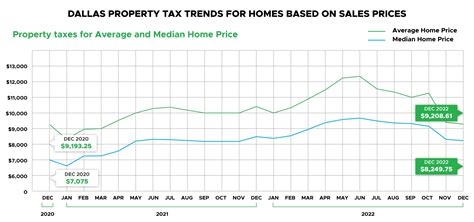
Personal Property Tax Lookup

Property taxes are an essential part of any jurisdiction's revenue stream, and personal property taxes, in particular, play a significant role in funding local services and infrastructure. These taxes are typically levied on tangible assets owned by individuals, such as vehicles, boats, and even business equipment. The process of determining the tax liability for personal property can be complex, as it involves assessing the value of various assets and applying specific tax rates. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of personal property tax lookup, exploring the intricacies of the process, the various assessment methods, and the impact of these taxes on individuals and businesses.
Understanding Personal Property Taxes

Personal property taxes are a type of ad valorem tax, meaning they are based on the assessed value of the property. Unlike real estate taxes, which are primarily associated with land and buildings, personal property taxes focus on movable assets. These taxes are an essential source of revenue for local governments, helping to fund vital services like education, public safety, and infrastructure maintenance.
The assessment and collection of personal property taxes vary across jurisdictions, with different states and municipalities employing unique methods and timelines. Understanding these variations is crucial for individuals and businesses to ensure compliance and manage their tax obligations effectively.
Types of Personal Property Subject to Taxation
Personal property subject to taxation can encompass a wide range of assets, including:
- Vehicles: Cars, motorcycles, trucks, and other motorized vehicles are commonly taxed based on their assessed value and age.
- Boats and Aircraft: Watercraft, yachts, and aircraft are often subject to personal property taxes, with assessments typically considering factors like size and age.
- Business Equipment: For businesses, personal property taxes may extend to machinery, furniture, and other tangible assets used in daily operations.
- Mobile Homes: In some areas, mobile homes and manufactured housing are treated as personal property and are taxed accordingly.
- Leased Property: Leased vehicles and equipment may also be subject to personal property taxes, with the responsibility often falling on the lessee.
Assessment Methods and Valuation
The valuation process for personal property taxes can vary significantly, and jurisdictions often employ different methods to determine the assessed value of assets. Here are some common assessment techniques:
- Cost Approach: This method assesses the value of property based on its original cost, less depreciation. It is commonly used for vehicles and equipment.
- Market Value Approach: Property is valued based on its current market value, considering factors like age, condition, and comparable sales. This approach is often used for boats and aircraft.
- Income Approach: For business equipment, the potential income generated by the asset is considered to determine its value.
- Statutory Assessment: In some cases, jurisdictions may have specific statutes or regulations that dictate how certain types of personal property should be assessed.
It's important to note that assessment methods can vary not only between jurisdictions but also within the same jurisdiction for different types of personal property. Understanding the specific assessment guidelines in your area is crucial for accurate tax planning.
The Personal Property Tax Lookup Process
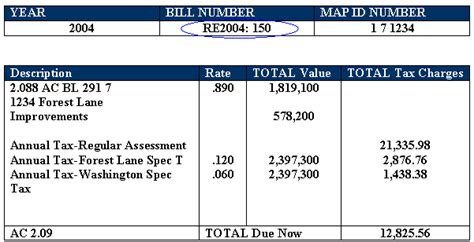
Locating personal property tax information and understanding your tax liability can be a complex process. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the personal property tax lookup journey:
Step 1: Determine Taxing Jurisdiction
The first step is to identify the taxing authority responsible for assessing and collecting personal property taxes in your area. This could be a county, city, or other local government entity. Different jurisdictions may have varying tax rates and assessment methods, so pinpointing the correct authority is essential.
Step 2: Understand Assessment Periods
Personal property taxes are often assessed on an annual or biennial basis. Understanding the assessment period for your jurisdiction is crucial, as it dictates when you should expect to receive your tax bill and when payments are due.
Step 3: Locate Assessment Records
Once you’ve identified the taxing authority and assessment period, the next step is to locate your assessment records. These records contain vital information about your personal property, including the assessed value and any applicable tax rates.
Assessment records are typically available online through the taxing authority’s website. You may need to create an account or log in to access your specific records. If online access is not available, you can often request assessment records in person or by mail from the tax assessor’s office.
Step 4: Review and Understand the Assessment
Upon receiving your assessment records, take the time to review them carefully. Ensure that all personal property listed is accurate and that the assessed values are reasonable based on the asset’s age and condition. If you have any questions or concerns about the assessment, contact the tax assessor’s office for clarification.
Step 5: Calculate Your Tax Liability
Using the assessed values and applicable tax rates from your assessment records, calculate your estimated tax liability. This step is crucial for budgeting and financial planning. Many taxing authorities provide online calculators or tax estimation tools to assist with this process.
Step 6: Explore Payment Options
Personal property taxes are typically due by a specific deadline, often coinciding with the assessment period. Explore the payment options available to you, which may include online payments, direct debit, or traditional mail-in payments. Some jurisdictions may offer installment plans or other payment arrangements for those facing financial hardship.
Step 7: Stay Informed and Prepare for Future Assessments
Stay updated on any changes to tax rates or assessment methods in your jurisdiction. Personal property tax laws can evolve, and staying informed ensures you remain compliant with the latest regulations. Additionally, consider maintaining accurate records of your personal property to simplify future assessments and tax planning.
Impact of Personal Property Taxes
Personal property taxes have a significant impact on individuals and businesses, influencing financial planning and decision-making. Here’s a closer look at the implications of these taxes:
Financial Burden on Individuals
For individuals, personal property taxes can represent a substantial financial burden, especially for those with multiple vehicles or valuable assets. These taxes can impact household budgets and may require careful financial planning to ensure timely payments.
Business Operations and Planning
Businesses must factor personal property taxes into their operational costs. These taxes can affect profit margins and influence decisions about equipment purchases, leasing arrangements, and overall financial strategies. Accurate tax planning is essential for businesses to maintain compliance and manage their tax obligations effectively.
Economic Impact on Communities
Personal property taxes play a crucial role in funding local services and infrastructure. The revenue generated from these taxes directly impacts the quality of education, public safety, and overall community development. As such, personal property taxes are a vital component of a community’s economic health and sustainability.
Strategies for Managing Personal Property Taxes
Navigating personal property taxes can be challenging, but there are strategies to help individuals and businesses manage their tax obligations more effectively:
Stay Informed and Proactive
Keep yourself informed about changes in tax rates, assessment methods, and deadlines. Being proactive ensures you are prepared for upcoming assessments and can plan your finances accordingly.
Maintain Accurate Records
Keep detailed records of your personal property, including purchase dates, original costs, and any significant maintenance or upgrades. Accurate records can simplify the assessment process and provide evidence in case of disputes.
Explore Tax Relief Options
Many jurisdictions offer tax relief programs or exemptions for certain types of personal property or for individuals facing financial hardship. Research these options and determine if you are eligible for any tax relief measures.
Consider Leasing vs. Purchasing
For businesses, leasing equipment or vehicles may be more tax-efficient than purchasing, as the tax liability may fall on the lessor rather than the lessee. Evaluate the tax implications of leasing versus purchasing to make informed decisions.
Seek Professional Advice
If you have complex personal property holdings or face unique tax situations, consider seeking advice from tax professionals or accountants. They can provide personalized guidance and help you navigate the complexities of personal property tax laws.
Future Trends and Implications
As technology and tax laws evolve, the landscape of personal property taxes is likely to change. Here are some potential future trends and their implications:
Digital Assessment and Tax Collection
The increasing adoption of digital technologies may lead to more efficient and accurate assessment processes. Digital records and automated valuation tools could streamline the tax collection process, reducing administrative burdens for both taxpayers and taxing authorities.
Expansion of Taxable Personal Property
As technology advances, new types of personal property may become subject to taxation. For example, with the rise of electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, these assets could be included in personal property tax assessments in the future.
Tax Reform and Simplification
Efforts to simplify tax codes and harmonize assessment methods across jurisdictions could make personal property tax processes more consistent and transparent. This could benefit taxpayers by reducing complexity and improving compliance.
Community Engagement and Transparency
Increased transparency in tax assessments and collections can foster community engagement and trust. Taxing authorities may invest in better communication strategies to educate taxpayers about the purpose and impact of personal property taxes, ensuring a more informed and supportive community.
Conclusion
Personal property taxes are a vital component of local government revenue, and understanding the lookup process, assessment methods, and impact is essential for individuals and businesses. By staying informed, maintaining accurate records, and employing effective tax management strategies, taxpayers can navigate the complexities of personal property taxes with confidence. As the tax landscape evolves, staying attuned to future trends and implications will be crucial for effective financial planning and community engagement.
What happens if I don’t pay my personal property taxes on time?
+Failure to pay personal property taxes on time can result in penalties, interest charges, and, in some cases, legal consequences. It’s important to understand the specific consequences in your jurisdiction and plan your payments accordingly.
Can I appeal my personal property tax assessment if I disagree with the value assigned to my property?
+Yes, many jurisdictions provide a process for taxpayers to appeal their assessments if they believe the value assigned to their personal property is inaccurate. It’s important to review the appeal process in your area and gather evidence to support your case.
Are there any exemptions or deductions available for personal property taxes?
+Yes, some jurisdictions offer exemptions or deductions for certain types of personal property, such as agricultural equipment or property owned by veterans. It’s worth exploring these options to see if you qualify for any tax relief measures.
How often do personal property tax assessments occur, and can they change from year to year?
+Personal property tax assessments typically occur annually or biennially, depending on the jurisdiction. Assessments can change from year to year based on various factors, including changes in tax rates, asset values, or assessment methodologies.
Can I pay my personal property taxes online, and what are the benefits of online payment options?
+Yes, many taxing authorities offer online payment options for personal property taxes. Benefits include convenience, faster processing, and the ability to track payment status. Online payments can also reduce administrative burdens and provide a more efficient tax payment experience.