate | Total Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Atlanta | 3.9% | 7.9% |
| Savannah | 3.0% | 7.0% |
| Athens | 2.0% | 6.0% |

The above table provides a glimpse into the local sales tax variations across different cities in Georgia. These rates are subject to change, and it is always advisable to check with the relevant local authorities for the most up-to-date information.
Exemptions and Special Cases
While most retail sales are subject to sales tax, Georgia does provide exemptions for certain items and transactions. These exemptions are designed to promote specific policy objectives, such as encouraging economic development or supporting essential services.
- Groceries: Many staple food items, including bread, milk, and eggs, are exempt from sales tax. This exemption is intended to reduce the tax burden on essential goods and promote food security.
- Prescription Drugs: Sales of prescription medications are exempt from sales tax, ensuring that necessary healthcare items are more affordable for Georgia residents.
- Industrial Machinery: Sales of industrial machinery and equipment used in manufacturing processes are often exempt to encourage industrial growth and competitiveness.
However, it is important to note that the exemption landscape is complex and subject to change. It is always recommended to consult official sources or tax professionals for the most accurate and up-to-date information on sales tax exemptions in Georgia.
The Role of Sales Tax in Georgia’s Economy
Sales tax plays a pivotal role in Georgia’s economy, influencing consumer spending patterns, business operations, and government fiscal policies. Understanding its impact is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and consumers alike.
Impact on Consumer Spending
The sales tax rate directly affects the purchasing power of consumers. A higher sales tax rate can deter consumers from making discretionary purchases, potentially leading to a decline in retail sales. Conversely, a lower rate can stimulate consumer spending, particularly for big-ticket items. For example, a consumer might choose to delay a significant purchase if the sales tax rate increases, impacting the timing and volume of sales for businesses.
Effect on Business Operations
Businesses in Georgia must navigate the complexities of sales tax collection and remittance. This includes registering with the Georgia Department of Revenue, calculating the appropriate tax rate for each transaction, and accurately reporting and paying the collected taxes. The administrative burden of sales tax compliance can be significant, particularly for small businesses with limited resources. Moreover, businesses must stay abreast of any changes in sales tax laws and rates to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
Government Revenue and Fiscal Policy
Sales tax is a vital source of revenue for the state government, funding essential services and infrastructure projects. The revenue generated from sales tax helps finance public education, healthcare, transportation, and other critical public services. The state’s ability to set and adjust sales tax rates provides a degree of flexibility in fiscal policy, allowing for adjustments in response to economic conditions or policy priorities.
Sales Tax Collection and Compliance
The process of collecting and remitting sales tax is a critical responsibility for businesses operating in Georgia. Understanding the intricacies of this process is essential for ensuring compliance and avoiding potential penalties.
Registration and Reporting
Businesses must register with the Georgia Department of Revenue to obtain a sales and use tax certificate of registration. This certificate authorizes the business to collect and remit sales tax. The registration process typically involves providing basic business information, such as the legal name, address, and contact details. Once registered, businesses are assigned a unique account number, which is used for all tax-related transactions and correspondence.
Businesses are required to report and remit sales tax on a regular basis, typically on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis, depending on the volume of sales. The reporting process involves calculating the total sales tax collected during the reporting period, completing the appropriate tax forms, and submitting the payment by the due date.
Sales Tax Calculation and Remittance
Calculating the correct sales tax rate for each transaction can be complex, especially in areas with varying local tax rates. Businesses must ensure that they apply the correct rate based on the location of the sale. This often involves maintaining detailed records of sales transactions, including the date, location, and amount of each sale.
Remitting the collected sales tax is a critical responsibility. Businesses must ensure that they pay the correct amount by the due date to avoid penalties and interest. The payment process typically involves logging into the Georgia Department of Revenue's online portal, verifying the calculated tax amount, and making the payment using a credit card, electronic funds transfer, or other approved methods.
Future Implications and Policy Considerations
Sales tax in Georgia is subject to ongoing policy discussions and potential changes. Understanding the future implications and considerations can help stakeholders prepare for potential shifts in the tax landscape.
Potential Rate Changes
The sales tax rate in Georgia is subject to legislative review and potential adjustments. While the current rate of 4% has remained stable for several years, there have been proposals to either increase or decrease the rate to address fiscal challenges or promote economic development. Stakeholders, including businesses and consumers, should stay informed about any proposed changes and their potential impact.
Expanding Exemptions
There is ongoing debate about expanding sales tax exemptions to promote specific policy objectives. For example, there have been discussions about exempting certain renewable energy technologies or promoting the sales tax exemption for groceries to include a wider range of food items. Such exemptions can have a significant impact on consumer behavior and business operations, making them a critical consideration for policymakers.
Exploring Alternative Tax Structures
Georgia, like many states, is exploring alternative tax structures to enhance revenue generation and promote economic fairness. One potential alternative is a value-added tax (VAT), which is a consumption tax similar to sales tax but with a different collection and remittance process. A VAT can be more efficient in terms of administration and may provide a broader tax base. However, implementing a VAT would require significant legislative and administrative changes, and its potential impact on businesses and consumers would need careful consideration.
Conclusion
Sales tax in Georgia is a complex yet critical component of the state’s fiscal and economic landscape. Understanding the rates, exemptions, collection processes, and economic implications is essential for businesses, consumers, and policymakers. By staying informed and engaged, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of sales tax and contribute to a vibrant and sustainable economic environment in Georgia.
How often do sales tax rates change in Georgia?
+Sales tax rates in Georgia can change periodically, often as a result of legislative actions. While the state sales tax rate has remained stable at 4% for several years, local sales tax rates can change more frequently, particularly when there are changes in county or municipal budgets or when new initiatives require funding.
Are there any online resources for businesses to stay updated on sales tax changes in Georgia?
+Yes, the Georgia Department of Revenue provides an online resource center with up-to-date information on sales tax rates, exemptions, and other relevant tax topics. This includes news updates, tax guides, and tools to help businesses stay compliant. The website is a valuable resource for businesses to stay informed about any changes in sales tax laws and regulations.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with sales tax regulations in Georgia?
+Non-compliance with sales tax regulations in Georgia can result in significant penalties. These may include late payment penalties, interest charges on unpaid taxes, and even criminal charges in cases of deliberate tax evasion. It is crucial for businesses to stay compliant to avoid these penalties and maintain a good standing with the Georgia Department of Revenue.