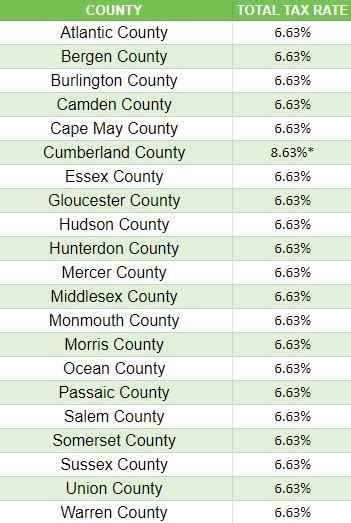
Property Taxes Indiana
Understanding property taxes is crucial for homeowners and potential buyers, especially in the context of Indiana, a state known for its vibrant communities and diverse real estate market. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of property taxes in Indiana, shedding light on the factors that influence tax assessments, the processes involved, and the strategies homeowners can employ to navigate this essential aspect of homeownership.
The Dynamics of Property Taxes in Indiana
Property taxes in Indiana play a significant role in funding essential services, including schools, roads, emergency services, and local government operations. The state’s tax system is designed to ensure a fair distribution of financial responsibilities among property owners, with assessments based on the value of their real estate holdings.
Tax Assessment Process
Indiana employs a comprehensive assessment system to determine the taxable value of properties. This process, overseen by the Indiana Department of Local Government Finance (DLGF), involves the following key steps:
- Property Appraisal: Trained assessors conduct regular appraisals to estimate the market value of properties. This value serves as the basis for tax assessments.
- Assessment Ratio: Indiana applies an assessment ratio, typically 100%, to the appraised value to arrive at the assessed value. However, this ratio may vary between counties.
- Tax Rate Calculation: Local taxing units, such as counties, cities, and school districts, set tax rates based on their revenue needs. These rates are then applied to the assessed value to determine the property tax liability.
Factors Influencing Property Tax Rates
Property tax rates in Indiana can vary significantly between different areas. Here are some key factors that contribute to these variations:
- Location: Tax rates can differ between counties, cities, and even within municipalities. Urban areas often have higher tax rates to support a broader range of services and infrastructure.
- Property Type: The type of property, whether residential, commercial, or agricultural, can influence tax rates. Different tax schedules may apply to each category.
- Assessment Accuracy: Accurate property assessments are crucial. If a property’s value is underestimated, the owner may pay less tax than they should. Conversely, overassessment can lead to higher tax bills.
- Local Budget Needs: Tax rates are set based on the financial requirements of local governments and service providers. Areas with higher service demands or ambitious development plans may have higher tax rates.
Tax Bills and Payment Schedules
Property owners in Indiana receive tax bills detailing their liability for the year. These bills are typically sent twice a year, with due dates aligned with the tax year’s halves. Late payments may incur penalties and interest.
Strategies for Managing Property Taxes
Navigating the property tax landscape can be challenging, but homeowners have options to optimize their tax obligations and ensure fairness. Here are some strategies to consider:
Understanding Assessment Notices
Homeowners receive assessment notices periodically, informing them of changes to their property’s assessed value. It’s essential to review these notices carefully:
- Review Assessments: Compare the assessed value with recent sale prices of similar properties in the area. If the assessment seems significantly higher, it may be worth appealing.
- Appeal Process: Indiana provides a formal process for appealing property assessments. Homeowners can contest their assessments based on inaccurate valuations or discrepancies in comparable sales data.
Tax Deductions and Exemptions
Indiana offers various tax deductions and exemptions to eligible homeowners, reducing their tax liability. Some key options include:
- Homestead Deduction: Homeowners who use their property as their primary residence can claim a deduction, reducing the assessed value and, consequently, the tax bill. This deduction is particularly beneficial for older homeowners.
- Veterans’ Exemptions: Indiana provides property tax exemptions for qualifying veterans and their surviving spouses. These exemptions can significantly reduce tax obligations.
- Other Exemptions: Certain properties, such as those used for religious or charitable purposes, may be eligible for exemptions. Additionally, disabled individuals may qualify for tax relief.
Property Tax Abatements
Indiana counties and municipalities can offer tax abatements to encourage economic development and attract new businesses. These abatements reduce property taxes for a specified period, often tied to job creation or investment commitments.
The Future of Property Taxes in Indiana
As Indiana’s real estate market evolves, property tax policies are likely to adapt to meet changing needs. Here are some potential future developments:
Technology-Driven Assessments
Advancements in technology may lead to more accurate and efficient property assessments. Drones and satellite imagery could aid in gathering data, reducing the need for physical inspections.
Tax Reform Initiatives
Ongoing discussions about tax reform in Indiana could result in changes to the assessment process or tax rates. These reforms aim to ensure a fair and sustainable tax system.
Community Engagement
Local governments and communities may increasingly involve residents in tax policy decisions. Town hall meetings and online platforms could provide avenues for homeowners to voice their concerns and suggest improvements.
| County | Average Property Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Marion County | 1.08% |
| Hamilton County | 1.03% |
| St. Joseph County | 1.02% |
| Allen County | 1.01% |
| Lake County | 1.00% |
How often are property tax assessments conducted in Indiana?
+Property tax assessments in Indiana are typically conducted every few years, with some counties assessing properties annually. The assessment schedule may vary between counties, so it’s advisable to check with your local assessor’s office.
Can I appeal my property tax assessment if I disagree with it?
+Yes, Indiana provides a formal appeals process. Homeowners can contest their assessments if they believe the valuation is inaccurate or if they can provide evidence of discrepancies in comparable sales data. It’s important to understand the appeal process and gather relevant documentation.
Are there any tax relief programs for seniors or low-income homeowners in Indiana?
+Indiana offers various tax relief programs, including the Senior Citizen Deduction and the Circuit Breaker Deduction, which can provide financial assistance to eligible seniors and low-income homeowners. These programs aim to reduce the tax burden for vulnerable populations.