Pa Tax Rate

Welcome to this comprehensive exploration of the Pennsylvania Tax Rate, a topic of great importance for both residents and businesses within the state. Understanding the intricacies of tax laws and rates is crucial for financial planning and ensuring compliance with state regulations. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of Pennsylvania's tax system, covering various aspects to help you navigate this complex yet essential financial landscape.
Unraveling the Pennsylvania Tax Landscape
The Keystone State, with its rich history and diverse economy, has a tax system that reflects its unique characteristics. Pennsylvania’s tax rates are structured to support the state’s infrastructure, education, and various public services, impacting both individuals and businesses. Let’s delve into the specifics of this tax landscape.
Individual Income Tax: A Progressive Approach
Pennsylvania employs a progressive income tax system, which means that the tax rate increases as an individual’s income rises. This approach aims to ensure fairness and provide a more balanced contribution from taxpayers with varying income levels. Here’s a breakdown of the income tax rates as of the latest information available:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to $34,000 | 3.07% |
| $34,001 - $85,000 | 3.59% |
| $85,001 - $162,000 | 3.87% |
| Over $162,000 | 4.95% |

It's important to note that these rates are subject to change, and it's advisable to consult official sources for the most current information. Additionally, Pennsylvania offers various tax credits and deductions to reduce the overall tax liability for individuals. Some of these include credits for low-income individuals, elderly taxpayers, and those with disabilities.
Corporate Tax Rates: Encouraging Business Growth
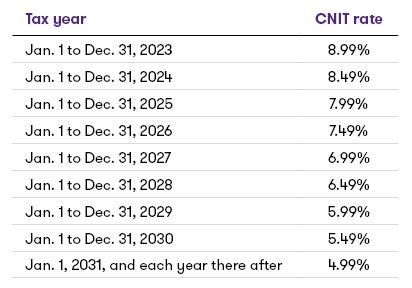
For businesses operating in Pennsylvania, the corporate tax rate is a key consideration. The state imposes a 9.99% corporate net income tax on C-corporations and S-corporations. This rate is applicable to both resident and non-resident corporations doing business within the state. However, there are certain tax incentives and abatements available to promote economic development and attract new businesses.
Pennsylvania's Economic Development Tax Credit, for instance, provides eligible businesses with a tax credit of up to 80% of the corporate net income tax liability. This credit is designed to encourage job creation and investment in the state. Additionally, the Research and Development Tax Credit aims to foster innovation by offering a credit for qualified research expenses.
Sales and Use Tax: A Significant Revenue Source
The Pennsylvania Sales and Use Tax applies to the sale, lease, or rental of tangible personal property, as well as various services. As of my last update, the base sales tax rate is 6%, which can be higher in certain jurisdictions that levy additional local taxes. This tax is a significant source of revenue for the state and is used to fund various public services and infrastructure projects.
Certain items, such as groceries, clothing, and footwear, are exempt from sales tax to provide some relief to consumers. Additionally, Pennsylvania offers a Sales Tax Holiday during specific periods, typically for back-to-school shopping, to boost economic activity and save families money.
Property Tax: Local Assessments and Variations
Property taxes in Pennsylvania are primarily assessed and collected at the local level, with rates varying across counties and municipalities. The millage rate, which is the tax rate per thousand dollars of assessed property value, is determined by local taxing authorities. This rate can range from less than 1 mill to over 100 mills, depending on the locality.
Pennsylvania also has a homestead exemption program that provides a tax relief benefit to eligible homeowners. This program reduces the assessed value of a homeowner's property, resulting in a lower property tax bill. The eligibility criteria and exemption amount vary based on the county and the homeowner's income.
The Impact of Tax Rates on the Pennsylvania Economy
Pennsylvania’s tax rates play a crucial role in shaping the state’s economic landscape. While the progressive income tax structure aims to maintain fairness, it also influences individual financial planning and investment decisions. The corporate tax rate, along with various incentives, impacts business decisions and the state’s competitiveness in attracting new enterprises.
The sales and use tax, being a significant revenue source, has a direct impact on consumer spending and business operations. Property taxes, though locally assessed, contribute to the funding of essential services like education and infrastructure. Understanding these tax rates and their implications is vital for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike.
Navigating Tax Obligations: Expert Insights
Future Outlook: Tax Reform and Economic Trends
As Pennsylvania continues to evolve economically, the tax landscape is likely to undergo changes. Ongoing discussions around tax reform, driven by both economic and political factors, may lead to adjustments in tax rates and structures. Staying informed about these potential changes is crucial for financial planning and business strategy.
Additionally, the state's commitment to economic development and job creation is expected to influence tax policies. Monitoring the impact of these initiatives on tax rates and incentives will be essential for businesses and investors looking to thrive in the Keystone State.
Conclusion: A Complex Yet Navigable Tax System
The Pennsylvania tax system, with its diverse tax rates and incentives, presents both opportunities and challenges for individuals and businesses. Understanding this landscape is a crucial step in financial planning and ensuring compliance with state regulations. This article has provided an in-depth analysis, but it’s essential to stay updated with the latest tax laws and regulations to make informed decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current sales tax rate in Pennsylvania?
+The base sales tax rate in Pennsylvania is 6%. However, local jurisdictions may add additional sales tax, resulting in a higher rate in certain areas.
Are there any tax incentives for businesses in Pennsylvania?
+Yes, Pennsylvania offers various tax incentives for businesses, including the Economic Development Tax Credit and the Research and Development Tax Credit. These incentives aim to encourage job creation and investment.
How often are Pennsylvania’s tax rates updated?
+Tax rates in Pennsylvania can be subject to periodic updates, typically aligned with legislative changes or budget considerations. It’s advisable to check official sources for the most current information.
Are there any tax credits available for individuals in Pennsylvania?
+Yes, Pennsylvania offers tax credits for individuals, such as the Low-Income Tax Credit, the Elderly Tax Credit, and the Disability Tax Credit. These credits can reduce an individual’s tax liability.
How are property taxes determined in Pennsylvania?
+Property taxes in Pennsylvania are assessed and collected at the local level, with rates varying across counties and municipalities. The millage rate, determined by local authorities, is a key factor in calculating property taxes.