Paycheck After Taxes Texas
When it comes to understanding your paycheck after taxes in the state of Texas, there are several factors to consider. Texas has a unique tax landscape compared to many other states, as it does not impose a personal income tax on its residents. However, there are still various deductions and withholdings that can impact your take-home pay. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the details of paycheck deductions in Texas, providing you with valuable insights to navigate your financial situation effectively.
Understanding Paycheck Deductions in Texas

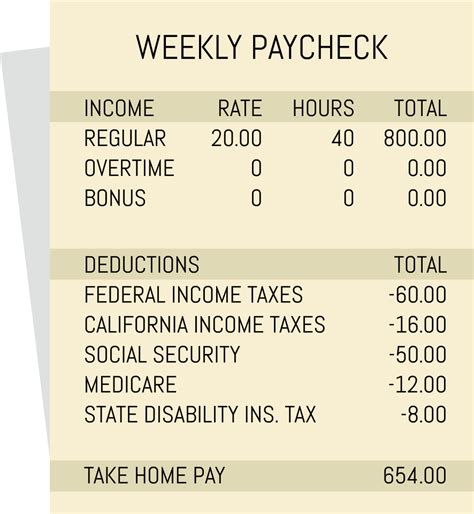
In Texas, the primary sources of paycheck deductions are federal income tax, Social Security and Medicare taxes, and potential state and local taxes, despite the absence of a personal income tax at the state level. Let’s break down each of these deductions and explore how they affect your take-home pay.
Federal Income Tax Withholding
Federal income tax is a significant deduction from your paycheck, and it is determined by your tax filing status, income level, and the number of allowances claimed on your W-4 form. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) uses tax brackets to calculate the amount of federal income tax you owe. These brackets range from 10% to 37%, and your income determines which bracket you fall into.
It’s important to note that Texas residents are still subject to federal income tax laws. Therefore, it is crucial to understand your federal tax obligations and ensure accurate withholding to avoid surprises at tax time. The IRS provides a tax withholding estimator to help you determine the appropriate number of allowances to claim on your W-4.
Social Security and Medicare Taxes
Social Security and Medicare taxes are mandatory deductions from your paycheck, regardless of your state of residence. These taxes fund the Social Security and Medicare programs, which provide benefits to eligible individuals. The Social Security tax rate is currently set at 6.2% for employees, while the Medicare tax rate is 1.45%. Together, these deductions amount to 7.65% of your taxable income.
It’s worth mentioning that employers also contribute an equal amount of Social Security and Medicare taxes on behalf of their employees. This means that, in total, 15.3% of your taxable income is dedicated to these programs.
Potential State and Local Taxes
While Texas does not impose a personal income tax, some local jurisdictions within the state may have their own taxes. These can include local income taxes, sales taxes, or property taxes. It is essential to research and understand the tax landscape in your specific area to accurately calculate your overall tax obligations.
For example, some cities in Texas, such as Austin and El Paso, have a local sales tax that is added to the state sales tax. Understanding these local taxes is crucial when budgeting and planning your financial affairs.
| Tax Category | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Federal Income Tax | 10% to 37% (varies based on income) |
| Social Security Tax | 6.2% |
| Medicare Tax | 1.45% |
| Potential Local Taxes | Varies by jurisdiction (e.g., sales tax, property tax) |
Optimizing Your Paycheck After Taxes

Understanding your paycheck deductions is the first step towards optimizing your financial situation. Here are some strategies to consider to make the most of your take-home pay in Texas:
Review Your W-4 Form
The W-4 form is a crucial document that determines the amount of federal income tax withheld from your paycheck. It is essential to review and update your W-4 regularly to ensure accurate withholding. The IRS provides a W-4 calculator to help you determine the appropriate number of allowances based on your personal circumstances.
Maximize Tax-Advantaged Accounts
Texas residents can take advantage of various tax-advantaged accounts to reduce their taxable income and increase their take-home pay. These accounts include:
- 401(k) Plans: Contribute to your employer-sponsored 401(k) plan, if available. These contributions are made on a pre-tax basis, reducing your taxable income and lowering your federal income tax liability.
- Traditional IRA: If you are eligible, consider contributing to a traditional Individual Retirement Account (IRA). Contributions to a traditional IRA may be tax-deductible, depending on your income and whether you or your spouse has access to a retirement plan at work.
- Health Savings Account (HSA): If you have a high-deductible health plan, you may be eligible to contribute to an HSA. HSAs offer triple tax advantages: pre-tax contributions, tax-free growth, and tax-free withdrawals for qualified medical expenses.
Utilize Tax Credits and Deductions
Research and take advantage of any applicable tax credits and deductions when filing your federal and, if applicable, local tax returns. These can significantly reduce your tax liability and increase your refund. Some common tax credits and deductions include:
- Child Tax Credit: If you have qualifying children, you may be eligible for the Child Tax Credit, which can provide a significant reduction in your tax liability.
- Education Credits: The American Opportunity Tax Credit and the Lifetime Learning Credit can help offset the cost of higher education expenses.
- Deductions for Charitable Contributions: If you donate to qualified charities, you may be able to deduct these contributions from your taxable income.
Stay Informed and Seek Professional Advice
The tax landscape can be complex, and it is essential to stay informed about any changes or updates that may impact your financial situation. Consider subscribing to reputable tax-related newsletters or following trusted financial advisors and experts to stay up-to-date.
Additionally, if you have complex financial circumstances or specific questions, it is always beneficial to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor. They can provide personalized advice and ensure you are taking advantage of all available tax benefits and strategies.
How does Texas’s lack of personal income tax affect my take-home pay compared to other states?
+Texas’s absence of a personal income tax means that residents generally have a higher take-home pay compared to states with income tax. This can provide significant financial benefits, especially for higher-income earners. However, it’s important to consider the overall cost of living and other local taxes when comparing states.
Are there any potential disadvantages to Texas’s tax structure?
+While Texas’s tax structure offers benefits, there may be potential disadvantages. The lack of a personal income tax can result in less funding for state programs and services, which may impact the quality of public services and infrastructure. Additionally, the reliance on sales and property taxes can disproportionately affect lower-income individuals.
What is the best way to ensure accurate tax withholding on my paycheck?
+To ensure accurate tax withholding, it is crucial to review and update your W-4 form regularly. The IRS provides resources, such as the Tax Withholding Estimator and W-4 Calculator, to help you determine the appropriate number of allowances. Additionally, staying informed about any changes in your personal circumstances, such as marriage, childbirth, or job changes, can help you adjust your withholding accordingly.