Ga Tax Payments

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Georgia tax payments. In this article, we will delve into the world of Georgia's tax system, providing you with all the information you need to navigate the process smoothly and efficiently. Whether you're a resident, a business owner, or simply curious about the tax landscape of the Peach State, we've got you covered.
Understanding the intricacies of tax payments is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. Georgia, with its unique tax structure and regulations, offers a distinct experience. From income tax to sales tax and property tax, we will explore the various types of taxes and guide you through the payment processes.
Unraveling the Georgia Tax System

The Georgia Department of Revenue plays a pivotal role in managing the state's tax system. With a range of responsibilities, from enforcing tax laws to providing guidance and support to taxpayers, they ensure the smooth functioning of the state's financial infrastructure.
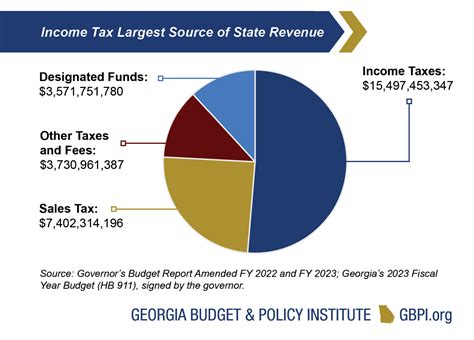
Georgia's tax system is designed to fund essential services, such as education, healthcare, infrastructure development, and more. It is a crucial aspect of the state's economy, contributing to its growth and stability.
Types of Taxes in Georgia
Georgia imposes various taxes to generate revenue and support its operations. Let's take a closer look at some of the key tax types:
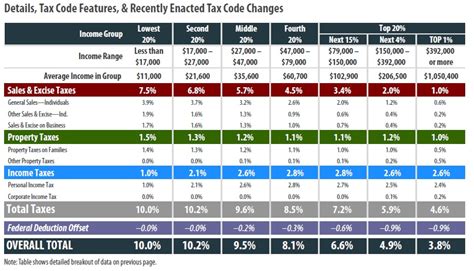
- Income Tax: Georgia levies income tax on individuals and businesses. The state's income tax system is progressive, with rates ranging from 1% to 6% based on income brackets. Understanding your income tax obligations is essential for accurate filing and timely payments.
- Sales and Use Tax: This tax is applied to the sale of goods and certain services within the state. The standard sales tax rate in Georgia is 4%, but local municipalities may add additional taxes, resulting in varying rates across the state. Businesses must collect and remit these taxes to the state.
- Property Tax: Property taxes are assessed on real estate and personal property. The rate varies depending on the county and the type of property. Homeowners and business owners are responsible for paying property taxes, which fund local services and infrastructure.
- Corporate Income Tax: Corporations doing business in Georgia are subject to corporate income tax. The tax rate is currently set at 6%, and businesses must file returns and make payments accordingly.
- Excise Taxes: Georgia imposes excise taxes on specific goods and services, such as gasoline, tobacco, and alcohol. These taxes are often used to fund specific programs or initiatives.
Understanding these tax types and their applicability to your situation is crucial for compliance and avoiding penalties.
Navigating Tax Payments in Georgia

Georgia offers a user-friendly online platform for taxpayers to manage their tax obligations. The Georgia Tax Center, accessible via the Department of Revenue's website, provides a range of services, including:
- Online tax filing for individuals and businesses.
- Payment options for various tax types.
- Tax account management and history.
- Access to tax forms and publications.
- Tax guidance and support resources.
Let's explore the process of making tax payments in Georgia, step by step:
Step 1: Register and Create an Account
To begin your tax journey in Georgia, you need to register with the Georgia Tax Center. Create an account by providing your personal or business information, depending on your tax obligations.
Step 2: Determine Your Tax Obligations
Assess your tax situation and determine the types of taxes you are liable to pay. This step is crucial to ensure you meet all your tax obligations accurately.
Step 3: Access Tax Forms and Publications
The Georgia Tax Center provides a comprehensive library of tax forms and publications. Download the necessary forms for your specific tax type and carefully follow the instructions provided.
Step 4: Calculate Your Tax Liability
Using the provided forms and your financial information, calculate your tax liability. This step is critical to ensure you pay the correct amount and avoid underpayment penalties.
Step 5: Choose Your Payment Method
Georgia offers a range of payment methods to suit different preferences and needs. You can choose to pay online, by mail, or in person at authorized locations. Each method has its own set of instructions and requirements.
Online payments are generally the most convenient and efficient option, offering real-time processing and confirmation. You can make payments using credit or debit cards, e-checks, or direct transfers.
For mail payments, ensure you use the correct address and include all necessary documentation. In-person payments may be an option for certain taxes, but be sure to check the accepted methods and locations.
Step 6: Make Your Payment
Follow the instructions for your chosen payment method and ensure you meet the deadline. Late payments may result in penalties and interest charges.
Step 7: Keep Records and Receipts
It is essential to maintain a record of your tax payments and receipts. These documents serve as proof of compliance and can be crucial in case of audits or inquiries.
| Tax Type | Payment Due Date |
|---|---|
| Income Tax | April 15th of each year (or the next business day if it falls on a weekend or holiday) |
| Sales and Use Tax | Varies based on filing frequency (monthly, quarterly, or annually) |
| Property Tax | Typically due in March or April, but may vary by county |
| Corporate Income Tax | April 15th for calendar year filers |

Common Tax Payment Scenarios and Solutions
Tax payments can sometimes present challenges. Let's address some common scenarios and provide practical solutions:
Scenario 1: Late Payment Penalties
If you find yourself unable to make a tax payment on time, it's important to act promptly. Contact the Georgia Department of Revenue to discuss your situation and explore potential solutions. They may offer payment plans or waive penalties under certain circumstances.
Scenario 2: Tax Refund Delays
In some cases, tax refunds may take longer than expected. If you haven't received your refund within the estimated timeframe, reach out to the Department of Revenue. They can provide updates and assist with any issues that may be causing the delay.
Scenario 3: Tax Disputes
Should you have a disagreement with the Department of Revenue regarding your tax obligations, there are avenues for dispute resolution. You can request an informal conference, file a formal protest, or appeal to the State Office of Administrative Hearings. Understanding your rights and seeking professional advice can be beneficial in these situations.
The Future of Tax Payments in Georgia
As technology advances, Georgia's tax system is evolving to keep pace. The state is investing in modernizing its tax infrastructure, aiming to enhance efficiency and convenience for taxpayers.
With the increasing adoption of digital solutions, we can expect to see more online tools and resources for tax management. The Georgia Tax Center is expected to expand its services, offering an even more comprehensive platform for taxpayers.
Additionally, Georgia is exploring ways to streamline the tax filing and payment process, potentially introducing new options such as automatic payments and direct deposits. These initiatives aim to reduce administrative burdens and improve the overall taxpayer experience.
Stay tuned for future updates and improvements to Georgia's tax payment system, as the state continues to prioritize accessibility and convenience for its residents and businesses.
Conclusion
Understanding and navigating the world of tax payments in Georgia is essential for compliance and financial well-being. By familiarizing yourself with the state's tax system, utilizing the available resources, and staying informed, you can ensure a smooth and stress-free tax payment journey.
Remember, the Georgia Department of Revenue is here to support you. Don't hesitate to reach out for guidance and stay up to date with the latest tax news and developments. Your tax obligations are an important contribution to the state's prosperity, and with the right knowledge and tools, you can navigate them confidently.
What is the income tax rate in Georgia for the current year?
+Georgia’s income tax rates vary based on income brackets. For the current year, the rates range from 1% to 6%, with higher income levels attracting higher tax rates. It’s important to refer to the latest tax guidelines and consult with a tax professional to determine your specific income tax obligations.
How often do I need to file sales tax returns in Georgia?
+The filing frequency for sales tax returns depends on your business’s sales volume. If your annual sales exceed a certain threshold, you may be required to file monthly. However, smaller businesses may file quarterly or annually. It’s best to consult the Department of Revenue’s guidelines or seek professional advice to determine your specific filing frequency.
Are there any tax incentives or credits available in Georgia for businesses?
+Yes, Georgia offers various tax incentives and credits to encourage economic growth and support specific industries. These include job tax credits, research and development credits, and more. To explore these opportunities, visit the Department of Revenue’s website or consult with a tax professional who can guide you through the available options.