Punishment For Tax Evasion

Tax evasion is a serious offense that carries significant legal consequences. It is an act of deliberate deception or omission aimed at avoiding the payment of taxes owed to the government. The implications of tax evasion extend beyond financial penalties, as it undermines the foundation of a fair and equitable tax system, impacting society as a whole. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of tax evasion, including its definition, common methods, and the severe punishments that individuals and businesses may face for committing this crime.
Understanding Tax Evasion: Definition and Methods

Tax evasion, also known as tax fraud, is a criminal act that involves the intentional misrepresentation or concealment of financial information to avoid paying taxes. It is a deliberate attempt to deceive tax authorities and evade one’s legal obligations. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) defines tax evasion as “the illegal attempt to evade the assessment or collection of a tax imposed by federal law.”
There are numerous methods employed by individuals and entities to evade taxes. Some common tactics include:
- Underreporting Income: This is perhaps the most prevalent form of tax evasion. It involves intentionally failing to report all sources of income or underreporting the actual amount earned. For instance, a business owner might omit cash transactions from their records or a freelancer might fail to declare all of their earnings.
- Overstating Deductions: Taxpayers may attempt to inflate their deductions by claiming false or exaggerated expenses. This reduces their taxable income and, consequently, the amount of tax owed.
- Falsifying Records: Manipulating financial records is another tactic used to evade taxes. This can involve creating fake invoices, altering bank statements, or fabricating documents to support false claims.
- Hiding Assets: Some individuals or businesses hide their assets to avoid paying taxes on them. This can be done by transferring assets to offshore accounts, using shell companies, or even concealing cash in secret locations.
- Falsifying Returns: Tax evasion can also occur when individuals or businesses file false tax returns. This includes providing incorrect information, such as claiming non-existent dependents or business expenses.
- Illegal Tax Schemes: There are various illegal tax schemes and scams that promise to help individuals avoid paying taxes. These schemes often involve complex structures and are designed to mislead tax authorities.
It is important to note that tax evasion is distinct from tax avoidance, which is the legal use of tax laws and regulations to reduce one's tax liability. Tax evasion, on the other hand, is an illegal activity that carries severe consequences.
Punishments for Tax Evasion: A Comprehensive Overview

The punishment for tax evasion can be severe, as governments around the world take a firm stance against those who attempt to circumvent their tax obligations. The penalties are designed to deter potential offenders and maintain the integrity of the tax system. Here is an overview of the punishments commonly associated with tax evasion:
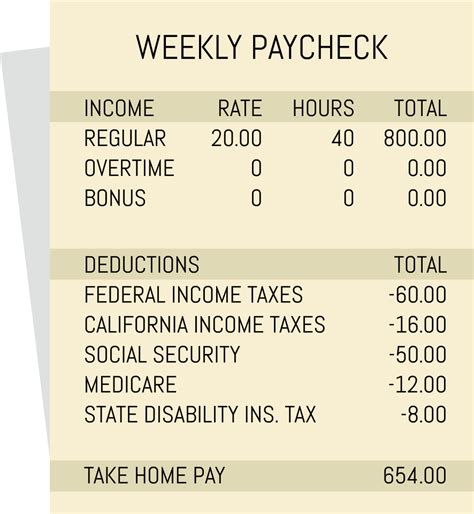
1. Financial Penalties
The most common form of punishment for tax evasion is financial penalties. These penalties can be substantial and often include the following components:
- Back Taxes: Tax evaders are typically required to pay the full amount of taxes they owed, including any interest accrued during the period of evasion.
- Fines: In addition to back taxes, individuals and businesses found guilty of tax evasion may face significant fines. These fines can be a percentage of the evaded taxes or a flat rate determined by the jurisdiction.
- Civil Penalties: Tax authorities may impose civil penalties for various tax-related offenses, including evasion. These penalties can be substantial and are designed to deter future non-compliance.
For example, in the United States, the IRS has the authority to impose a penalty of up to 75% of the evaded tax liability. This penalty, known as the "civil fraud penalty," is applicable when the taxpayer has intentionally attempted to evade taxes.
2. Criminal Charges and Imprisonment
Tax evasion is not only a financial matter; it is also a criminal offense. Depending on the severity and nature of the offense, individuals or businesses found guilty of tax evasion may face criminal charges and imprisonment. The specific penalties vary by jurisdiction, but here are some common consequences:
- Criminal Prosecution: Tax evaders may be subject to criminal prosecution, which can result in a criminal record and potential jail time. The severity of the punishment depends on factors such as the amount of taxes evaded and the intent of the offender.
- Jail Sentence: In many countries, tax evasion is considered a felony offense. Convicted individuals can face prison sentences ranging from a few months to several years. The length of the sentence often correlates with the amount of taxes evaded and the offender's prior criminal history.
- Probation and Community Service: In some cases, especially for first-time offenders or those who cooperated with authorities, the court may impose probation instead of imprisonment. Probation can include conditions such as regular reporting to a probation officer, community service, or participation in financial counseling programs.
It is important to note that tax evasion is often investigated and prosecuted by specialized agencies or departments within the government. These agencies, such as the IRS in the United States or HM Revenue and Customs in the United Kingdom, have the expertise and resources to detect and pursue tax evasion cases.
3. Legal and Professional Consequences
Tax evasion can have far-reaching consequences beyond financial penalties and criminal charges. It can also impact an individual’s or business’s legal and professional standing:
- Loss of Professional Licenses: Certain professions, such as accountants, lawyers, and financial advisors, require licenses to practice. If found guilty of tax evasion, these professionals may face the revocation or suspension of their licenses, effectively ending their careers in that field.
- Reputation Damage: Tax evasion can severely damage an individual's or business's reputation. The public disclosure of tax evasion charges or convictions can lead to loss of trust from clients, partners, and the community, making it difficult to conduct business or maintain a positive public image.
- Bankruptcy and Business Closure: The financial penalties associated with tax evasion can be devastating for businesses. In some cases, the accumulated fines and back taxes may lead to bankruptcy and the closure of the business.
4. International Cooperation and Extradition
In an increasingly globalized world, tax evasion often extends beyond national borders. Governments have recognized the need for international cooperation to combat this crime effectively. Here are some ways in which international collaboration can impact tax evaders:
- Information Exchange: Many countries have entered into agreements for the exchange of tax-related information. This allows tax authorities to share information about individuals or entities suspected of tax evasion, making it more difficult for tax evaders to hide their assets or income across borders.
- Offshore Account Disclosure: In recent years, there has been a global effort to crack down on offshore tax havens. Countries are now requiring individuals and businesses to disclose their offshore accounts and assets, making it harder for tax evaders to hide their wealth.
- Extradition: In cases where tax evaders flee to another country to avoid prosecution, extradition treaties can facilitate their return to face justice in their home country. This ensures that tax evaders cannot escape the consequences of their actions by seeking refuge in foreign jurisdictions.
5. Voluntary Disclosure Programs
In an effort to encourage individuals and businesses to come forward and disclose their tax evasion activities, many governments offer voluntary disclosure programs. These programs provide an opportunity for taxpayers to rectify their tax affairs without facing criminal charges. Here’s how they work:
- Disclosure Process: Individuals or businesses can voluntarily disclose their previously unreported income or assets to tax authorities. This typically involves filing amended tax returns and paying the taxes owed, along with interest and potential penalties.
- Benefits of Voluntary Disclosure: By participating in these programs, taxpayers can avoid criminal prosecution and reduce the financial penalties they would otherwise face. It provides an opportunity to come clean and resolve their tax issues while minimizing the legal and financial consequences.
- Time Limits: Voluntary disclosure programs often have specific time limits or deadlines by which taxpayers must come forward. Missing these deadlines may result in the loss of the benefits offered by the program and potential criminal charges.
It is important to consult with legal and tax professionals to understand the specific voluntary disclosure programs available in your jurisdiction and the potential benefits and limitations they offer.
6. The Role of Whistleblowers
Whistleblowers play a crucial role in detecting and prosecuting tax evasion cases. They are individuals who come forward with information about tax evasion activities, often from within an organization or as a result of personal knowledge. Here’s how whistleblowers contribute to the fight against tax evasion:
- Providing Evidence: Whistleblowers can provide valuable evidence and insider knowledge about tax evasion schemes, helping tax authorities build strong cases against offenders. This evidence can be crucial in securing convictions and recovering evaded taxes.
- Incentives for Whistleblowers: Many jurisdictions have implemented whistleblower reward programs to encourage individuals to come forward with information about tax evasion. These programs offer monetary rewards, a percentage of the recovered taxes, to whistleblowers who provide information that leads to successful prosecutions.
- Anonymity and Protection: To encourage whistleblowing, governments often provide anonymity and protection to individuals who report tax evasion. This ensures that whistleblowers can come forward without fear of retaliation or harm.
Whistleblower programs have proven to be effective in uncovering complex tax evasion schemes and bringing perpetrators to justice. They are an essential tool in maintaining the integrity of the tax system and ensuring that tax evaders are held accountable.
Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of Tax Evasion and Punishments
To further illustrate the severity of tax evasion and the punishments that can be imposed, let’s examine a few real-life case studies:
Case Study 1: The Al Capone Example
Al Capone, the notorious American gangster, is often associated with tax evasion. Despite his involvement in various criminal activities, including bootlegging and organized crime, it was tax evasion that ultimately led to his downfall. In 1931, Capone was convicted of tax evasion and sentenced to eleven years in prison. This case served as a powerful reminder that even the most powerful and influential individuals are not above the law when it comes to tax evasion.
Case Study 2: A High-Profile Celebrity
In recent years, a well-known celebrity faced tax evasion charges. This individual, who shall remain unnamed for legal reasons, was accused of failing to report millions of dollars in income and using offshore accounts to hide assets. The case gained significant media attention and resulted in a lengthy legal battle. Ultimately, the celebrity was found guilty and faced a substantial fine, along with community service and a period of probation.
Case Study 3: Corporate Tax Evasion
Corporate tax evasion is a significant concern for governments worldwide. One notable case involves a large multinational corporation that was accused of using complex tax structures and transfer pricing to minimize its tax liability. The company was found guilty of tax evasion and faced hefty fines, as well as negative public scrutiny. This case highlights the efforts of governments to crack down on corporate tax evasion and ensure that businesses pay their fair share.
Preventing Tax Evasion: Strategies and Recommendations
To prevent tax evasion and promote compliance with tax laws, governments and individuals can implement various strategies. Here are some recommendations:
1. Education and Awareness
Promoting tax literacy and awareness is crucial in preventing tax evasion. Governments and tax authorities should invest in educational campaigns to inform taxpayers about their rights and responsibilities. Clear and accessible information about tax laws, reporting requirements, and the consequences of tax evasion can help individuals make informed decisions and avoid potential pitfalls.
2. Simplification of Tax Systems
Complex tax systems can create opportunities for evasion. Governments should strive to simplify tax laws and regulations, making them more transparent and easier to understand. A simplified tax system can reduce the likelihood of intentional evasion and minimize the potential for confusion or errors.
3. Strengthening Tax Enforcement
Governments should allocate adequate resources to tax enforcement agencies to enhance their ability to detect and prosecute tax evasion. This includes investing in technology, training tax auditors and investigators, and ensuring they have the necessary tools to identify and investigate suspicious activities.
4. International Cooperation
As tax evasion often transcends borders, international cooperation is essential. Governments should continue to strengthen their collaborative efforts by signing tax information exchange agreements, sharing best practices, and coordinating their efforts to combat cross-border tax evasion.
5. Ethical Business Practices
Businesses play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the tax system. They should adopt ethical business practices and ensure that their tax affairs are conducted transparently and in compliance with the law. Implementing internal controls and conducting regular tax audits can help identify potential areas of non-compliance and address them proactively.
Conclusion: The Impact of Tax Evasion and the Importance of Compliance

Tax evasion is a serious crime that undermines the foundation of a fair and just society. The punishments for tax evasion are designed to deter potential offenders and maintain the integrity of the tax system. From financial penalties to criminal charges and legal consequences, the implications of tax evasion are far-reaching.
By understanding the methods of tax evasion and the severe punishments that follow, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions and choose to comply with tax laws. Compliance not only ensures that everyone pays their fair share but also contributes to the overall well-being of society by funding essential public services and infrastructure.
As we strive for a more equitable and just society, it is crucial to recognize the importance of tax compliance and the role it plays in building a stronger and more prosperous community. By working together and adhering to tax laws, we can create a system that benefits everyone and ensures a brighter future for generations to come.
What is the maximum penalty for tax evasion?
+The maximum penalty for tax evasion can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the severity of the offense. In some cases, individuals or businesses found guilty of tax evasion may face imprisonment, fines, and additional financial penalties. It is important to consult the specific laws and regulations of your country to understand the potential consequences.
Can tax evasion charges be reduced or avoided through negotiation?
+In certain circumstances, tax evasion charges may be reduced or resolved through negotiation with tax authorities. This often involves voluntary disclosure programs, where taxpayers come forward and cooperate with authorities to rectify their tax affairs. However, the outcome of negotiations can vary, and it is advisable to seek professional legal and tax advice.
What are the signs that an individual or business may be engaging in tax evasion?
+Signs of tax evasion can include inconsistent financial records, unexplained wealth, suspicious offshore activities, or a pattern of underreporting income. Tax authorities often use advanced analytics and data mining techniques to identify potential tax evasion cases. If you suspect tax evasion, it is best to report it to the appropriate authorities.
Are there any circumstances where tax evasion is considered a lesser offense?
+In some cases, tax evasion may be considered a lesser offense if it is the result of an honest mistake or an unintentional oversight. However, the distinction between an honest mistake and intentional evasion can be complex and depends on the specific circumstances and intent of the taxpayer. It is essential to seek professional advice to understand the potential consequences.
How can individuals and businesses ensure tax compliance and avoid tax evasion charges?
+To ensure tax compliance and avoid tax evasion charges, individuals and businesses should maintain accurate financial records, report all income, and claim legitimate deductions. Seeking professional tax advice and staying informed about tax laws and regulations can help prevent potential issues. Additionally, being proactive in rectifying any errors or discrepancies can demonstrate good faith and mitigate potential penalties.